Device Configuration 5 - 89
5. Select Add to define a new Bridge VLAN configuration, Edit to modify the configuration of an existing Bridge VLAN
configuration or Delete to remove a VLAN configuration.
Figure 5-50 Network - Bridge VLAN Configuration screen
6. If adding a new Bridge VLAN configuration, use the spinner control to define a VLAN ID from 1 - 4095. This value must be
defined and saved before the General tab can become enabled and the remainder of the settings defined.
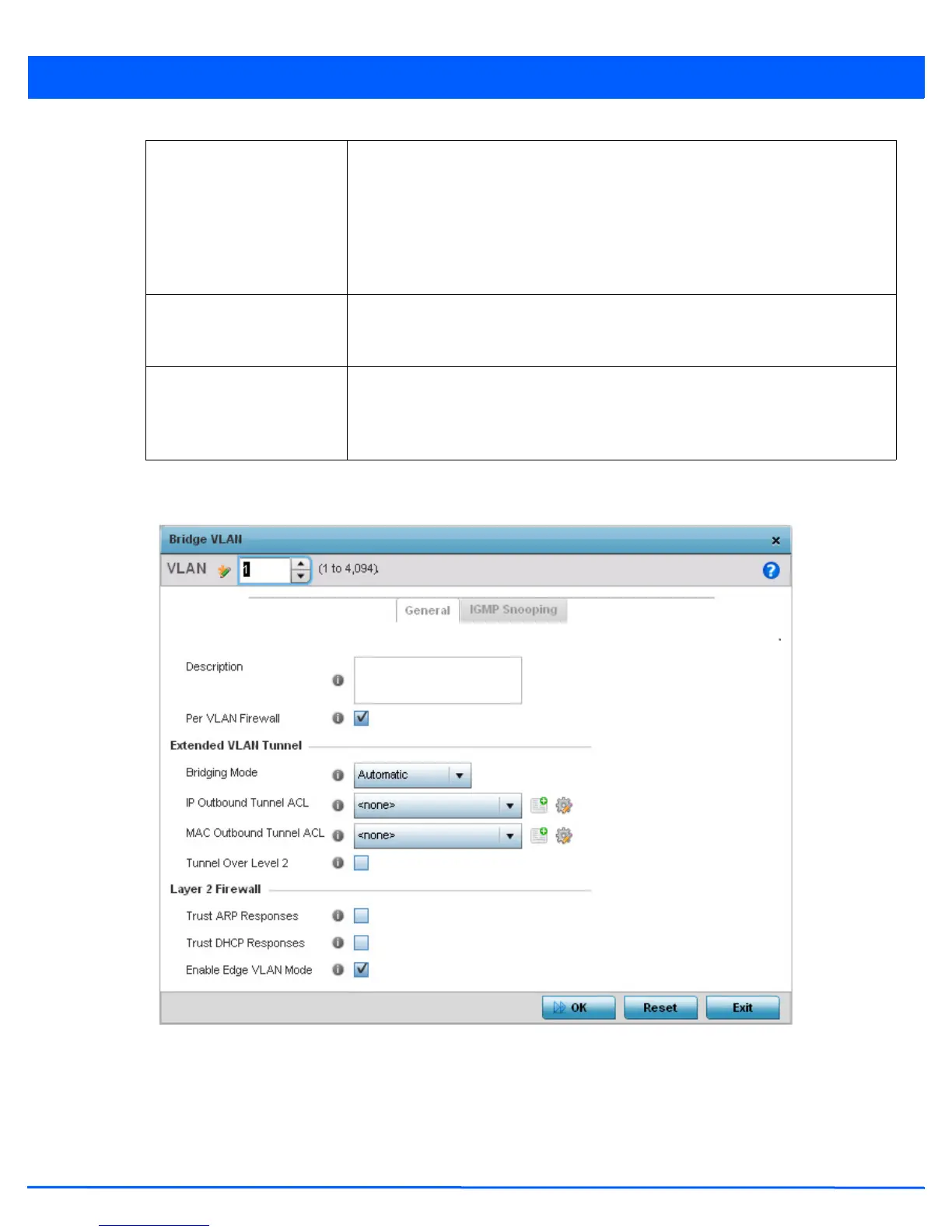
7. If creating a new Bridge VLAN, provide a Description (up to 64 characters) unique to the VLAN’s specific configuration to
help differentiate it from other VLANs with similar configurations.
Edge VLAN Mode Defines whether the VLAN is currently in edge VLAN mode. An edge VLAN is the VLAN
where hosts are connected. For example, if VLAN 10 is defined with wireless clients
and VLAN 20 is where the default gateway resides, VLAN 10 should be marked as an
edge VLAN and VLAN 20 shouldn’t be marked as an edge VLAN. When defining a VLAN
as edge VLAN, the firewall enforces additional checks on hosts in that VLAN. For
example, a host cannot move from an edge VLAN to another VLAN and still keep
firewall flows active.
Trust ARP Response When ARP trust is enabled, a green check mark displays. When disabled, a red “X”
displays. Trusted ARP packets are used to update the IP-MAC Table to prevent IP spoof
and arp-cache poisoning attacks.
Trust DHCP Responses When DHCP trust is enabled, a green check mark displays. When disabled, a red “X”
displays. When enabled, DHCP packets from a DHCP server are considered trusted and
permissible within the network. DHCP packets are used to update the DHCP Snoop
Table to prevent IP spoof attacks.

 Loading...
Loading...











