SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
940043-002 INTEGRATED ENTERPRISE NETWORK 5-15
High-Speed Bus Extension
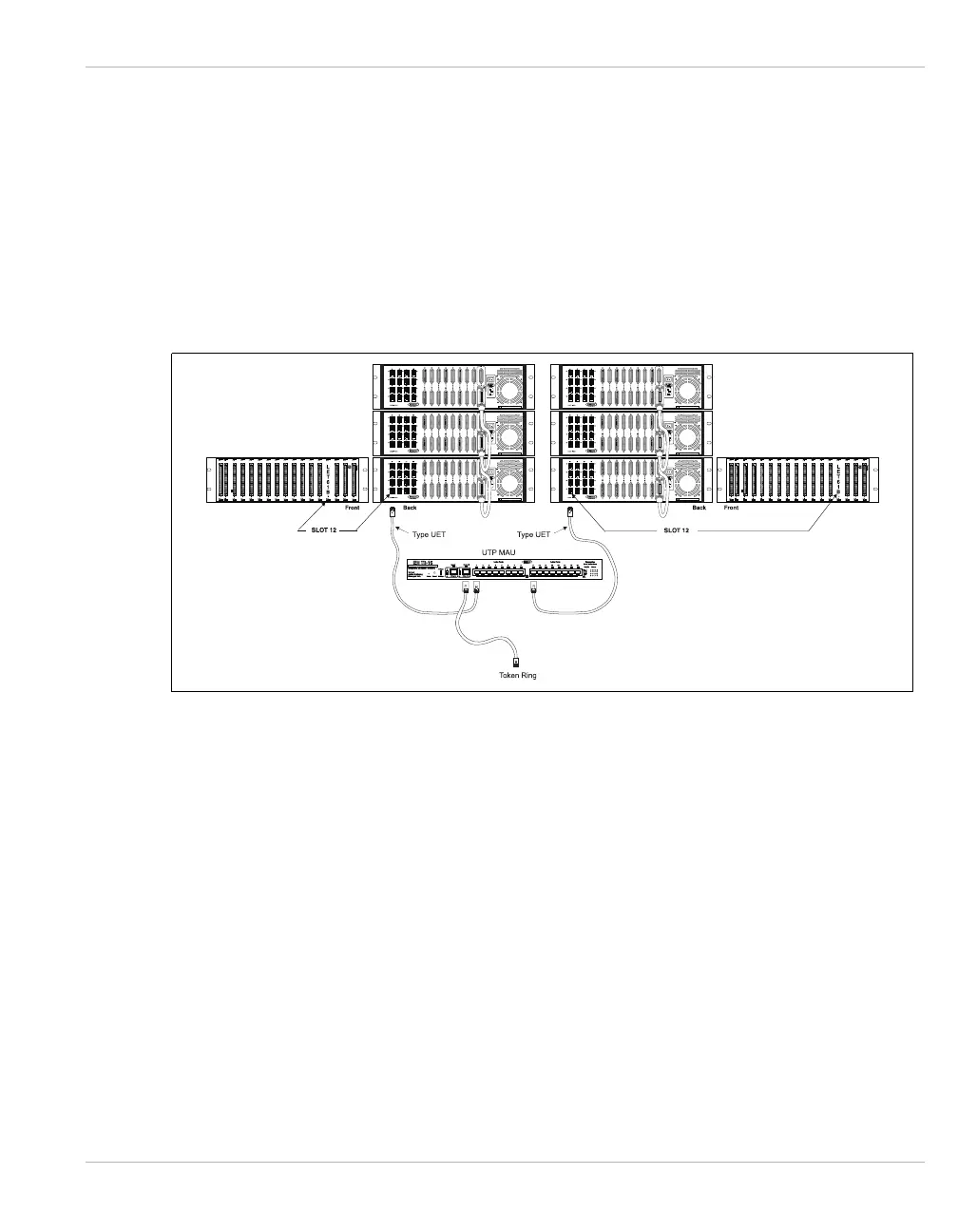
You can extend the high-speed bus by using the Ethernet or Token Ring bus extension. The
Ethernet and Token Ring bus extension is required when your network requirements exceed
three chassis per node.
The standard bus is also extended by grouping three chassis, using the Hypercom Type B
cable, and connecting these groups using the Ethernet or Token Ring bus extension. Refer
to CHAPTER 4, Type B for more information about the Hypercom Type B cable. Figure 5-10
illustrates the Ethernet high-speed bus extension.
Figure 5-10 Ethernet High-Speed Bus Extension
The Ethernet bus extension uses the LET61B port processor and may use 10Base-T or
10Base-2. 10Base-T requires an external UTP HUB. 10Base-2 requires an LEC01 for each
LET61B and appropriate thinned cable. The Token Ring bus extension uses the LET61B port
processor and requires a UTP or STP MAU. Refer to CHAPTER 3, Port Processors/Modules
for more information about the LET61B and LTR61B port processors.
Note: The Ethernet or Token Ring extended bus must not be shared with other LAN traffic.
All bus connected chassis appear as a single node to IENView. One node may support up
to 240 ports. This method of bus extension extends both the standard bus and high-speed
bus. Traffic across the extended bus is minimized to that which needs to cross to an
application interface in another chassis.
Note: Hypercom recommends that each chassis be assigned a range of bus addresses. This permits
the Token Ring or Ethernet bus extenders to filter unnecessary traffic from each chassis.
 Loading...
Loading...