Chapter 6: Gas Correction Factor (GCF)
95
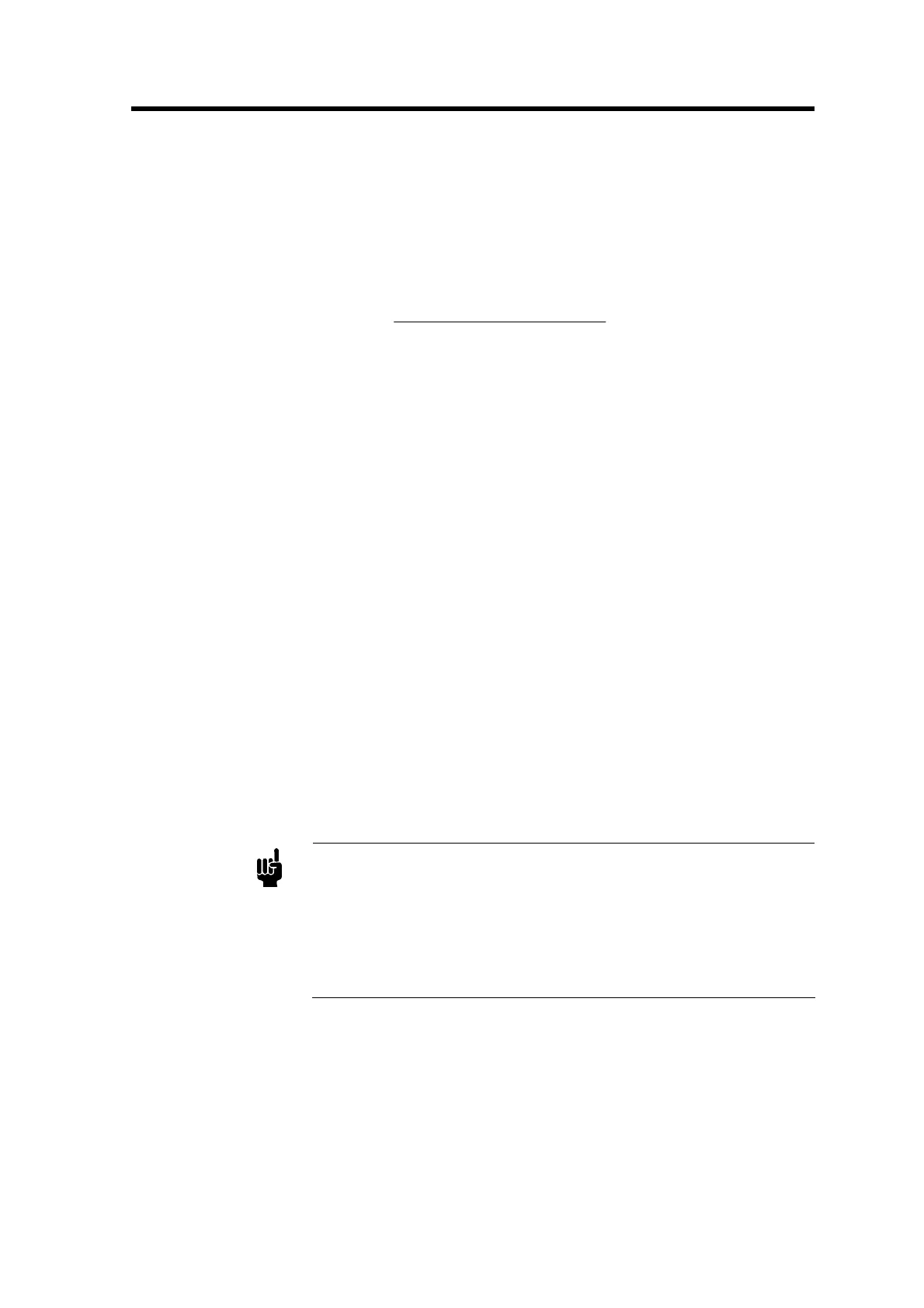
How To Calculate the GCF for Gas Mixtures
For gas mixtures, the calculated Gas Correction Factor is not simply the weighted average of each
component’s GCF. Instead, the GCF (relative to nitrogen) is calculated by the following equation:
nnn2211
nn2211
x
cpacpa cpa
s....a sa s(a 0,3106
GCF
ρρρ
....
)
21
++
=
where:
GCF
m
= gas correction factor for a gas mixture
0.3106 = (standard density of nitrogen) (specific heat of nitrogen)
a
1
,
a
2
,..an
= fractional flow of gases 1 through n
Note: a
1
through a
n
must add up to 1.0
s
1
,
s
2
,...sn
= Molecular Structure correction factor for gases 1 through n
where S equals:
1.030 for monatomic gases
1.000 for diatomic gases
0.941 for triatomic gases
0.880 for polyatomic gases
d1 through dn = standard density for gases 1 through n, in g/l
(at 0° C and 760 mmHg)
cp1 through cpn = specific heat of gases 1 through n, in cal/g° C
Note
1. When using the GCF, the accuracy of the flow reading may vary by
± 5%, however, the repeatability will remain ± 0.2% of FS.
2. The linearity and accuracy may be improved by calibrating the unit
with the process gas or using a gas with equivalent properties
(surrogate gas). Contact MKS for more information.
3. All MKS readouts have gas correction adjustment controls to
provide direct readout.
 Loading...
Loading...