QX-830 Compact Industrial Scanner User’s Manual 3-9
Hardware Installation
Port Routing
The physical advantages created by flexible signal routing and switching are enhanced
further by Port Routing, which can be configured in ESP. Port Routing eliminates the
need for dedicated “Host” and “Aux” ports in a traditional sense. With Port Routing, any
port can be defined as a Host or Aux port. Port Routing also allows users to define the
data types that are accessible from specific ports.
The primary benefit of Port Routing is that any type of data can be routed to any port, and
can be sent through multiple ports simultaneously. Multiple types of data can also be
appended to the symbol data that is output from the scanner to the host. Command data,
symbol data, extra symbol information, and diagnostic data are enabled by default in the QX-830.
The table below lists different types of data, with examples for each data type.
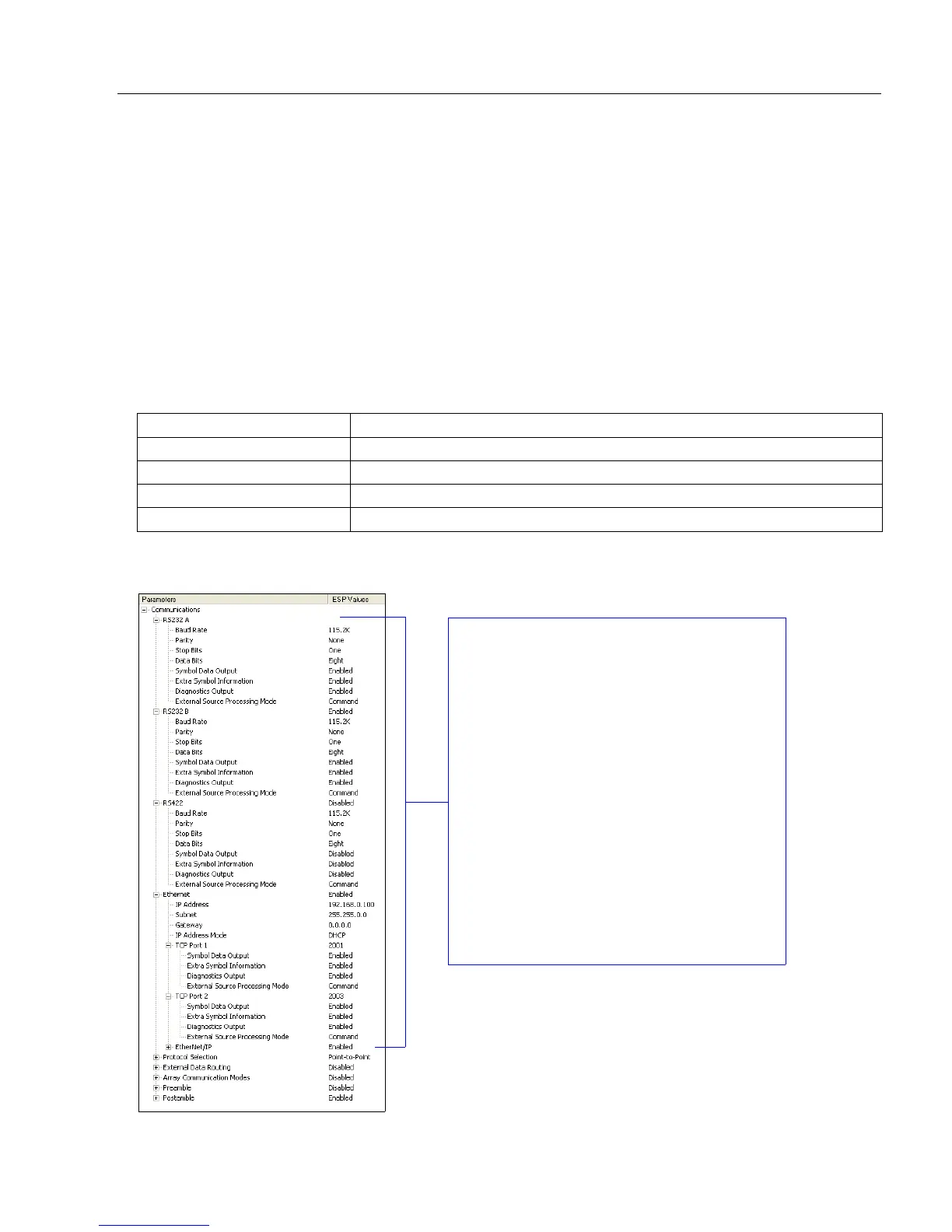
The screen capture below (from ESP) shows the QX-830’s four communications ports and
the parameters for each.
Data Type Example
Command Data Serial commands; scanner responses to serial commands.
Symbol Data Any string of data encoded in a symbol.
Extra Symbol Information Decodes per trigger, decode direction, configuration database index number.
Diagnostic Data Laser status, temperature, service message.
RS-232 A, RS-232 B, and RS-422 are
serial. RS-232 A is always enabled. RS-232
B and RS-422 can be enabled or disabled to
match the physical requirements of the
application. Ethernet can also be enabled
or disabled as required.
RS-232 A, RS-232 B, and RS-422 can be
configured for Baud Rate, Parity, Stop Bits,
Data Bits, Symbol Data Output, Extra Symbol
Information (Decodes Before Output, Symbol
Position Output, etc.), Diagnostics Output,
and External Source Processing Mode
(Command or Data).
Ethernet can be configured for IP Address,
Subnet Mask, Gateway, IP Address Mode
(Primary or Secondary TCP Port), Symbol
Data Output, Extra Symbol Information,
Diagnostics Output, and External Source
Processing Mode.
 Loading...
Loading...