Page 38
MegaRAID SAS Software User GuideChapter 2: Introduction to RAID
| RAID Levels
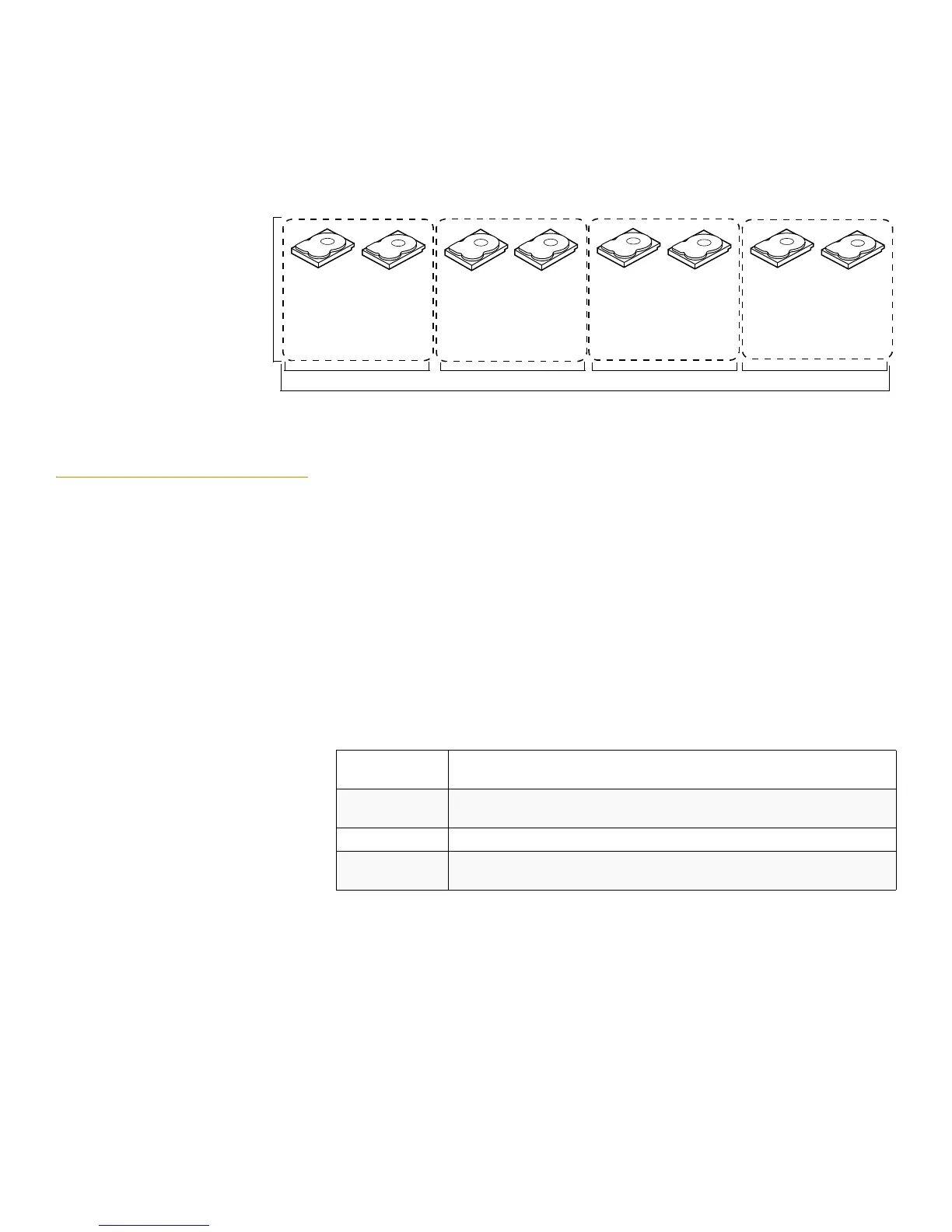
In Figure12, virtual drive 0 is created by distributing data across four drive groups
(drive groups 0 through 3).
Figure 12: RAID 10 Level Virtual Drive
2.5.9 RAID 50 RAID 50 provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 5. RAID 50 includes both parity
and disk striping across multiple drive groups. RAID 50 is best implemented on two
RAID 5 drive groups with data striped across both drive groups.
RAID 50 breaks up data into smaller blocks and then stripes the blocks of data to each
RAID 5 disk set. RAID 5 breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by
performing an exclusive-or on the blocks and then writes the blocks of data and parity
to each drive in the drive group. The size of each block is determined by the stripe size
parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set.
RAID level 50 can support up to eight spans and tolerate up to eight drive failures,
though less than total drive capacity is available. Though multiple drive failures can be
tolerated, only one drive failure can be tolerated in each RAID 5 level drive group.
Table13 provides an overview of RAID 50.
Segment 1
Segment 1
Duplicate
Segment 2
Segment 3
Duplicate
Segment 4
Duplicate
Segment 3
Segment 4
Segment 5
Segment 6
Segment 7
Segment 8
Segment 5
Duplicate
Segment 6
Duplicate
Segment 7
Duplicate
Segment 8
Duplicate
Segment 2
Duplicate
...
...
...
...
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
RAID 10
RAID 0
Table 13: RAID 50 Overview
Uses Appropriate when used with data that requires high reliability, high request
rates, high data transfer, and medium to large capacity.
Strong Points Provides high data throughput, data redundancy, and very good
performance.
Weak Points Requires 2 to 8 times as many parity drives as RAID 5.
Drives Eight spans of RAID 5 drive groups containing 3-32 drives each (limited by
the maximum number of devices supported by the controller)
 Loading...
Loading...























