IPv4 Communication Fundamentals
ECLYPSE User Guide 23
About Routers, Switches, and Hubs
The differences between a hub, switch, and router are discussed in the table below.
Every incoming data packet is repeated on every other port on the
device. Due to this, all traffic is made available on all ports which increase
data packet collisions that affect the entire network, thus limiting its data
carrying capacity.
A switch creates a one-to-one virtual circuit that directs IP packets
directly to the port that the destination computer is connected to.
A switch maintains a lookup table that contains the MAC addresses of all
the devices that are connected to the switch ports. The switch always
refers to its lookup table before it forwards data packets to the destination
devices.
Like a switch, a router learns the IP addresses of all devices connected to
any of its RJ-45 ports to create a routing table. If a data packet arrives at
the router’s port with a destination IP address that is:
Found in the router’s routing table, the router forwards the data
packet to the appropriate port for the device that has this IP
address.
For a network with a different network ID than the current
network ID, the router forwards the data packet to the uplink port
where the next router will again either recognize the network ID
and route the data packet locally or again forwards the data
packet to the uplink port. By being exposed to traffic, a router
adds to its routing table the pathways necessary to resolve a
data packet’s pathway to its final destination, by passing through
one or more routers if necessary.
Table 3-1: Difference between a Hub, Switch, and Router
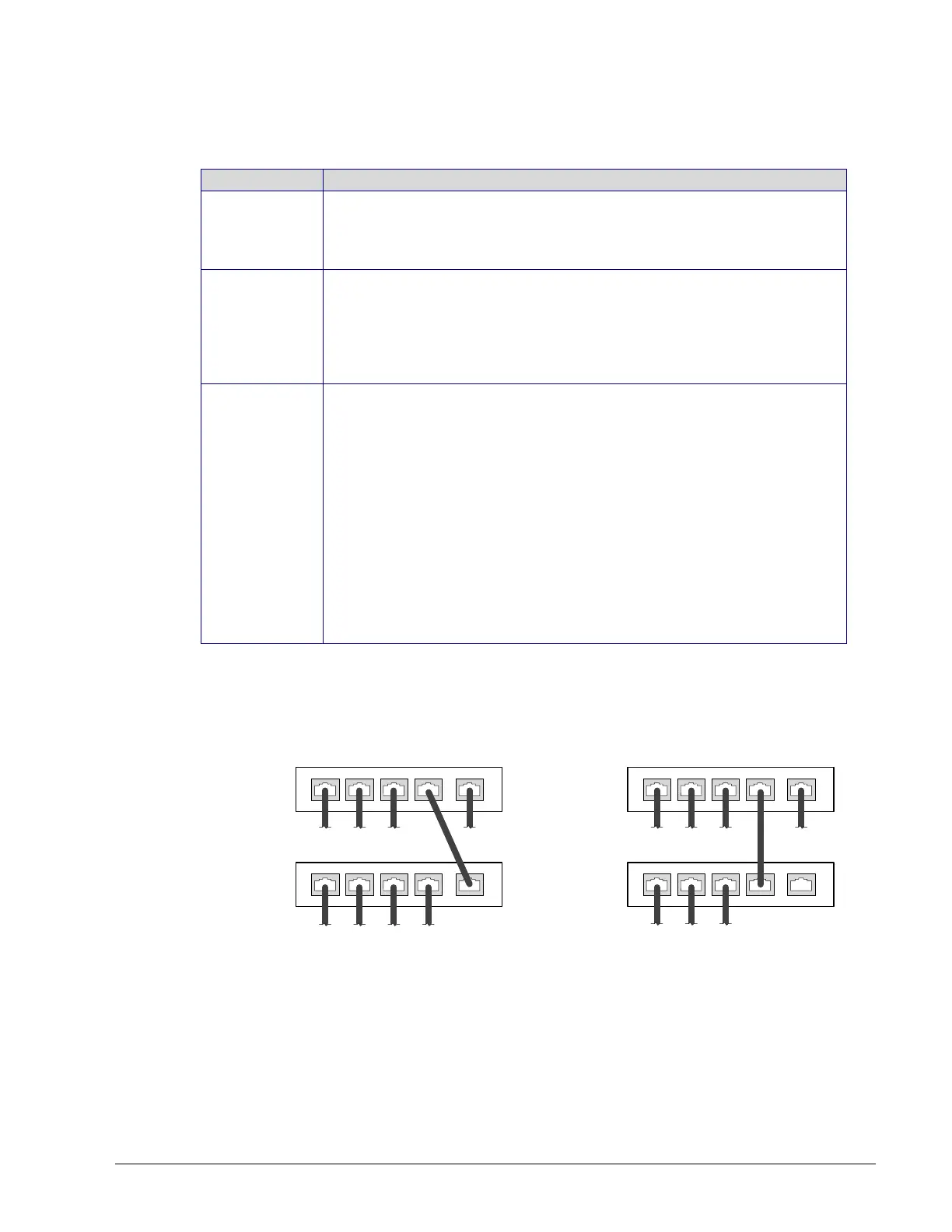
Connecting a Router
The way a router is connected to other devices changes its function.
1
UPLINK
2 3 4
1
UPLINK
2 3 4
ROUTER
A
ROUTER
B
Connection to use ROUTER A as a router
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
WAN
1
UPLINK
2 3 4
1
UPLINK
2 3 4
ROUTER
A
ROUTER
B
Connection to NOT use ROUTER A as a router
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
Device
To
WAN
UPLINK
Function is
Not Used
Figure 3-2: The Way a Router is Connected Changes its Function
On some routers, the uplink port is marked as WAN (Wide Area Network) and the numbered
ports are to be connected to the LAN (Local Area Network) devices.
 Loading...
Loading...