PROSINE 2.0 INVERTER•CHARGER USER’S MANUAL
74
445-0089-01-01
AC Bad Causes
If the input AC is not acceptable according to the configuration values you
have set, the AC Bad Cause screen in the Diagnostics menu indicates why.
Specific causes are listed in Table 7. You have the option of leaving the values
or changing them depending on your circumstances. If you want to change
configuration settings, see “Configure PROsine—Advanced Menu‚” on
page 48.
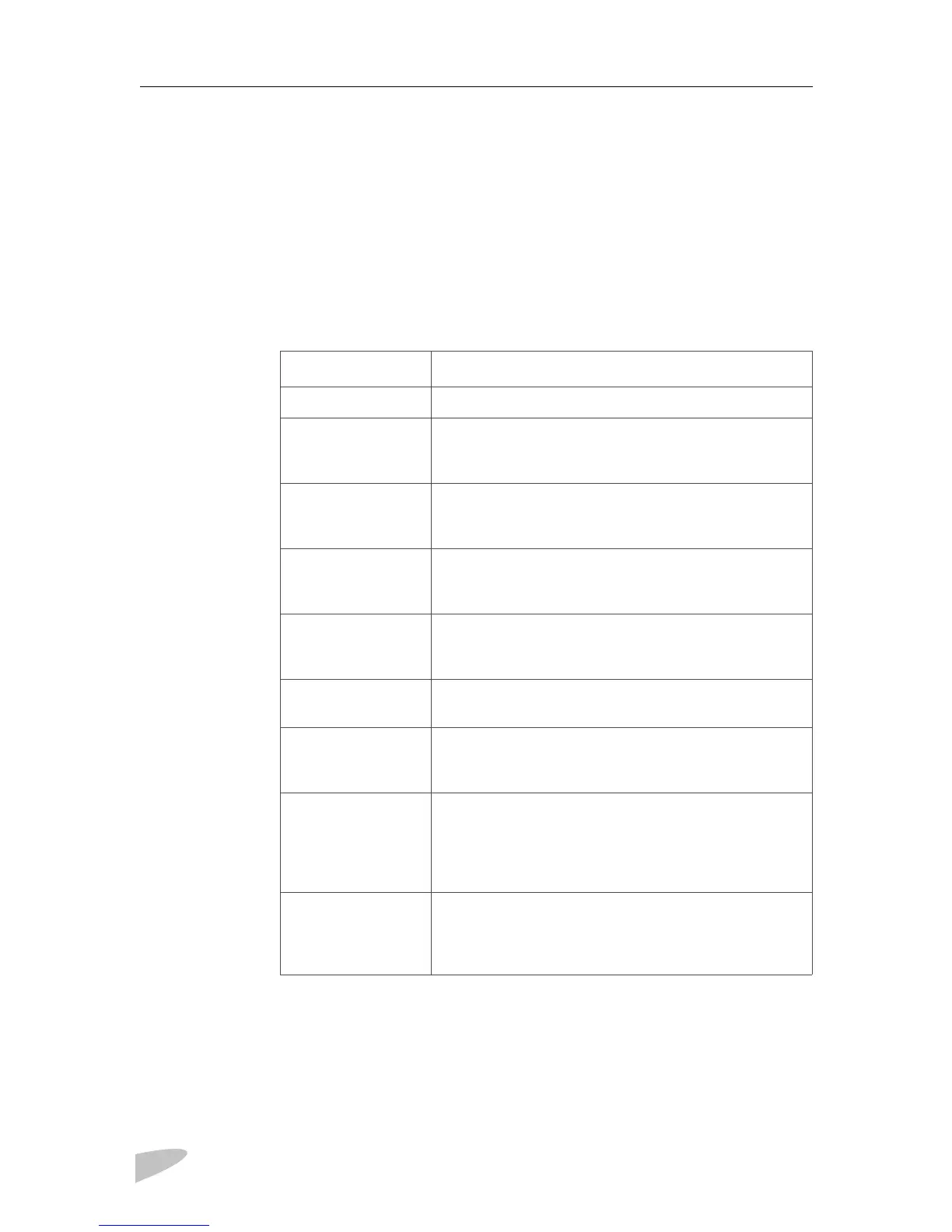
Table 7 AC Bad Causes
AC Bad Cause Details
None There is no problem with the AC input.
Low Cycle V In The rms voltage as calculated over one cycle (0.016s) was
less than the user-set minimum acceptable operating
voltage.
High Cycle V In The rms voltage as calculated over one cycle (0.016s) was
greater than the user-set maximum acceptable operating
voltage.
Low Average V In The rms voltage as calculated over 16 cycles (0.25s) was
less than the user-set minimum acceptable operating
voltage.
Hi Average V In The rms voltage as calculated over 16 cycles (0.25s) was
greater than the user-set maximum acceptable operating
voltage.
Low Frequency The frequency was less than the user-set minimum
acceptable operating frequency.
High Frequency The frequency was greater than the user-set maximum
acceptable operating frequency.
V In Cycle Delta The present cycle of shorepower is significantly different
from the previous cycle. This is a fast method of
recognizing an imminent power failure and is caused by a
sudden change in the waveshape, magnitude, or frequency
of the shorepower AC.
V In Step Delta The shorepower contains large, repetitive, sharp edges
which are incompatible with the PROsine and which you
may not want to pass to your loads. This might be caused
by a “modified sinewave” inverter or generator.

 Loading...
Loading...











