Statistics 13 - 119
13.3.23.5 NAT Translations
Firewall
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technique to modify network address information within IP packet headers in transit.
This enables mapping one IP address to another to protect wireless controller managed network address credentials. With
typical deployments, NAT is used as an IP masquerading technique to hide private IP addresses behind a single, public facing,
IP address.
NAT can provide a profile outbound Internet access to wired and wireless hosts connected to an access point. Many-to-one
NAT is the most common NAT technique for outbound Internet access. Many-to-one NAT allows an access point to translate
one or more internal private IP addresses to a single, public facing, IP address assigned to a 10/100/1000 Ethernet port or 3G
card.
To view the Firewall’s NAT translations:
1. Select the Statistics menu from the Web UI.
2. Select System from the navigation pane (on the left-hand side of the screen). Expand a RF Domain and select one of its
connected access points.
3. Select Firewall and expand the menu to reveal its sub menu items.
4. Select NAT Translations.
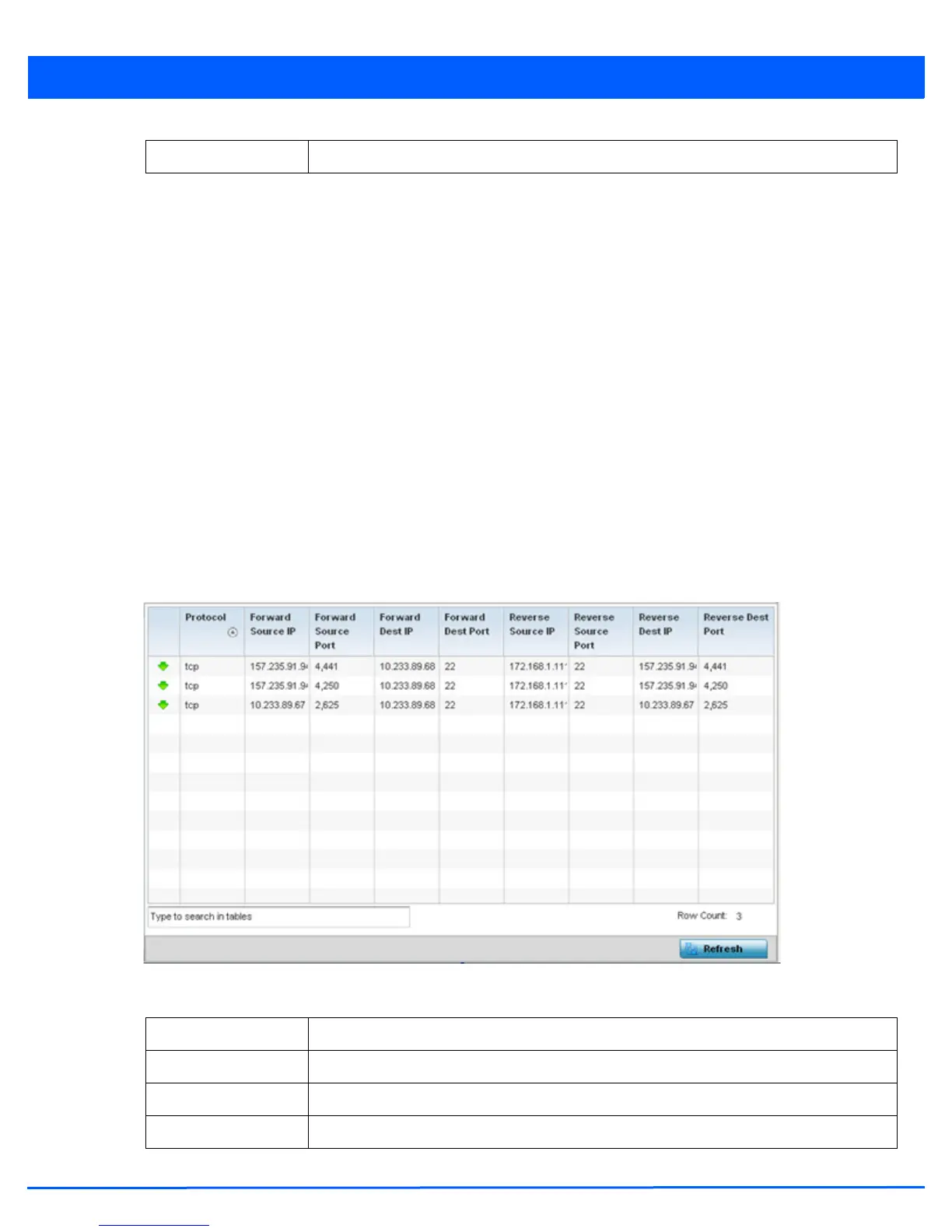
Figure 13-78 Access Point - Firewall Nat Translation screen
The NAT Translations screen displays the following:
Refresh Select the Refresh button to update the screen’s statistics counters to their latest values.
Protocol Lists the NAT translation IP protocol as either TCP, UDP or ICMP.
Forward Source IP Displays the source IP address for the forward NAT flow.
Forward Source Port Displays the source port for the forward NAT flow (contains ICMP ID if it is an ICMP flow).
Forward Dest IP Displays the destination IP address for the forward NAT flow.

 Loading...
Loading...











