Appendix E: Additional BCM2 Information
What is a Certificate Chain
If you are familiar with a certificate chain, you can ignore this topic
and refer to
Illustration - GMAIL SMTP Certificate Chain
(on page
596).
A certificate or a chain of certificates is used for trusting a TLS server
that you want to connect.
The receiver, such as BCM2, can trust a TLS server only after an
appropriate certificate (chain) which is "related to" that TLS server's
certificate is uploaded to the receiver.
How a certificate chain is generated:
To explain how a TLS server's certificate is "related to" the certificate
(chain) that is uploaded to the receiver, we assume that there are three
"related" certificates.
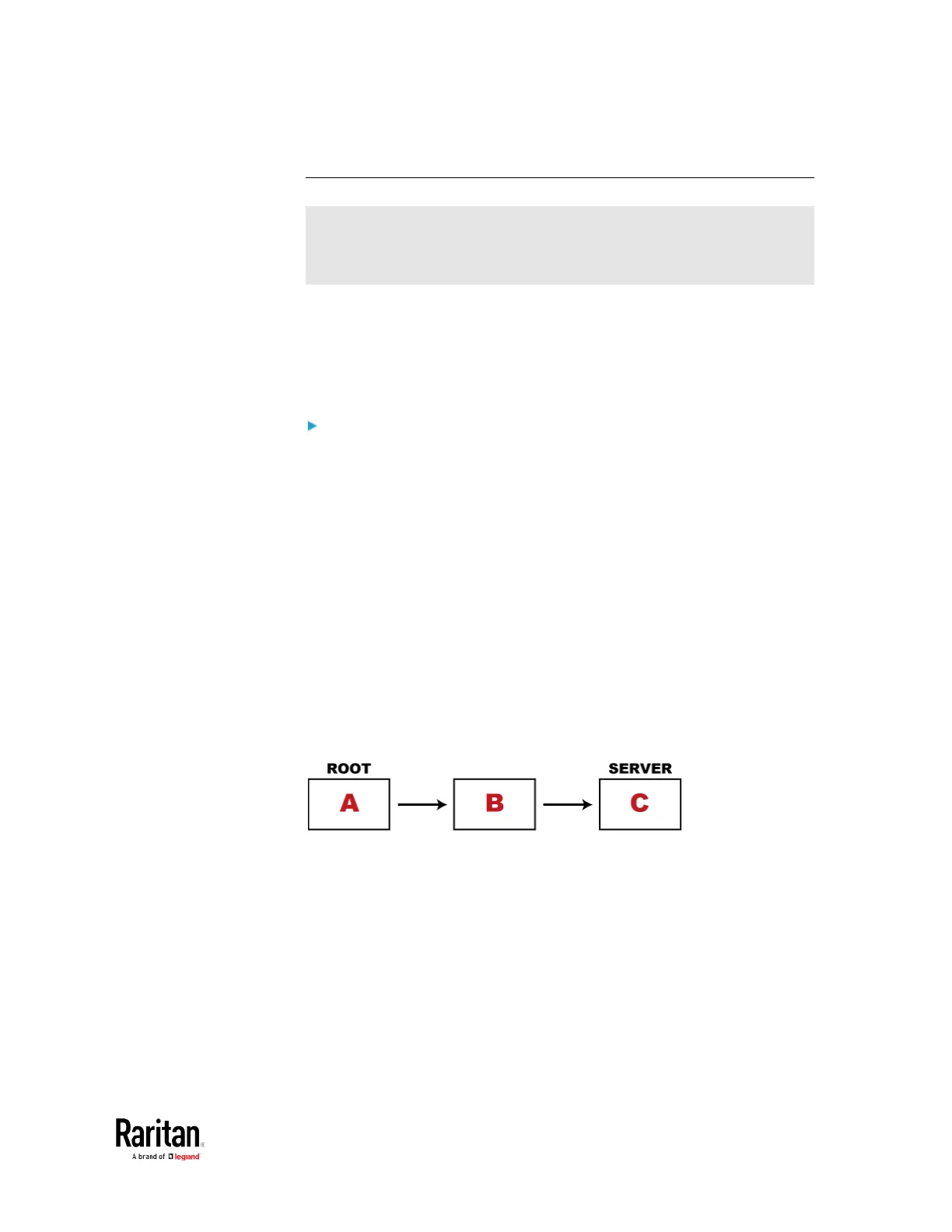
• Certificate C. The certificate issued to the TLS server you want to
connect.
'Certificate C' is issued by the certificate authority (CA) entity called
'Issuer B'.
• Certificate B. The certificate issued to 'Issuer B'.
'Certificate B' is issued by a CA entity called 'Issuer A', and it is an
intermediate certificate.
• Certificate A. The self-signed certificate issued by Issuer A. Issuer A
is a root CA.
The above three certificates form a certificate path, which is called the
"certificate chain".

 Loading...
Loading...