6 - 20 WiNG 5.5 Access Point System Reference Guide
11. Select OK when completed to update the WLAN’s WPA2-CCMP encryption configuration. Select Reset to revert back to its
last saved configuration.
WPA2-CCMP Deployment Considerations
WPA2-CCMP
Before defining a WPA2-CCMP supported configuration on a WLAN, refer to the following deployment guidelines to ensure the
configuration is optimally effective:
• Motorola Solutions recommends WPA2-CCMP be configured for all new (non visitor) WLANs requiring encryption, as it’s
supported by the majority of the hardware and client vendors using Motorola Solutions wireless networking equipment.
• WPA2-CCMP supersedes WPA-TKIP and implements all the mandatory elements of the 802.11i standard. WPA2-CCMP
introduces a new AES-based algorithm called CCMP, which replaces TKIP and WEP and is considered significantly more
secure.
6.1.2.10 WEP 64
Configuring WLAN Security
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security protocol specified in the IEEE Wireless Fidelity (Wi -Fi) standard. WEP is designed
to provide a WLAN with a level of security and privacy comparable to that of a wired LAN.
WEP can be used with open, shared, MAC and 802.1 X EAP authentications. WEP is optimal for WLANs supporting legacy
deployments when also used with 802.1X EAP authentication to provide user and device authentication and dynamic WEP key
derivation and periodic key rotation. 802.1X provides authentication for devices and also reduces the risk of a single WEP key
being deciphered.
WEP 64 uses a 40 bit key concatenated with a 24-bit initialization vector (IV) to form the RC4 traffic key. WEP 64 is a less robust
encryption scheme than WEP 128 (containing a shorter WEP algorithm for a hacker to potentially duplicate), but networks that
require more security are at risk from a WEP flaw. WEP is only recommended if there are client devices incapable of using
higher forms of security. The existing 802.11 standard alone offers administrators no effective method to update keys.
To configure WEP 64 encryption on a WLAN:
1. Select the Configuration tab from the Web UI.
2. Select Wireless.
3. Select Wireless LANs to display a high level display of existing WLANs.
4. Select the Add button to create an additional WLAN, or select Edit to modify the properties of an existing wireless
controller WLAN.
5. Select Security.
6. Select the WEP 64 radio button from within the Select Encryption field.
The screen populates with the parameters required to define a WEP 64 configuration for the WLAN.
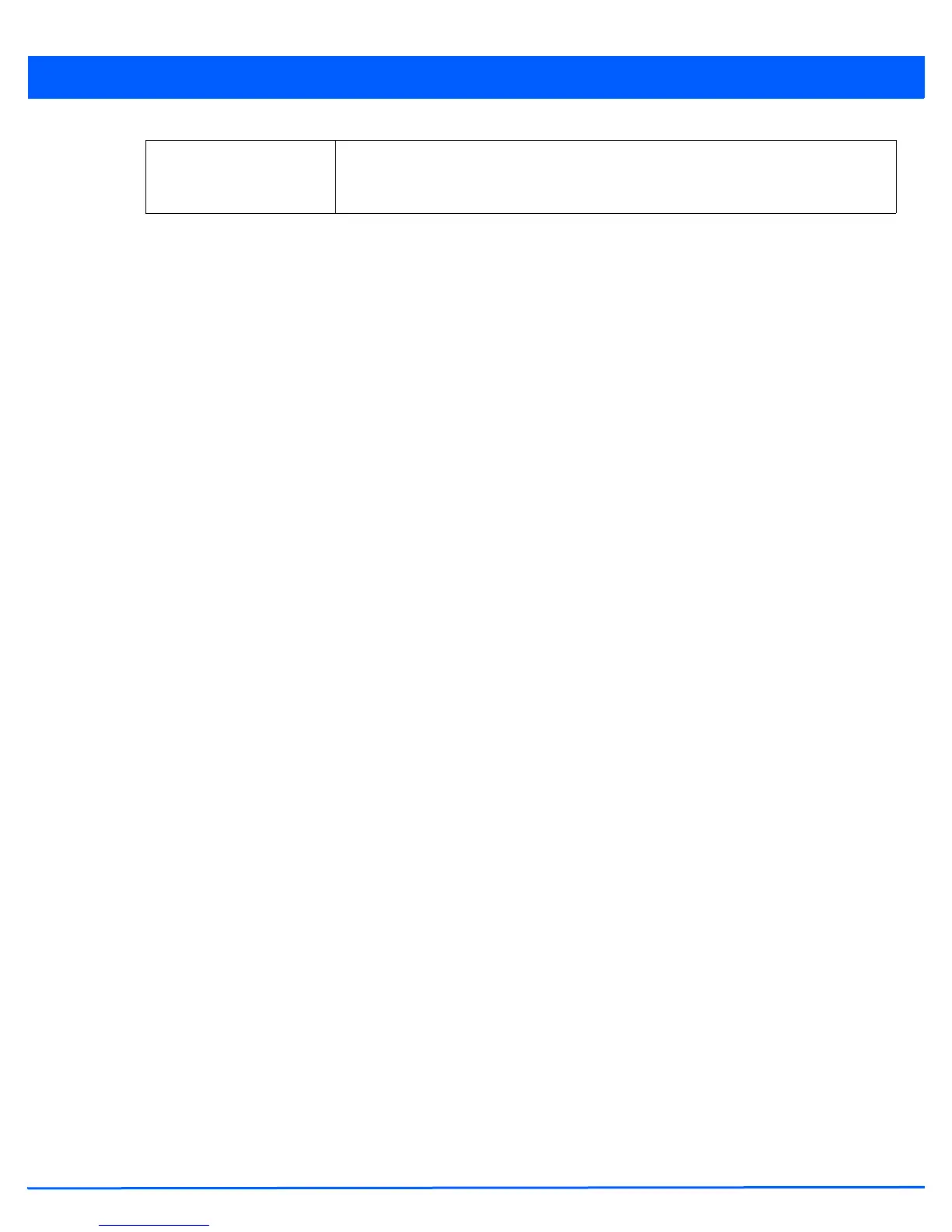
Use SHA256 Select this option to enable SHA-256 authentication key management suite. This suite
consists of a set of algorithms for key agreement, key derivation, key wrapping, and
content encryption and provide a minimum cryptographic security level of 128 bits.

 Loading...
Loading...











