When a device requests data from another by sending a frame with no data where RTR is
recessive, that frame is called a
. The device which is identified with this frame
starts transmitting the requested data frame(with same ID).
The physical layer can be of any medium but it has to support recessive/dominant signals for
using logical AND between different devices. In this sections we will talks about the typical
twisted-pair electrical medium with differential voltages.
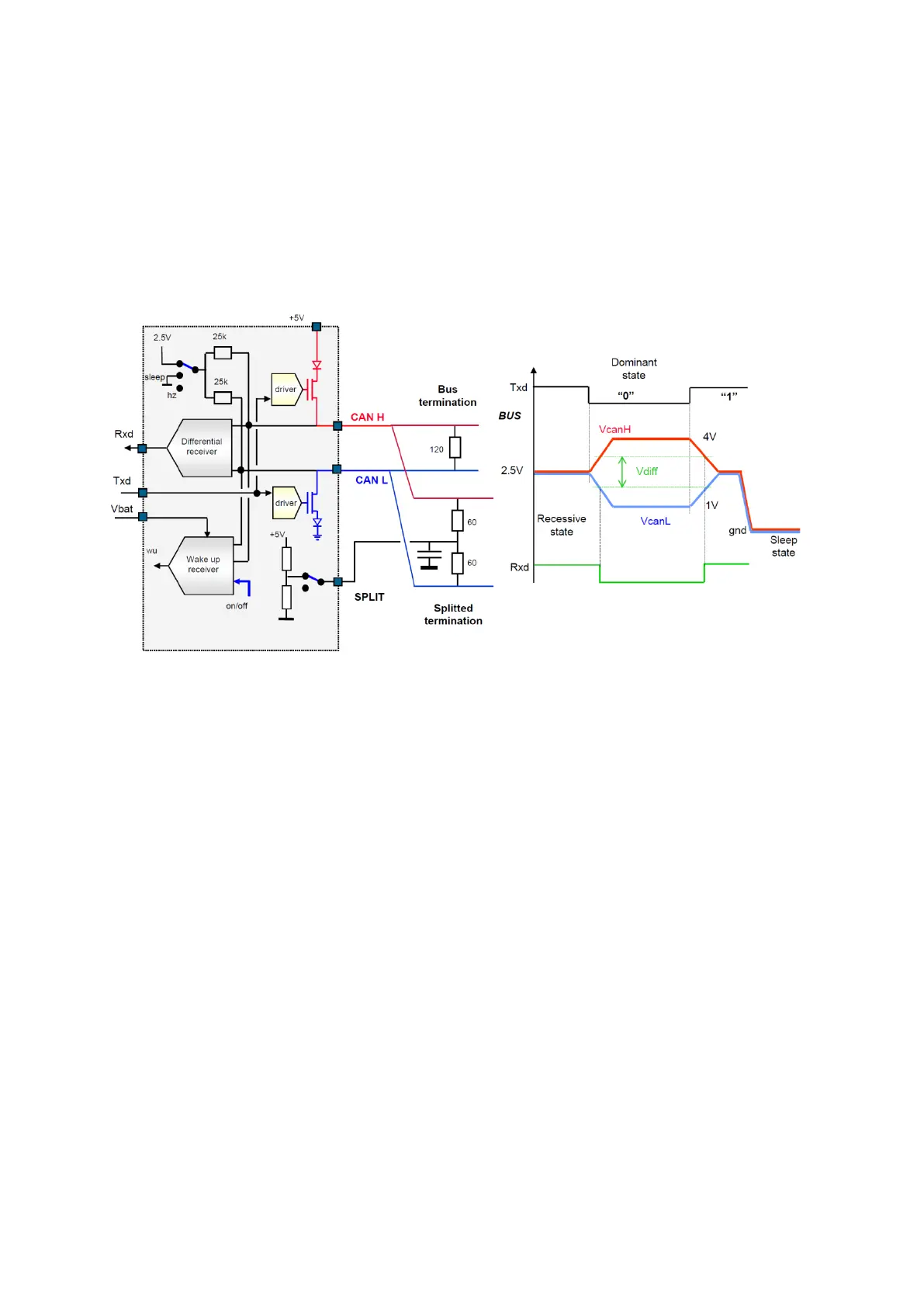
Figure 113/ A typical CAN transceiver and CANH/CANL signals
In high-speed CAN standard, CANH and CANL are derived from TX to from a differential voltage
with two states, ‘0’ the dominant state (CANH=3.5V, CANL=1.5V), and ‘1’ the recessive state
(CANH=CANL=2.5V). The RX signal is determined from CANH-CANL as, if the differential
voltage is above 0.9V then RX=’1’ and if it is less than 0.5V then RX=’0’.
CAN Transceivers of the devices at the edges of the can bus (the first and the last station) has to
use resistors as bus termination; either a 120 between CANH and CANL or a splitted
termination with two 60 with a reference voltage in the middle.
 Loading...
Loading...