3.2.2.1.2 Multipair Mode
If 2, 3 or 4 SHDSL channels are configured to operate in the multipair mode, they work at the
same clock frequency and line rate like one SHDSL channel with doubled, tripled or quadrupled
transmission capacity. Similarly to the independent channel, such a combined channel can
simultaneously transmit one or several E1 streams and one WAN stream. This transmission is
also plesiochronous. All E1 streams that are transmitted over one SHDSL interface should use
the same clock frequency per direction.
In multipair mode, one SHDSL channel serves as a “master” channel, while the other SHDSL
channels serve as “slave” channels. If the link in one channel fails, links in all other channels
break too and the procedure of connection/activation restarts.
The four-channel modems provide a possibility to organize pair-wise channels, i.e., these two
two-pair links will operate independently from each other.
The main application for the multipair mode is the increasing of the transmission range. In this
case, some channels operate at low transmission rates. In multipair mode some limitations are
imposed on the Baserate parameter.
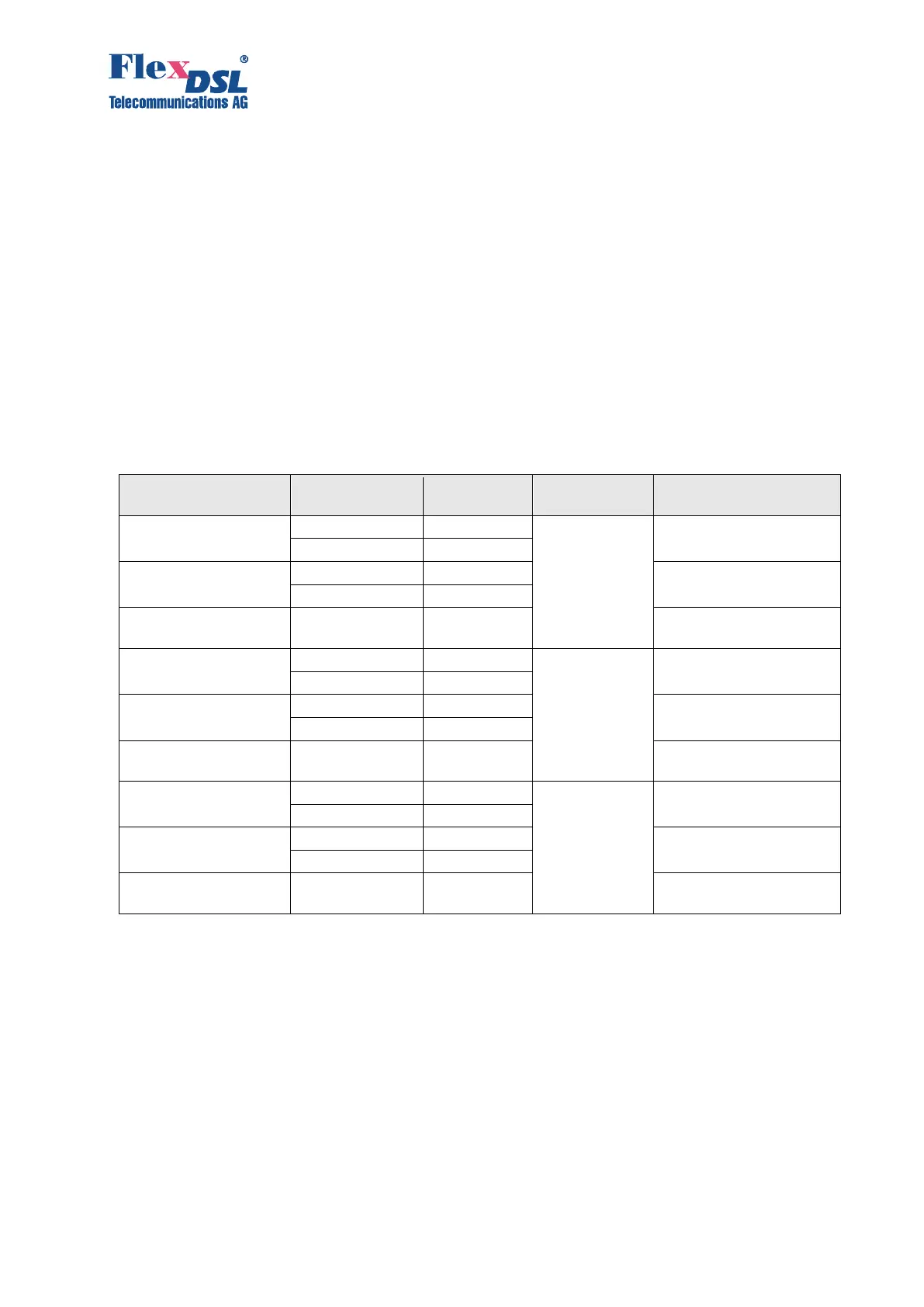
Table 3.5 Line settings per SHDSL interface, multipair mode.
The next figure shows an example of an Orion3 device working in four-pair operation mode (the
<MULTIPAIR> command is used to configure multipair operation mode). Four SHDSL channels
are combined into one group. Through this multipair channel one E1 stream and Ethernet packets
are transmitted. This mode allows increasing the transmission range, compared to the use of only
one single SHDSL channel, because the data rate of each SHDSL channel is lower (the
advantage in the transmission range will depend on the cable parameters and noise immunity).
 Loading...
Loading...