User's Manual 648 Document #: LTRT-89730
Mediant 3000
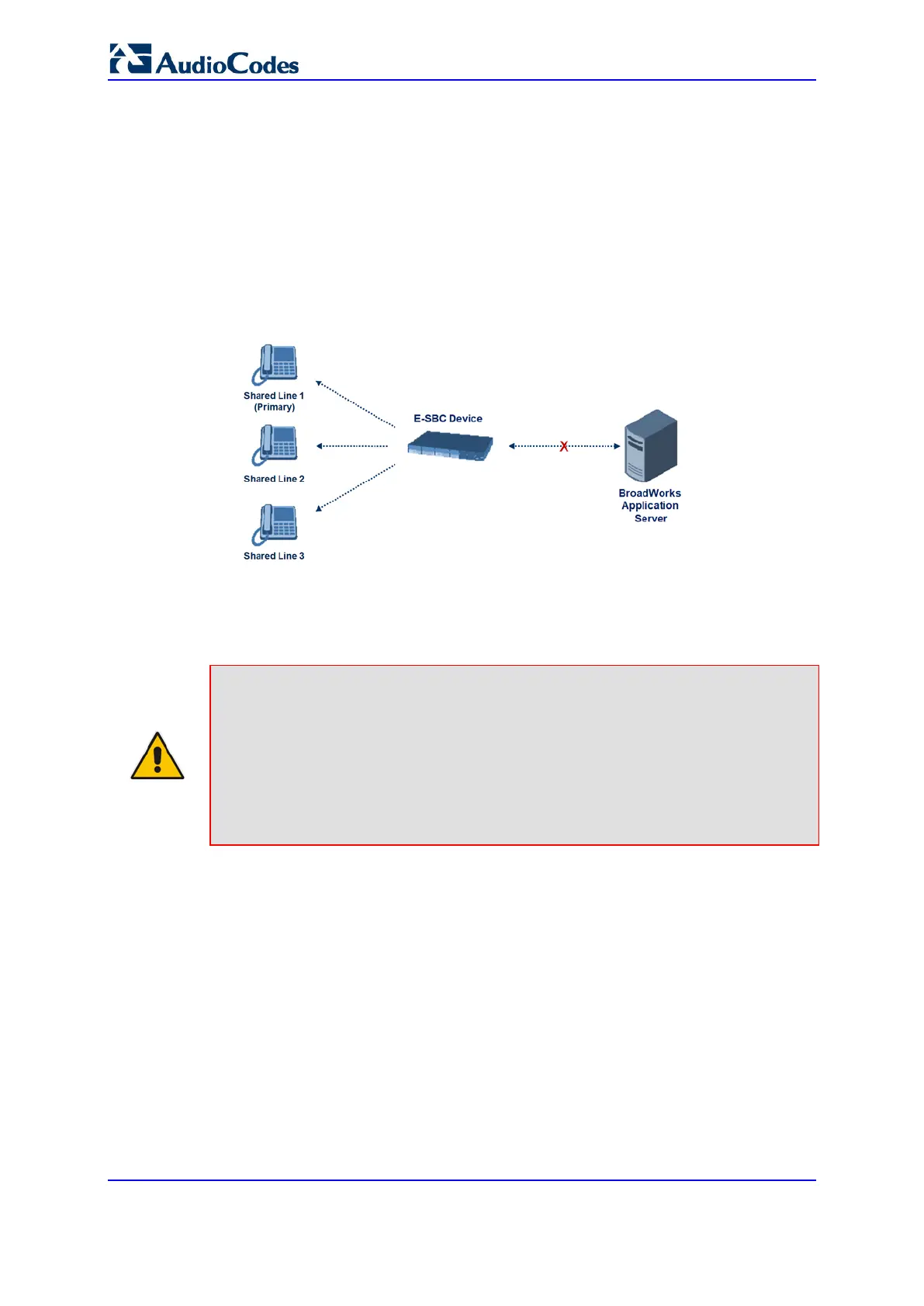
network connection between the device and the BroadSoft AS is down, the device
manages the Shared Call Appearance feature for the SIP clients.
This feature is supported by configuring a primary extension and associating it with
secondary extensions (i.e., shared lines) so that incoming calls to the primary extension
also ring at the secondary extensions. The call is established with the first extension to
answer the call and consequently, the ringing at the other extensions stop. For example,
assume primary extension number 600 is shared with secondary extensions 601 and 602.
In the case of an incoming call to 600, all three phone extensions ring simultaneously,
using the device's call forking feature as described in ''SIP Forking Initiated by SIP Proxy
Server'' on page 645. Note that incoming calls specific to extensions 601 or 602 ring only at
these specific extensions.
Figure 36-5: Call Survivability for BroadSoft's Shared Line Appearance
To configure this capability, you need to configure a shared-line, inbound manipulation rule
for registration requests to change the destination number of the secondary extension
numbers (e.g. 601 and 602) to the primary extension (e.g., 600). Call forking must also be
enabled. The following procedure describes the main configuration required.
Notes:
• The device enables outgoing calls from all equipment that share the same line
simultaneously (usually only one simultaneous call is allowed per a specific shared
line).
• You can configure whether REGISTER messages from secondary lines are
terminated on the device or forwarded transparently (as is), using the
SBCSharedLineRegMode parameter.
• The LED indicator of a shared line may display the wrong current state.
To configure the Shared Line feature:
1. In the IP Group table (see ''Configuring IP Groups'' on page 343), add a Server-type
IP Group for the BroadWorks server.
2. In the IP Group table, add a User-type IP Group for the IP phone users and set the
'SBC Client Forking Mode' parameter to Parallel so that the device forks incoming
calls to all contacts under the same AOR registered in the device's registration
database.
3. In the IP-to-IP Routing table (see ''Configuring SBC IP-to-IP Routing Rules'' on page
603), add a rule for routing calls between the above configured IP Groups.
4. In the IP to IP Inbound Manipulation table (see ''Configuring IP-to-IP Inbound
Manipulations'' on page 623), add a manipulation rule for the secondary extensions
(e.g., 601 and 602) so that they also register to the device's database under the
primary extension contact (e.g., 600):

 Loading...
Loading...











