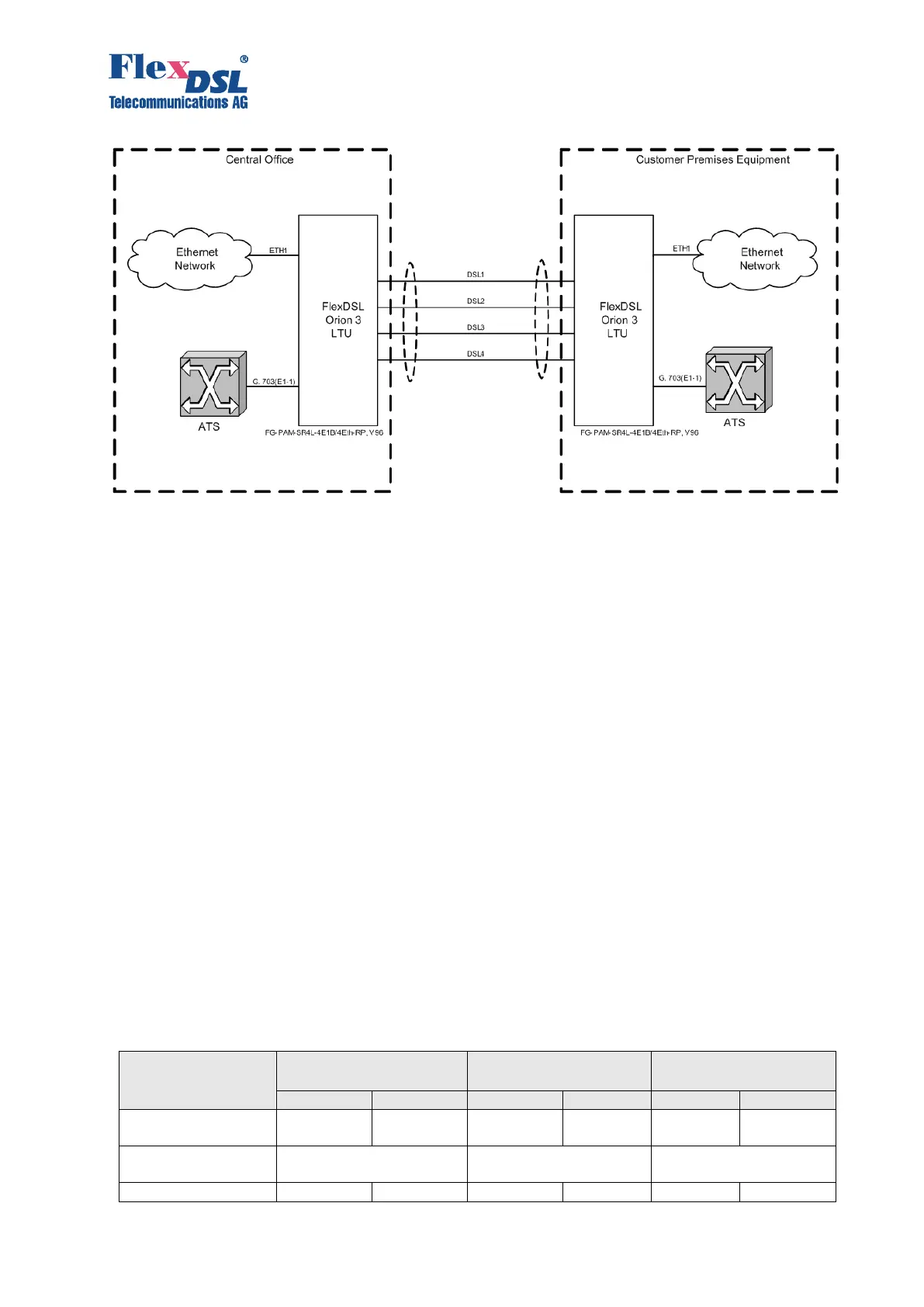
Figure 3.4 Example of four-pair multipair data transmission
3.2.2.1.3 Reservation Mode
Reservation is provisioned for 2- and 4-channel FlexDSL Orion3 devices. The main task of
reservation is to transmit the most important data even in the case of the failure of one or several
SHDSL connections. Reservation also takes care about an efficient bandwidth usage over all
SHDSL channels like the normal transmission modes.
Reservation will not guarantee a continuous transmission of important data in the case of a failure.
When one or several DSL connections fail, a sort-term loss of Ethernet packet and E1 data can
occur.
SHDSL channels with successive numbers (example: DSL-1, DSL-2 or DSL-2, DSL-3, DSL-4)
are merged into a group of channels with reservation. For these merged channels, the traffic in
the SHDSL channels with the lowest numbers has higher priority than the traffic with higher
numbers. For example, DSL-1 has a higher priority than DSL-2, and DSL-2 has a higher priority
than DSL-3. If the communication in one or several SHDSL channels inside the reservation group
is broken, remaining working channels transmit the data of the failed high-priority channels. At
any failure the system always operates as if the low-priority channels failed.
Consider the reservation with two channels: DSL-1 and DSL-2 (DSL-1 has a higher priority
compared to DSL-2). If the DSL-2 channel fails, the DSL-1 channel continues to operate without
any changes. If the DSL-1 channel fails, the DSL- 2 channel transmits the data of the DSL- 1
channel. Hence, the DSL-1 channel should transmit the high-priority data.
If the substitute channel has a lower transmission capacity than the main channel, the transmitted
data will be decreased. First, the volume of WAN data will be decreased up to 1 timeslot (TS,
64kbit/s), and then, the number of transmitted E1 timeslots will be decreased. If multiple E1
streams are transmitted, the streams at the end of the list will be decreased (if E1-1, E1-2 are in
the list, the E1-2 stream will be deleted). First, timeslots with large numbers are deleted. However,
there is an exception for TS 16, which, if transmitted, will be deleted before or after TS 0.
 Loading...
Loading...