Appendix 4 Temperature Correction (TC) Function
A4
The temperature correction function converts the resistance values of temperature-depen-
dent measurement targets such as copper wire into resistance values at a specific temper-
ature (known as the standard temperature) and displays the results.
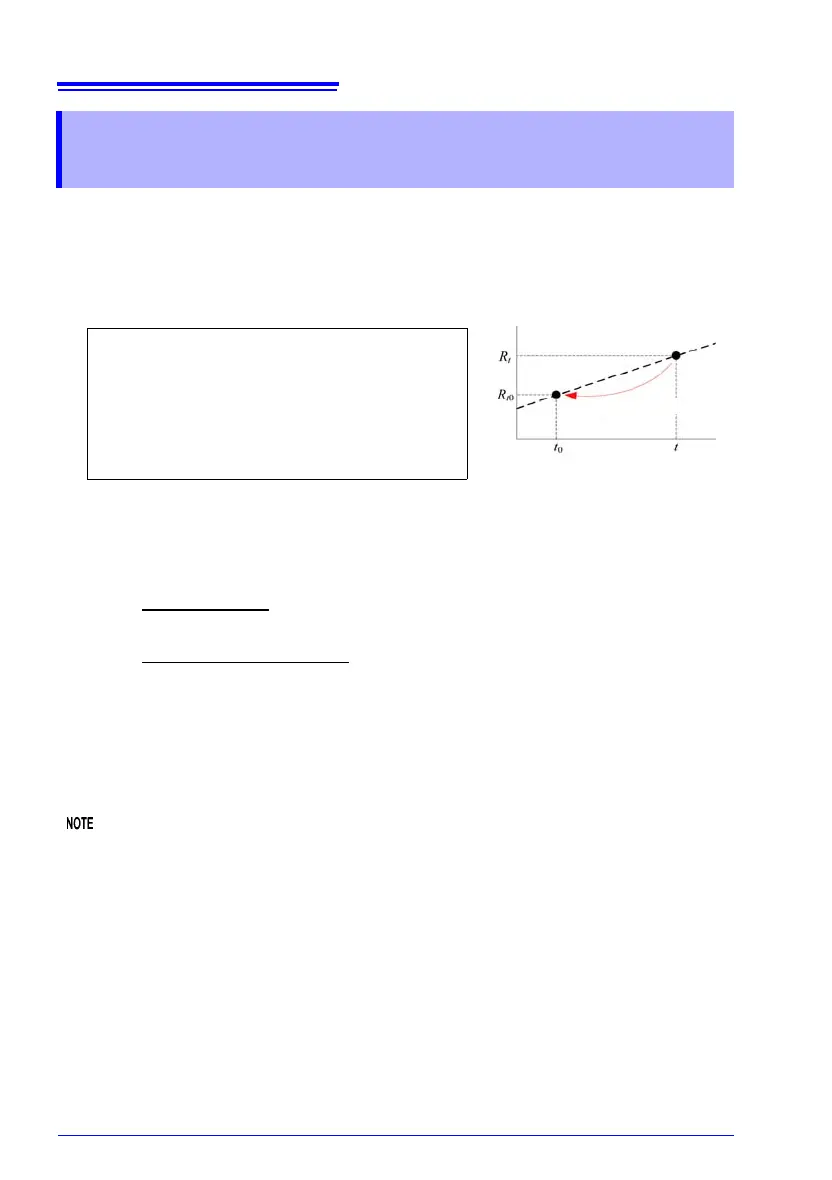
Resistances
R
t
and R
t0
below are the resistance values of the measurement target (having
resistance temperature coefficient at
t
0
°C of
α
t
0
) at t
°C and t
0
°C.
Example
If a copper measurement target (with resistance temperature coefficient of 3930 ppm/°C at
20°C) measures 100 at 30°C, its resistance at 20°C is calculated as follows:
Refer to the following for temperature correction settings and execution method:
See: "4.5 Correcting for the Effects of Temperature (Temperature Correction (TC))" (p.75)
See: "5.4 Performing Temperature Rise Test (Temperature Conversion Function (T))" (p.116)
• The temperature sensor detects only ambient temperature; not surface temperature.
• Allow the instrument to warm up before making measurements. Place the temperature
sensor near the measurement target and allow both the sensor and the target to ade-
quately adjust to the ambient temperature prior to use.
Appendix 4 Temperature Correction (TC)
Function
R
t
= R
t0
× { 1 +
α
t0
× ( t − t
0
) }
R
t
Actual measured resistance []
R
t
0
Corrected resistance []
t
0
Reference temperature [°C]
t Ambient temperature [°C]
α
t
0
Temperature coefficient at t
0
[1/°C]
Reference
temperature
Ambient
temperature
Correction
R
t0
=
R
t
1 +
α
t0
× ( t − t
0
)
=
100
1 + ( 3930 × 10
-6
) × (30 − 20)
= 96.22
 Loading...
Loading...