Version 7.0 559 Mediant 3000
User's Manual 28. SBC Overview
The device uses different local ports (e.g., for RTP, RTCP and fax) for each leg (inbound
and outbound). The local ports are allocated from the Media Realm associated with each
leg. The Media Realm assigned to the leg's IP Group (in the IP Group table) is used. If not
assigned to the IP Group, the Media Realm assigned to the leg's SIP Interface (in the SIP
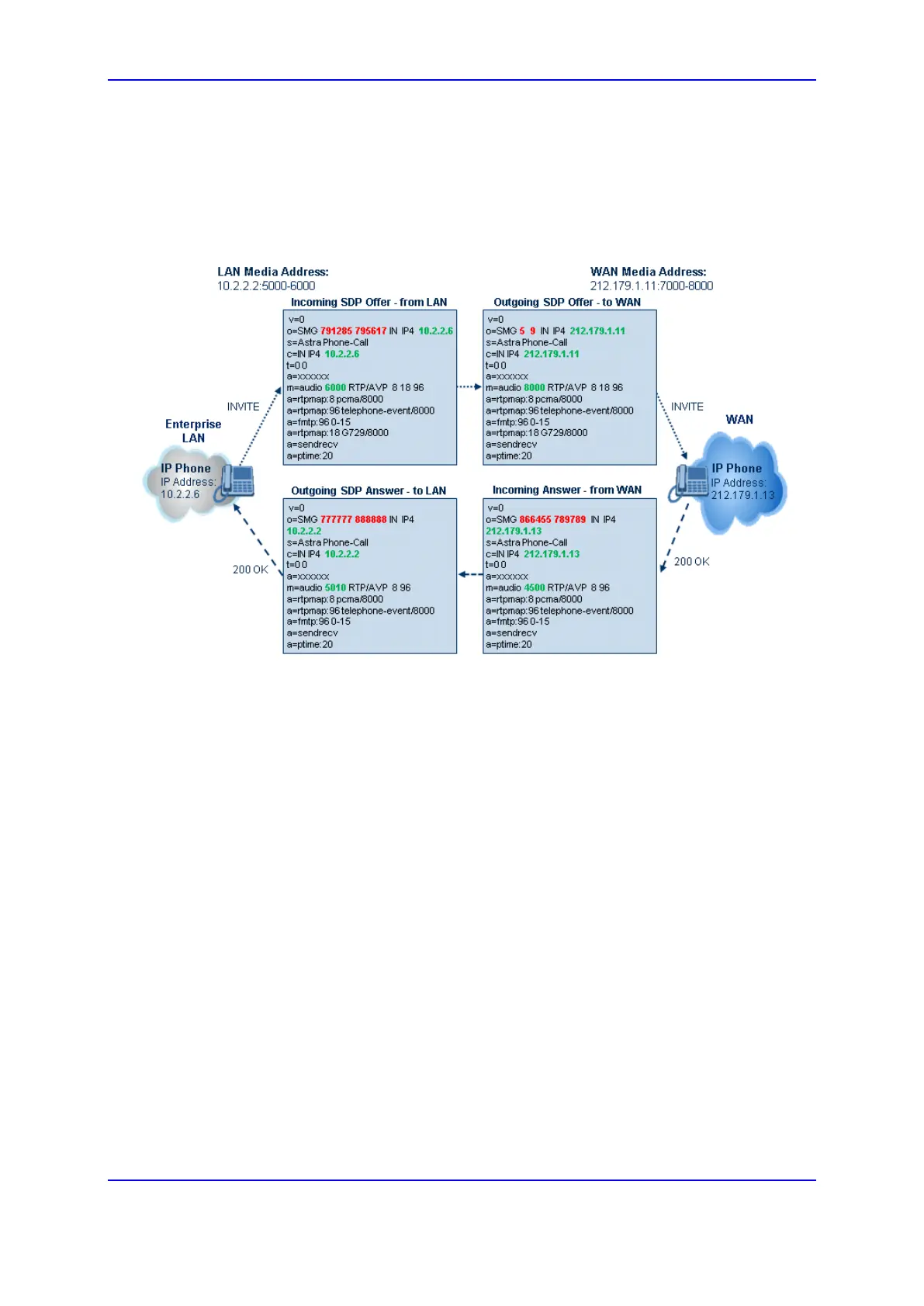
Interface table) is used. The following figure provides an example of SDP handling for a
call between a LAN IP Phone 10.2.2.6 and a remote IP Phone 212.179.1.13 on the WAN.
Figure 28-3: SDP Offer/Answer Example
28.5.2 Direct Media
You can configure the device to allow the media (RTP/SRTP) session to flow directly
between the SIP endpoints, without traversing the device. This is referred to as No Media
Anchoring (also known as Anti-Tromboning or Direct Media). SIP signaling continues to
traverse the device, with minimal intermediation and involvement, to enable certain SBC
capabilities such as routing. By default, the device employs media anchoring, whereby the
media session traverses the device, as described in ''Media Anchoring'' on page 558.
Direct media offers the following benefits:
Saves network bandwidth
Reduces the device's CPU usage (as there is no media handling)
Avoids interference in SDP negotiation and header manipulation on RTP/SRTP

 Loading...
Loading...











