L-VIS User Manual 230 LOYTEC
Version 6.2 LOYTEC electronics GmbH
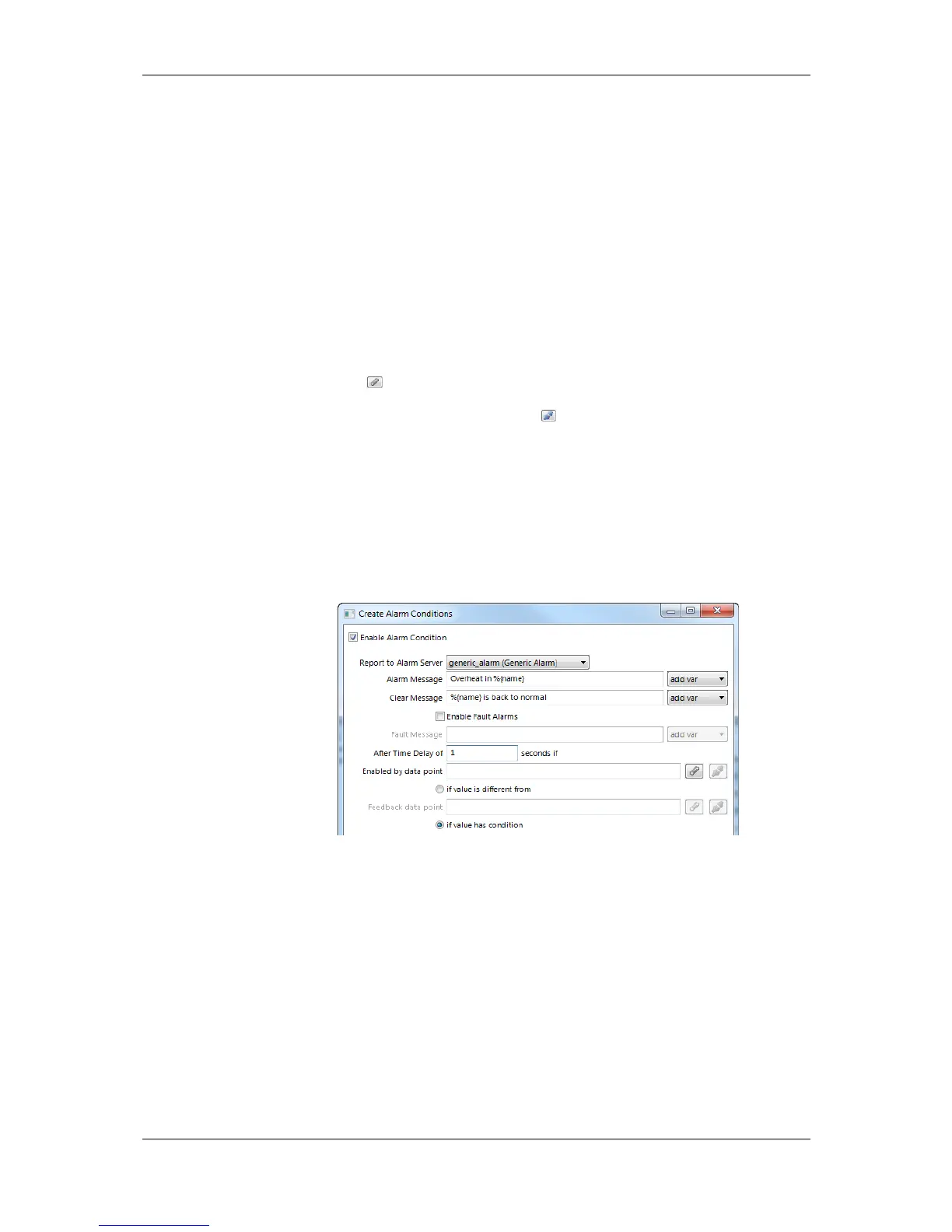
3. For the alarm condition, edit the following definitions which apply to all condition
types as shown in Figure 28. Select the Alarm Server which the alarm shall be
reported to. Typically, you will choose a generic alarm server.
4. Enter an Alarm Message. This is shown when the alarm becomes active. You may add
variable placeholders to this message by selecting one from the drop-down box add
var on the right-hand side. Enter a Clear Message. This is shown when the alarm
clears.
5. Check the option Enable Fault Alarms, if fault conditions (offline, unreliable) shall
generate fault alarms. If enabled, enter a Fault Message, which is displayed along with
the fault alarm when it occurs.
6. Optionally, enter a Time Delay, for which the condition must persist before the alarm
becomes active or is cleared again. The delay is entered in seconds.
7. By clicking you may attach a data point, which is evaluated for enabling the alarm.
This can also be done by editing the property relation ‘enableAlarm’ (see Section
10.6.9). Detach the data point by clicking .
8. Choose the option value is different from to define a feedback alarm. In this case the
setpoint value of the alarmed data point is compared against the feedback value. A
feedback data point can be attached for this purpose. This can also be done by editing
the property relation ‘feedbackRelation’ (see Section 10.6.9).
9. Choose the option value has condition to define a value alarm. In this case the data
point value is compared against the condition. Edit the condition in the box below this
option.
Figure 28: Common settings for an alarm condition.
10. For an analog feedback condition, fill in the alarm condition as shown in Figure 29. A
feedback alarm is generated, if the setpoint differs by – and differs by + value from
the feedback value. Enter a Deadband to account for hysteresis. Attach or detach data
points for those limits. This can also be done by editing the property relations
‘lowLimit’, ‘highLimit’, and ‘deadband’, respectively (see Section 10.6.9).

 Loading...
Loading...