87
(3)CYLINDER BLOCK, CRANKSHAFT,
PISTONS AND OIL PAN
1.Pistons, Piston Rings and Piston Pins
(1)Diameter of piston
Measure the diameter of the piston at its skirt
in a direction transverse to the piston pin with
a micrometer as shown in the illustration. If
the diameter exceeds the limit, replace the
piston. Select a new piston so that the differ-
ence between average weight of all pistons in
one engine does not exceed the standard.
Unit:mm(in.)
Item Nominal size Standard Limit
77.93 to
Standard 78.00 77.95 77.80
(3.0709) (3.0681 to (3.0630)
3.0689)
0.25 78.18to
Diameter (0.0098) 78.25 78.20 78.05
of piston oversize (3.0807) (3.0779to (3.0728)
3.0787)
0.50 78.43to
(0.0197) 78.50 78.45 78.30
oversize (3.0905) (3.0878to (3.0827)
Maximum permissible
difference between average 5(0.18)
weight of all pistons in one
engine, g(oz)
Unit:mm(in.)
Item Standard Limit
No.1 comp- 0.06 to 0.10 0.30(0.0118)
ression ring (0.0024 to 0.0039)
No.2 comp- 0.05 to 0.09 0.20(0.0079)
ression ring (0.0020 to 0.0035)
Oil ring 0.03 to 0.07 0.20(0.0079)
(0.0012 to 0.0028)
(b)If the clearance still exceeds the limit
after new piston rings have been
installed, replace the piston.
(3)Clearance between ends of piston ring
Put the piston ring in a gauge or in the bore in
a new cylinder block and measure the clear-
ance between the ends of the ring with a
feeler gauge as shown in the illustration. If the
clearance exceeds the limit, replace all the
rings.
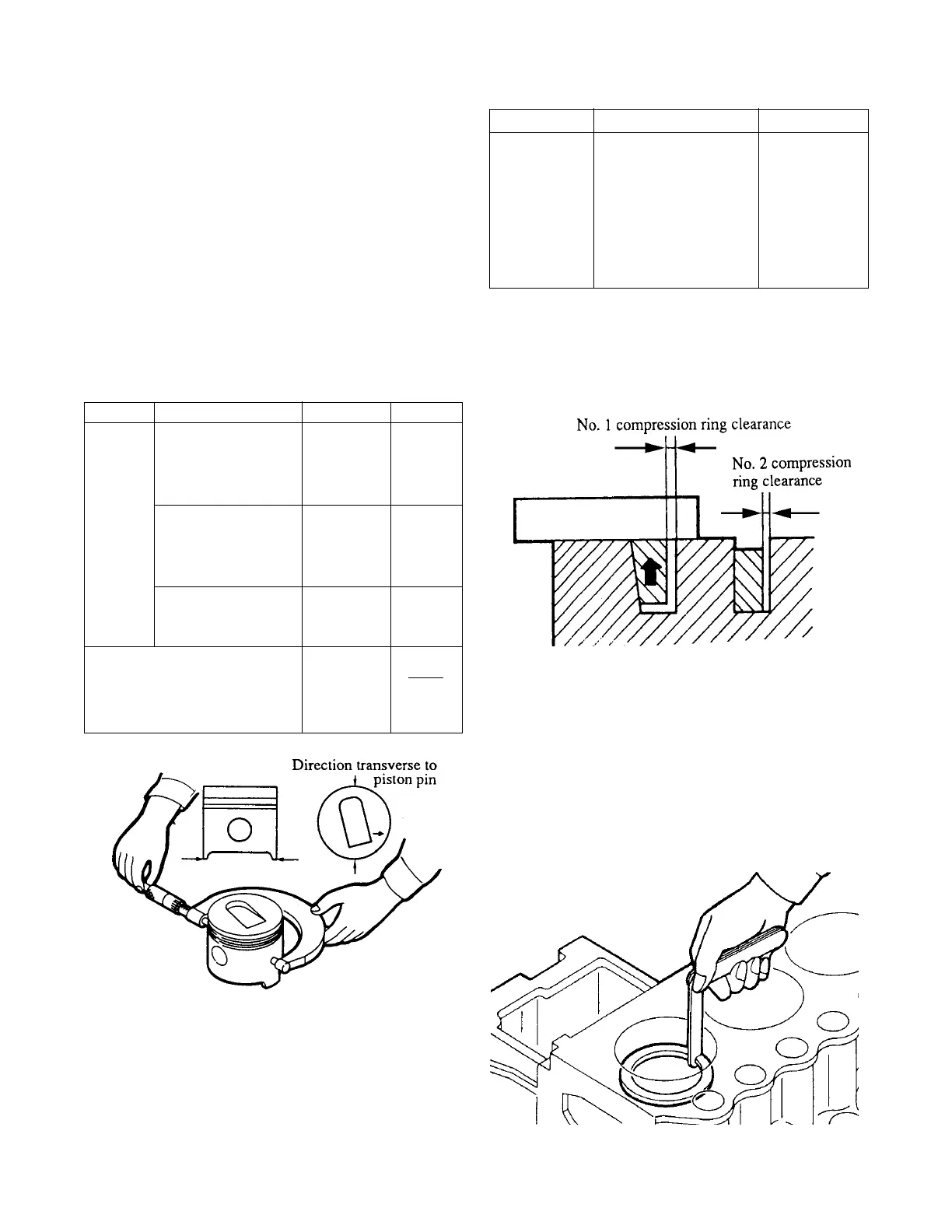
(2)Clearance between piston ring and groove
(a)Measure the clearance between the
groove and piston with a straight edge
and a feeler gauge as shown in the
illustration. If the clearance exceeds the
limit, replace the ring.

 Loading...
Loading...