46 N9912A FieldFox User’s Guide
Emulate a projected phase shift in your measurement. For example, if you
know that you need to add a cable and that the length of that cable will add a
certain phase shift to your measurement, you can use phase offset to add that
amount and simulate the complete device measurement.
You can set the phase offset independently for each measurement trace.
How to set Phase Offset
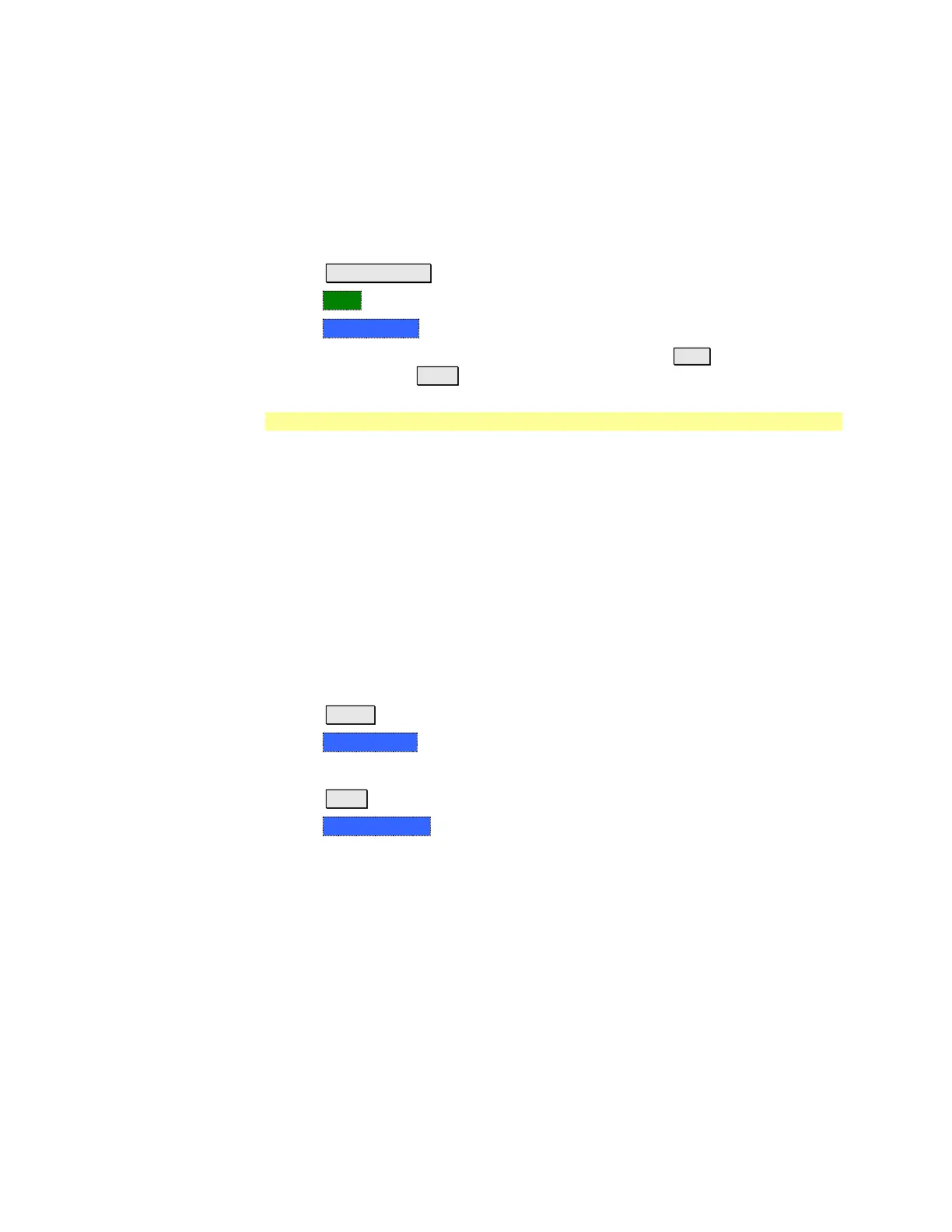
Press Scale / Amptd
Then More
Then Phase Offset
Enter a value in degrees using the numeric keypad, the ▲|▼ arrows, or the
rotary knob. Press Enter
Averaging
Averaging helps to reduce the effects of random noise on a measurement. You
specify the number of measurements to be averaged. The more measurements
averaged, the greater the amount of noise reduction. An average counter is
shown in the left edge of the screen as Avg <n> where <n> is the number of
measurements that are averaged.
Averaging can be set before or after calibration. When set before calibration,
each calibration standard is measured <n> times and averaged. More time is
needed to perform the calibration, but there will be less noise in the resulting
error terms which means that subsequent measurements will also have less
noise. In addition, noise is further reduced by continuing to average after
calibration.
How to set Averaging
Press BW 2.
Then Average <n> where <n> is the number of measurements to average.
Enter a value using the numeric keypad. Enter 1 for NO averaging.
Press Enter.
Then Average Mode Choose from the following:
o Sweep - Each data point is based on the average of the same data point
being measured over <n> consecutive sweeps. The average counter shows
the number of previous sweeps that have been averaged together to form the
current trace. When the counter reaches the specified count, then a ‘running
average’ of the last <n> sweeps is displayed.
o Point - Each data point is measured <n> times and averaged before going to
the next data point. On subsequent sweeps, averaging restarts by measuring
each data point again <n> times. The average counter is not updated because
data is not displayed until all the averages have been applied.
o Point averaging is usually faster than sweep averaging. However, you may
need to increase the Point Average count to obtain the same level of noise
reduction as with sweep averaging.
 Loading...
Loading...