• Also a next Regenerator receives the structure from the previous Regenerator and performs
configuration according to it.
• The Slave-Modem receives the stream structure from the last Regenerator in the link and
also performs configuration
• When the Slave-Modem receives configuration, it distributes the received E1 streams
information to its E1 ports. If the number of ports is not enough, it displays the RCONF alarm
and does not change the configuration of the E1 streams. Also if the E1 streams are not
distributed, the Slave-Modem receives the configurations of WAN. Therefore, the integrity
of the Ethernet link is supported.
The RCONF alarm (displayed by the <ALARM> command) means that the local and remote
equipment have incompatible configurations.
• The RCONF alarm is automatically not displayed if a DSL link, in which it was detected,
fails.
• If the device operates in the CA mode (automatic configuration of a link), the alarm is not
displayed when the device finally adjusts to the CO side (Master).
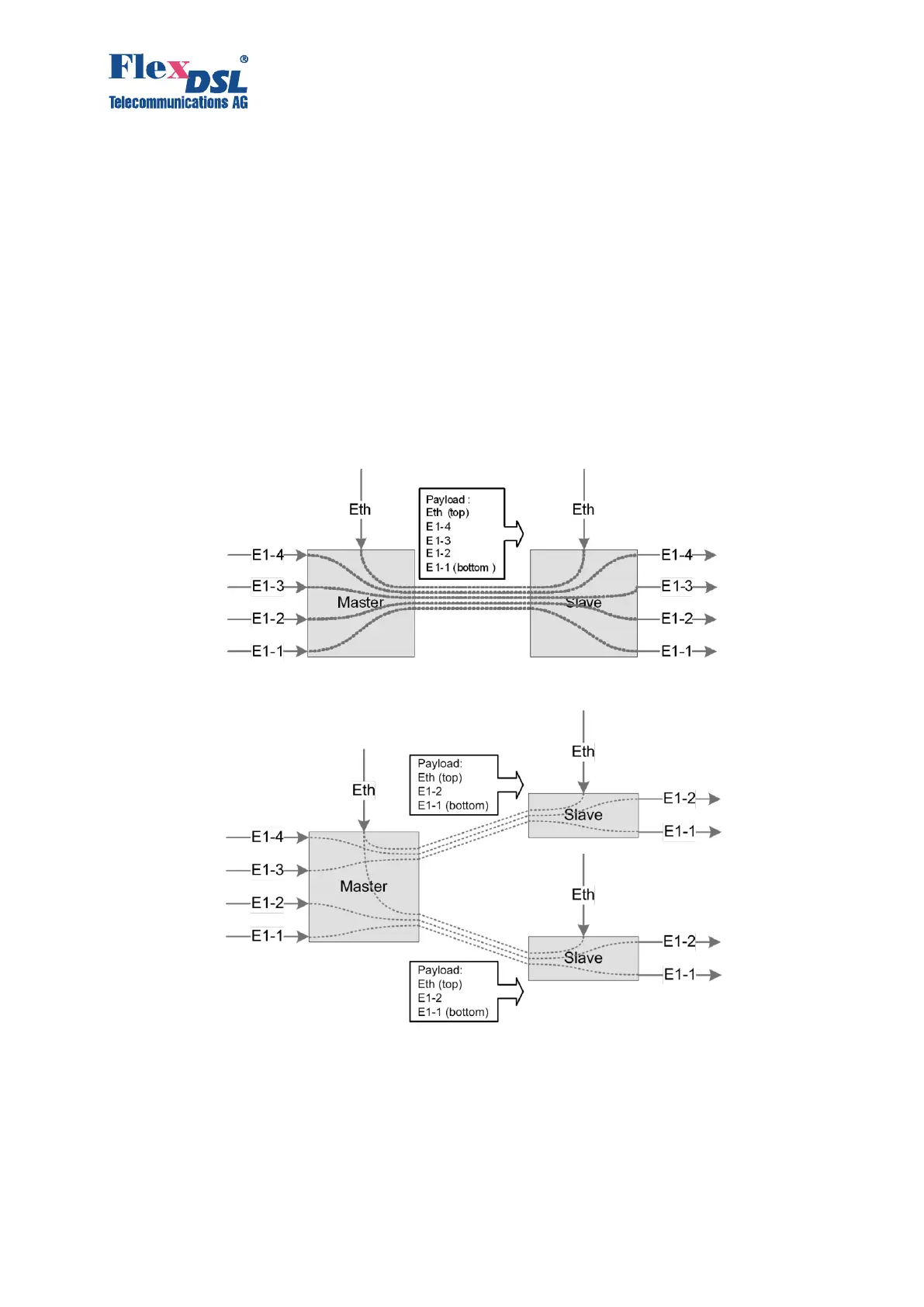
Figure 3.7 Automatic configuration Star-topology
A more complex case is the independent two-channel connection: two E1 streams and Ethernet
packets are transmitted in the first channel and the second channel. The Slave-Modem
determines the order of E1 interfaces for the streams from each DSL link only when the
communication in both links is established.
 Loading...
Loading...