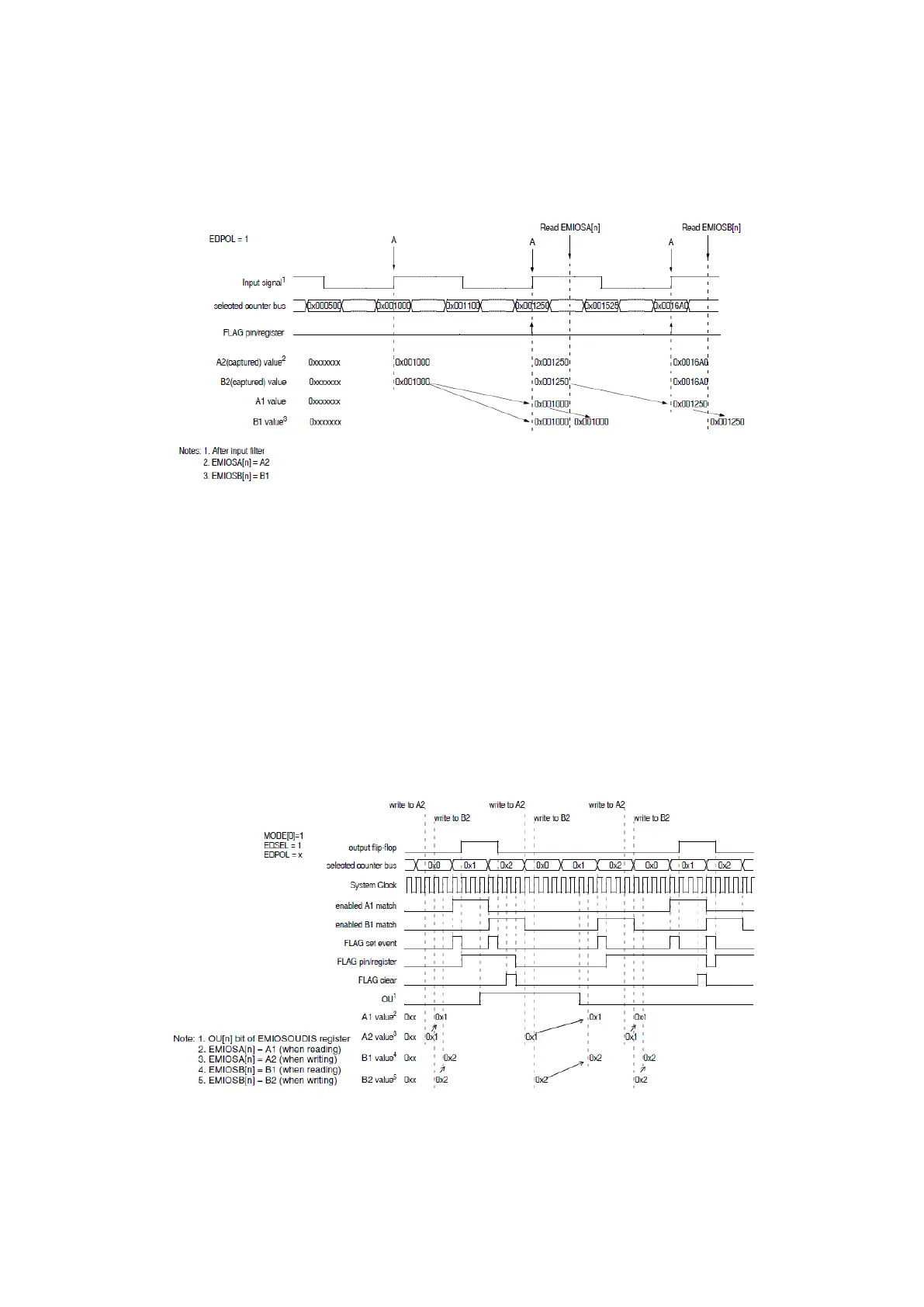
In order to get coherent measurement, a read on the register A (so A2) will disable transfers
from B2 to B1 and force a transfer from A1 to B1. The value in B1 will be intact for the upcoming
read on the register B. By subtracting B1 from A2, we can get the period. (See figure below for an
illustration of these register transfers).
Figure 52 : IPM Example (R.M. Rev8 – Fig. 24-26)
NOTE: If a period measurement happens during a counter roll over, maximum counter value has
to be added to A2 before subtracting B2.
DAOC: Double Action Output Compare
In the Double Action Output Compare mode a variable output pulse is generated by matches
occurring on comparators A and B. At initialisation, the output flip-flop is set to the complement
of the EDPOL.
Registers A and B write respectively to A2 and B2, and their data are transferred to A1 and B1 on
the next system clock cycle if OU is clear. The comparators A (and B) are enabled when a
transfer occurs to A1 (and B1), and then they are disabled on the next A (and B) matches.
Figure 53 : DAOC with transfer disabling (OU=1) example (R.M. Rev8 – Fig. 24-29)
When a match occurs on register A, the output is set to EDPOL, and on a match on register B, it is
set to complement of EDPOL. There is two possibilities for mode selection, MODE[0:6]=0000110
 Loading...
Loading...