IAAS: Addressed as a slave. When a master’s calling address is matched with the address
in the IBAD register, this flag is set.
IBB: Bus busy. When a START signal is detected, this flag is set and it is cleared when
STOP is detected and bus gets into the idle state.
IBAL: Arbitration Lost. If a loss of arbitration is detected then this flag is set. Here’s a list
of loss of arbitration situations:
o SDA is low when the master drives a high during an address or data transfer.
o SDA is low when the master drives a high during the acknowledge bit.
o A start signal is attempted while the bus is busy.
o A repeated start cycle is requested in slave mode.
o A stop condition is detected when the master didn’t request it.
SRW: Slave Read/Write. When IAAS is set, this bit indicated whether the slave has to
receive (0) or transmit(1). TXRX should be set according to this request.
RXAK: Received Acknowledge, this bit is set when no ACK signal is received.
IBIF: I-Bus Interrupt Flag, this flag is set on the following conditions: IBAL is set, TCF is
set, IAAS is set, RXAK is set during the master mode, bus going idle: IBB going from high
to low and BIIE set.
For generating interrupts, IBIE has to be enabled in the control register and then most of the
flags of the status register are activated. But an optional interrupt is related to the bus becoming
idle, this can be enabled by setting the BIIE bit of the I²C Bus Interrupt Config (IBIC) register.
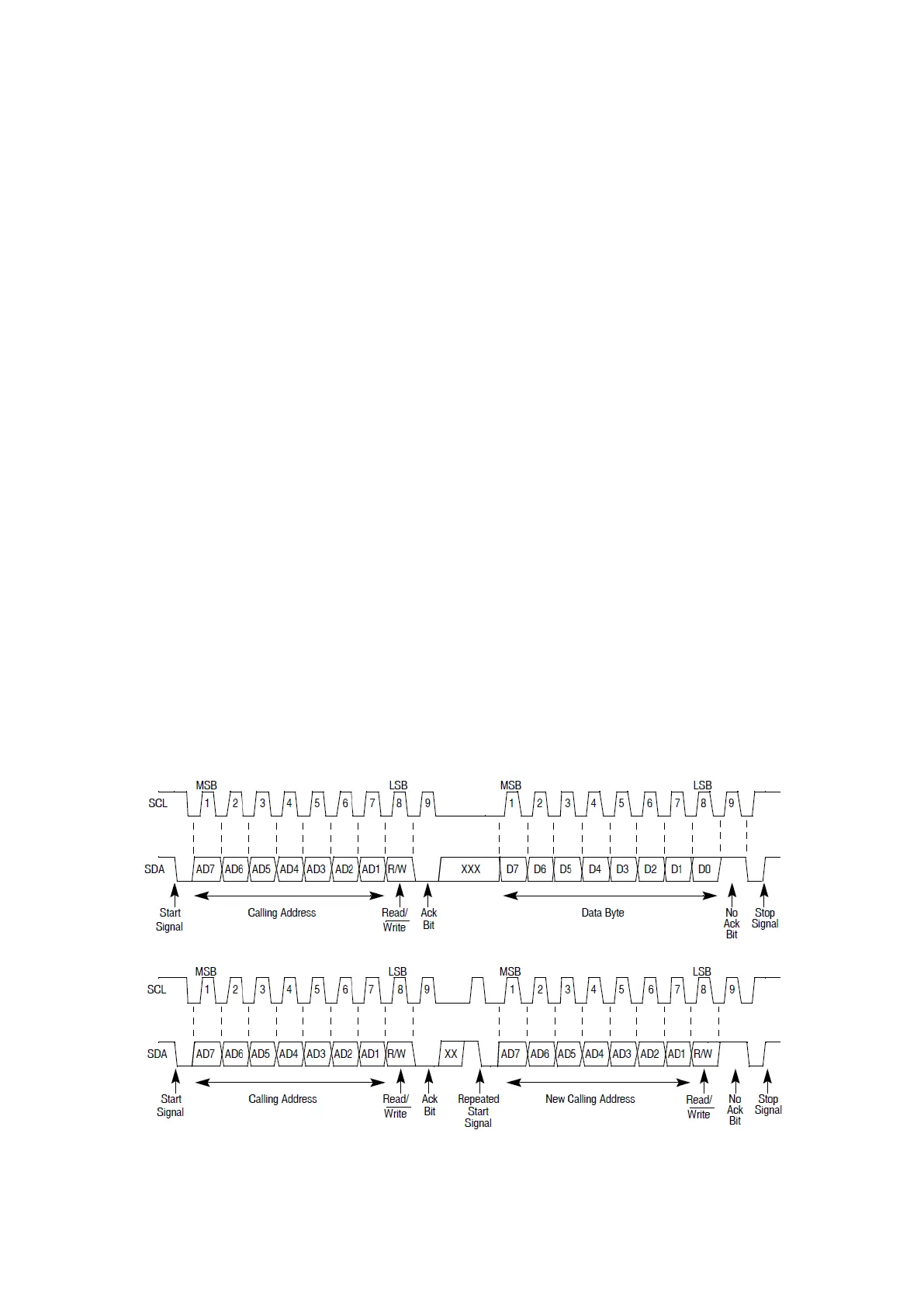
Data Setting
Data can be read from or written to the I²C Bus Data I/O Register (IBDR) who has an 8-bit data
field. In master Tx mode, when data is written to this register, the transfer is initiated. In master
mode, reading this register initiates next byte reception. In master mode, the first byte
transferred has to be the 7-bit address concatenated with the R/W
bit.
Figure 109 : I²C bus transmission signals (R.M. Rev8 – Fig. 20-10)
 Loading...
Loading...