Descriptions
56
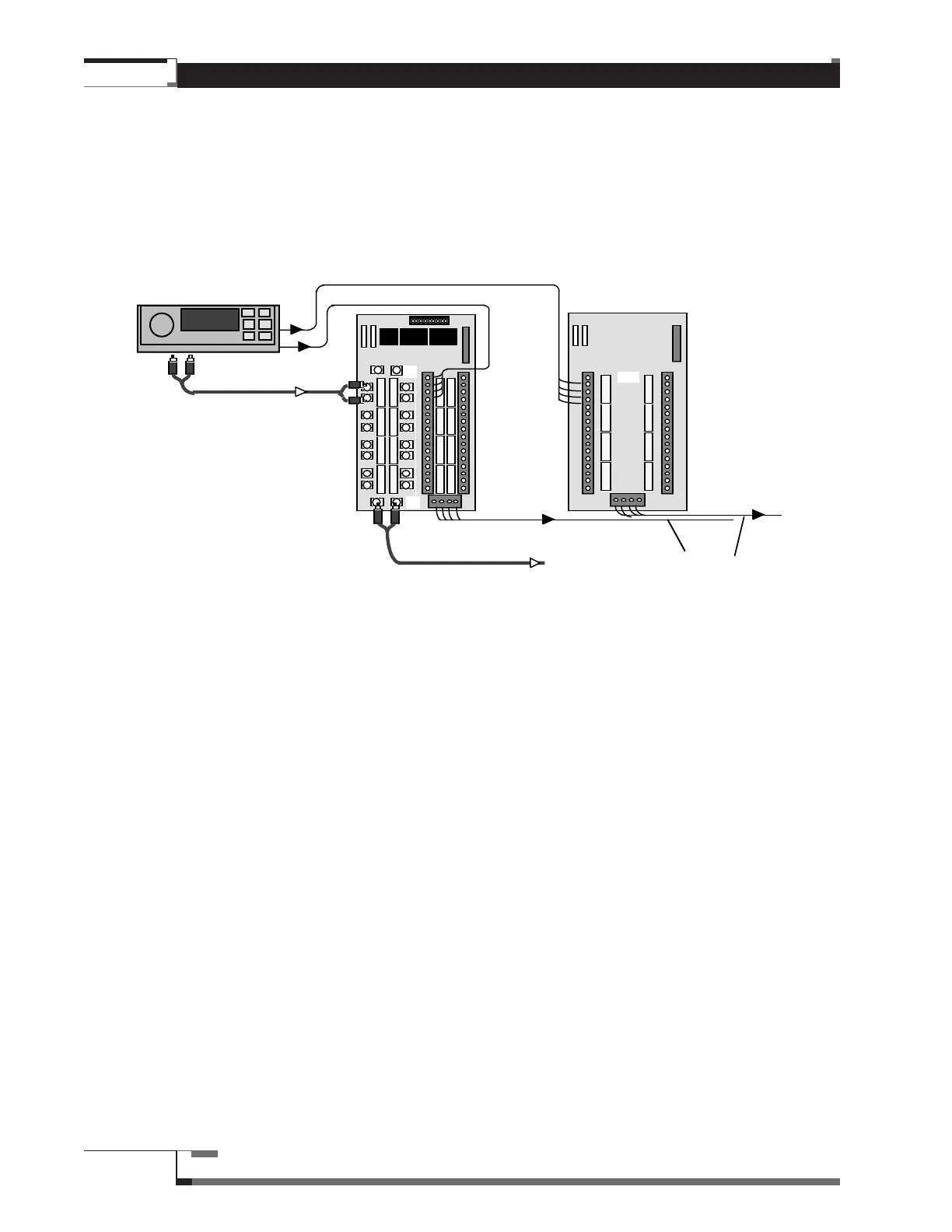
If more channel capacity is needed, two or more Switching Modules may be used in parallel. All Modules
switching the same components require the same DIP Switch “address.”
High Level Signals out to
Amplifier Bypass Positions
("A" of first Modules in
Amplifier Chains)
Low Level Signal Out
to Input of Amplifier
Chain
To Rear Amp
Bypass
To Front Amp Bypass
High Level Front Output
High Level Rear Output
Low Level
Output
Tape Deck #1
Spea
er (L
and
R)
1312
1410
Figure 30 – Using Two Modules to Switch One Component
For example, many Autosound tape decks output both low-level signals which would be routed to an
Amplifier bus, and front and rear 2-Channel high-level signals which would be routed past the Amplifier
Chains (via bypass) to the Speaker bus. The low-level side of a 1310 would switch the 2-Channel low-level
output, and the high-level side would switch half (e.g. rear) of the 4-Channel high-level output with a 1410
switching the other half (e.g. front). Both Switching Modules would be given the same DIP Switch
“address.”
When that deck is activated, all relays at that Position are switched to the Input/Output terminals
simultaneously. Then, if an Amplifier is not selected, the high level signals will bypass the Amplifier bus via
the “A” position on the first Module in the Amplifier Chain, and reach the Speaker bus. If an Amplifier is
selected, the high-level signal “dead ends” at the “A” Positions on the Amplifier Chain. The deck’s high and
low-level signals must be connected to the same Position on each side of the Module (e.g., the preamp
output connected to the “A” Position on the low-level side and the high-level output connected to the “A”
Position on the high-level side.)
 Loading...
Loading...