2-18 Installation Date Code 20001006
SEL-351 Instruction Manual
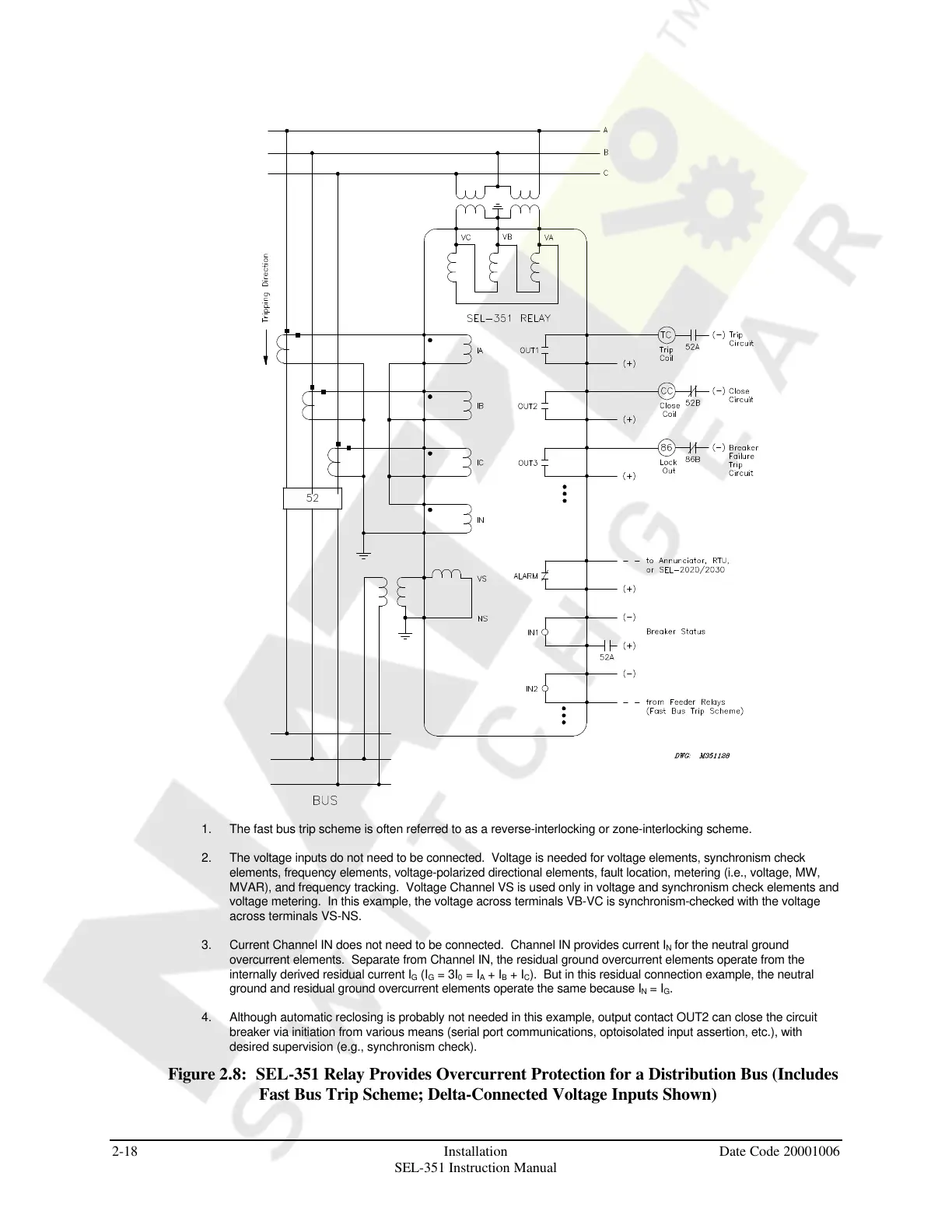
1. The fast bus trip scheme is often referred to as a reverse-interlocking or zone-interlocking scheme.
2. The voltage inputs do not need to be connected. Voltage is needed for voltage elements, synchronism check
elements, frequency elements, voltage-polarized directional elements, fault location, metering (i.e., voltage, MW,
MVAR), and frequency tracking. Voltage Channel VS is used only in voltage and synchronism check elements and
voltage metering. In this example, the voltage across terminals VB-VC is synchronism-checked with the voltage
across terminals VS-NS.
3. Current Channel IN does not need to be connected. Channel IN provides current I
N
for the neutral ground
overcurrent elements. Separate from Channel IN, the residual ground overcurrent elements operate from the
internally derived residual current I
G
(I
G
= 3I
0
= I
A
+ I
B
+ I
C
). But in this residual connection example, the neutral
ground and residual ground overcurrent elements operate the same because I
N
= I
G
.
4. Although automatic reclosing is probably not needed in this example, output contact OUT2 can close the circuit
breaker via initiation from various means (serial port communications, optoisolated input assertion, etc.), with
desired supervision (e.g., synchronism check).
Figure 2.8: SEL-351 Relay Provides Overcurrent Protection for a Distribution Bus (Includes
Fast Bus Trip Scheme; Delta-Connected Voltage Inputs Shown)
Courtesy of NationalSwitchgear.com
 Loading...
Loading...