User Manual
Advanced Console Server & RIM Gateway User Manual 111
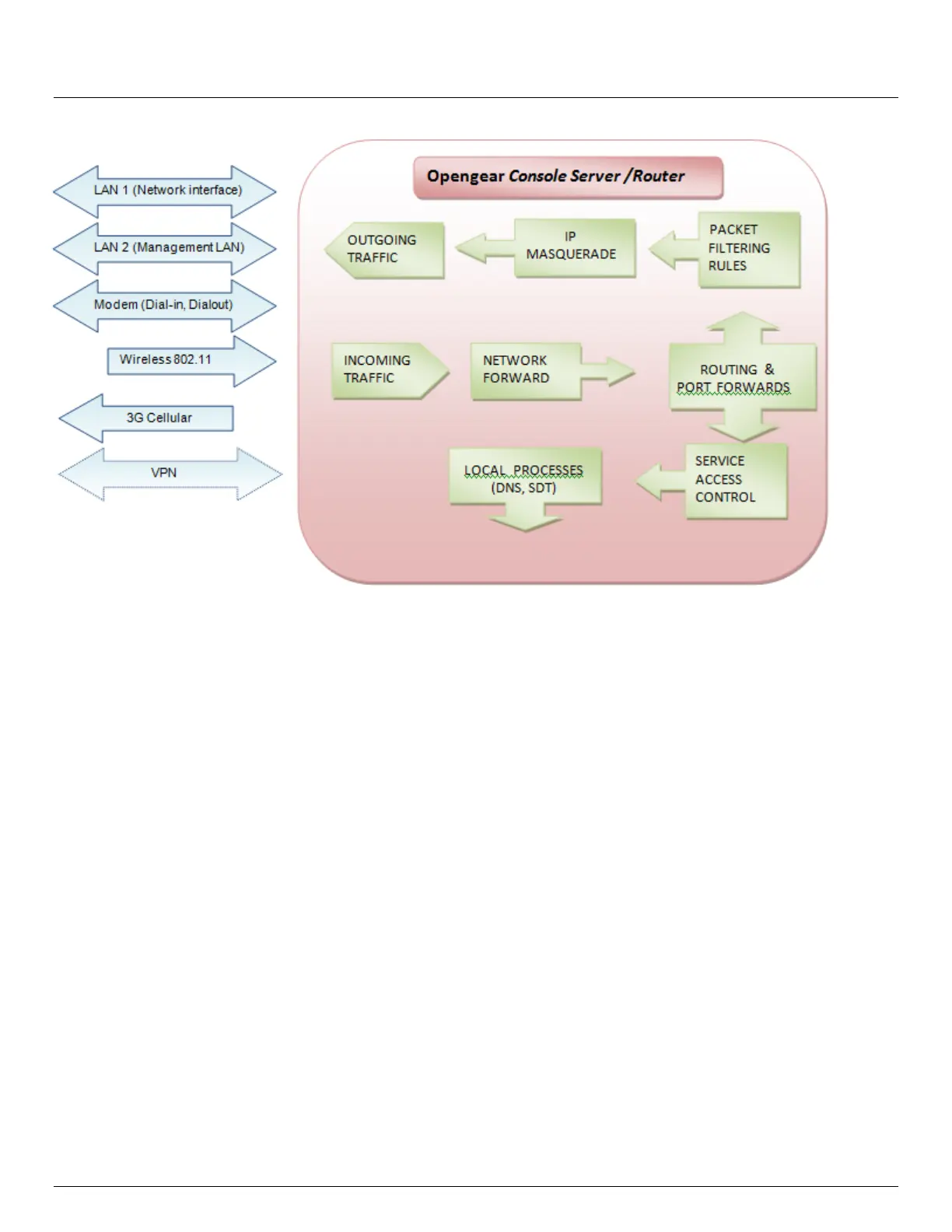
This enables the console server to function as an Internet or external network gateway, via cellular connections (e.g. ACM5004-
Gx cellular routers or other IM400, ACM5500 or ACM5000 model with external cellular modem) or via other Ethernet
networks on two Ethernet port models (IM42xx-2 and ACM500x-2 console servers):
Network Forwarding allows the network packets on one network interface (i.e. LAN1/ eth0) to be forwarded to
another network interface (i.e. LAN2/eth1 or dial-out/cellular). So locally networked devices can IP connect
through the console server to devices on remote networks.
IP Masquerading is used to allow all the devices on your local private network to hide behind and share the one
public IP address when connecting to a public network. This type of translation is only used for connections
originating within the private network destined for the outside public network, and each outbound connection is
maintained by using a different source IP port number.
When using IP Masquerading, devices on the external network cannot initiate connections to devices on the
internal network. Port Forwards allows external users to connect to a specific port on the external interface of the
console server/cellular router and be redirected to a specified internal address for a device on the internal
network.
With Firewall Rules, packet filtering inspects each packet passing through the firewall and accepts or rejects it
based on user-defined rules.
Then Service Access Rules can be set for connecting to the console server/router itself
5.8.1 Configuring network forwarding and IP masquerading
To use a console server as an Internet or external network gateway requires establishing an external network connection
(e.g. for the ACM5004-G setting up the 3G cellular link as detailed in Chapter 5) and then setting up forwarding and
masquerading.
 Loading...
Loading...