multi-VRF CE support is required in the switches. Because multi-VRF CE is a Layer 3 feature, each interface
in a VRF must be a Layer 3 interface.
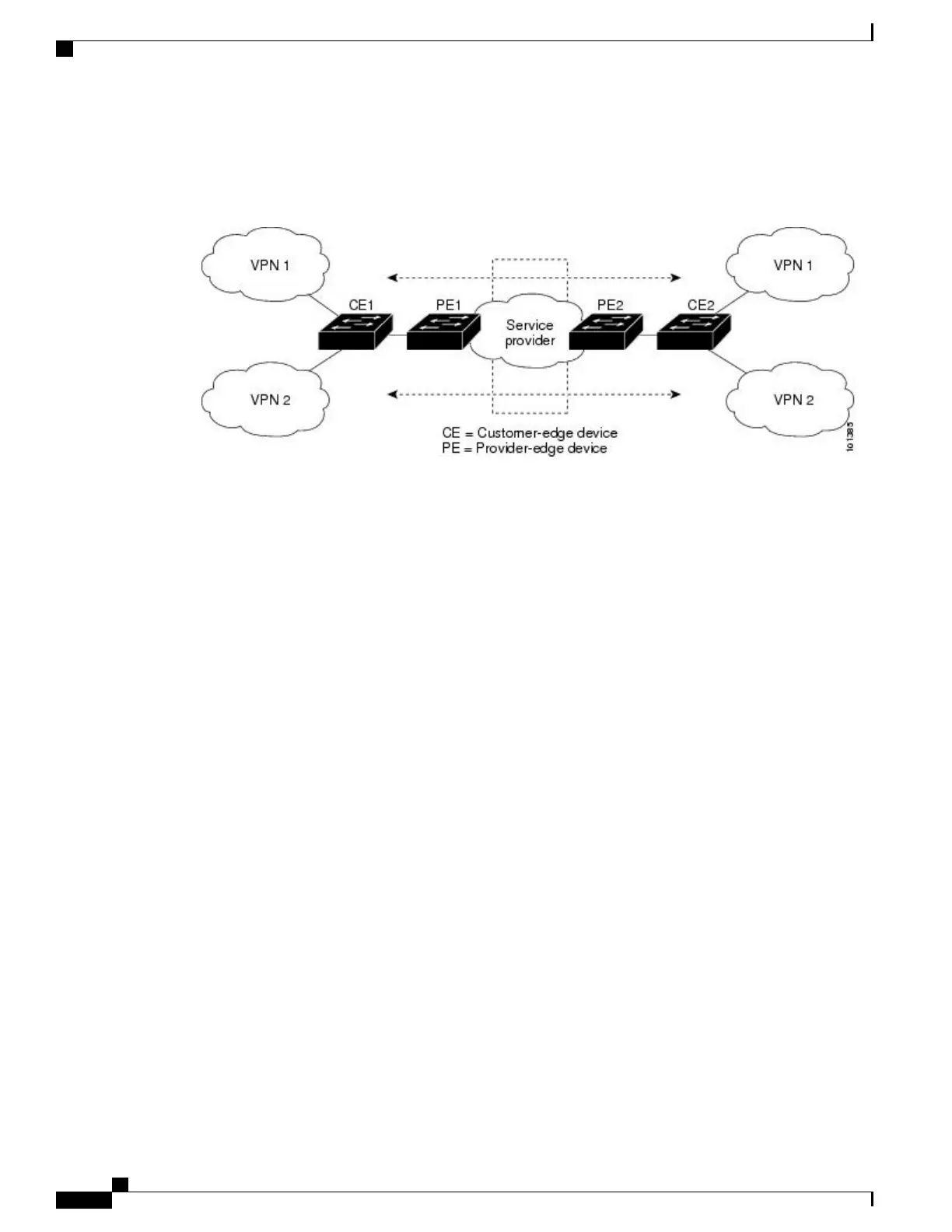
Figure 7: Switches Acting as Multiple Virtual CEs
When the CE switch receives a command to add a Layer 3 interface to a VRF, it sets up the appropriate
mapping between the VLAN ID and the policy label (PL) in multi-VRF-CE-related data structures and adds
the VLAN ID and PL to the VLAN database.
When multi-VRF CE is configured, the Layer 3 forwarding table is conceptually partitioned into two sections:
•
The multi-VRF CE routing section contains the routes from different VPNs.
•
The global routing section contains routes to non-VPN networks, such as the Internet.
VLAN IDs from different VRFs are mapped into different policy labels, which are used to distinguish the
VRFs during processing. For each new VPN route learned, the Layer 3 setup function retrieves the policy
label by using the VLAN ID of the ingress port and inserts the policy label and new route to the multi-VRF
CE routing section. If the packet is received from a routed port, the port internal VLAN ID number is used;
if the packet is received from an SVI, the VLAN number is used.
Packet-Forwarding Process
This is the packet-forwarding process in a multi-VRF-CE-enabled network:
•
When the switch receives a packet from a VPN, the switch looks up the routing table based on the input
policy label number. When a route is found, the switch forwards the packet to the PE.
•
When the ingress PE receives a packet from the CE, it performs a VRF lookup. When a route is found,
the router adds a corresponding MPLS label to the packet and sends it to the MPLS network.
•
When an egress PE receives a packet from the network, it strips the label and uses the label to identify
the correct VPN routing table. Then it performs the normal route lookup. When a route is found, it
forwards the packet to the correct adjacency.
•
When a CE receives a packet from an egress PE, it uses the input policy label to look up the correct
VPN routing table. If a route is found, it forwards the packet within the VPN.
Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9500 Switches)
160
Configuring IP Unicast Routing
Understanding Multi-VRF CE

 Loading...
Loading...











