222 Programming: Programming Contours
6.4 Path Contours—Cartesian Coordinates
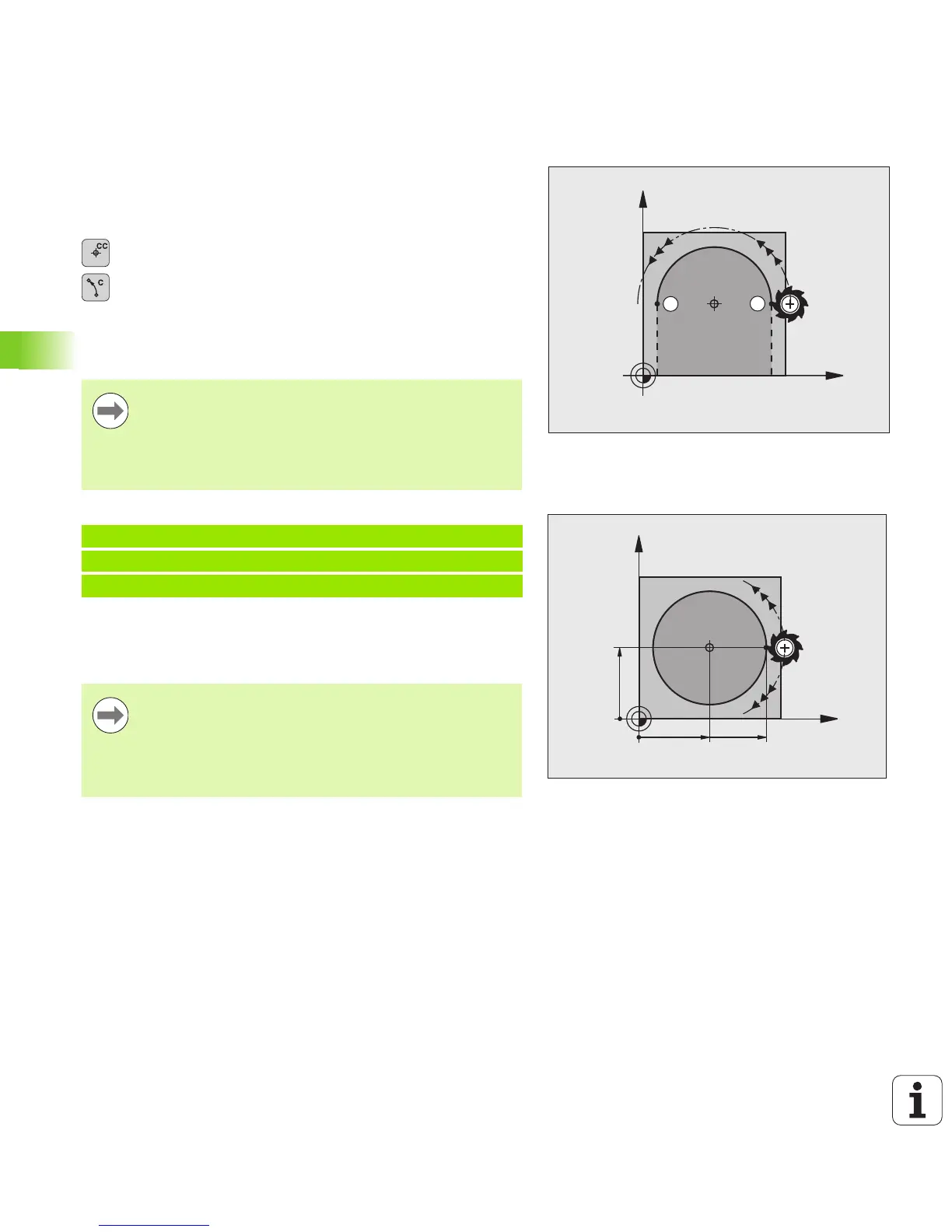
Circular path C around circle center CC
Before programming a circular arc, you must first enter the circle
center CC. The last programmed tool position will be the starting point
of the arc.
U Move the tool to the circle starting point.
U Enter the coordinates of the circle center
U Coordinates of the arc end point, and if necessary:
U Direction of rotation DR
U Feed rate F
U Miscellaneous function M
Example NC blocks
Full circle
For the end point, enter the same point that you used for the starting
point.
The TNC normally makes circular movements in the active
working plane. If you program circular arcs that do not lie
in the active working plane, for example C Z... X... DR+
with a tool axis Z, and at the same time rotate this
movement, then the TNC moves the tool in a spatial
circular arc, which means a circular arc in 3 axes.
5 CC X+25 Y+25
6 L X+45 Y+25 RR F200 M3
7 C X+45 Y+25 DR+
The starting and end points of the arc must lie on the
circle.
Input tolerance: up to 0.016 mm (selected with MP7431).
Smallest possible circle that the TNC can traverse:
0.0016 µm.

 Loading...
Loading...











