RL78/F13, F14 CHAPTER 16 SERIAL INTERFACE IICA
R01UH0368EJ0210 Rev.2.10 1064
Dec 10, 2015
(3) Slave operation
The processing procedure of the slave operation is as follows.
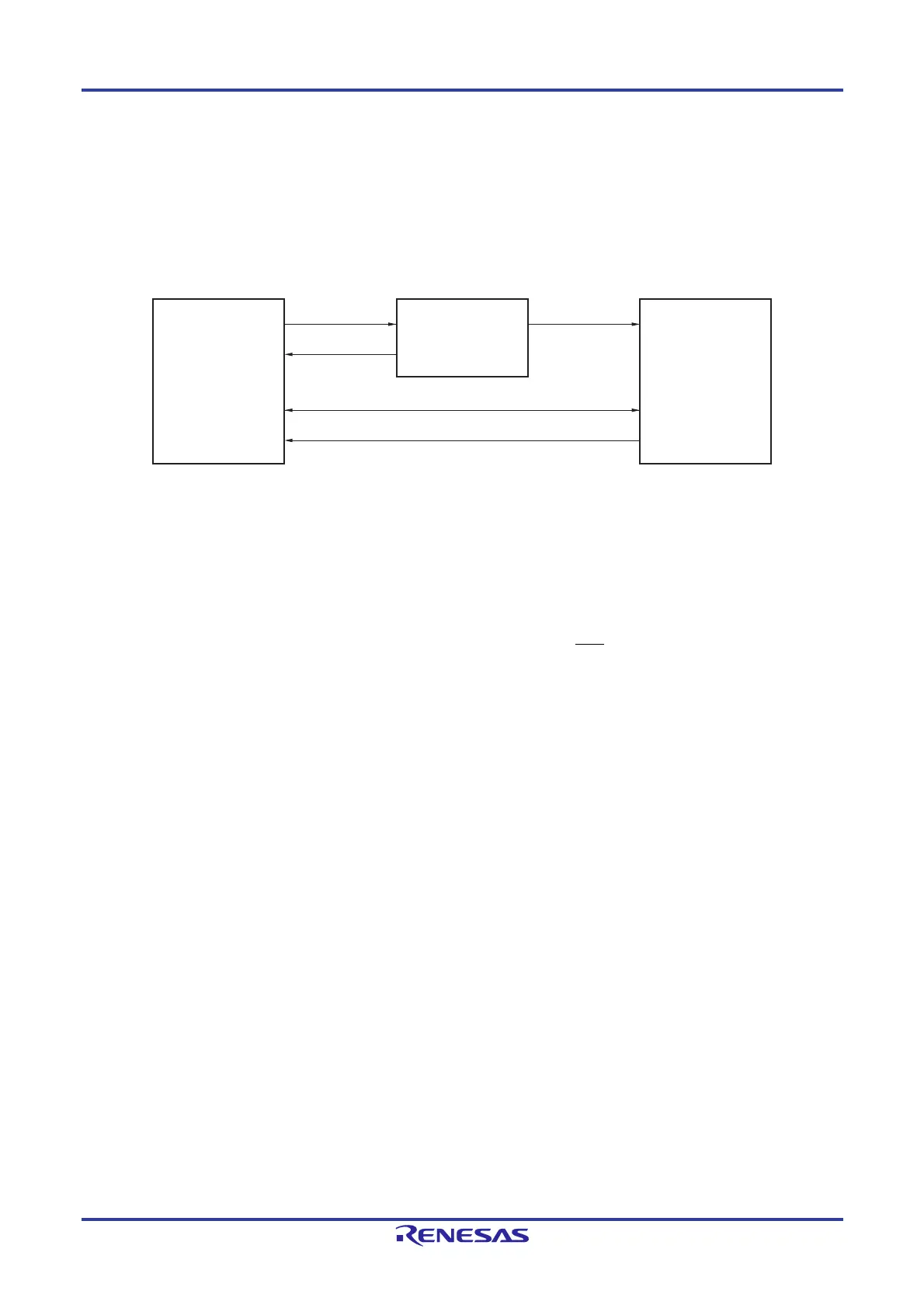
Basically, the slave operation is event-driven. Therefore, processing by the INTIICA0 interrupt (processing that must
substantially change the operation status such as detection of a stop condition during communication) is necessary.
In the following explanation, it is assumed that the extension code is not supported for data communication. It is also
assumed that the INTIICA0 interrupt servicing only performs status transition processing, and that actual data
communication is performed by the main processing.
Therefore, data communication processing is performed by preparing the following three flags and passing them to
the main processing instead of INTIICA0.
<1> Communication mode flag
This flag indicates the following two communication statuses.
Clear mode: Status in which data communication is not performed
Communication mode: Status in which data communication is performed (from valid address detection to
stop condition detection, no detection of ACK from master, address mismatch)
<2> Ready flag
This flag indicates that data communication is enabled. Its function is the same as the INTIICA0 interrupt for
ordinary data communication. This flag is set by interrupt servicing and cleared by the main processing. Clear
this flag by interrupt servicing when communication is started. However, the ready flag is not set by interrupt
servicing when the first data is transmitted. Therefore, the first data is transmitted without the flag being cleared
(an address match is interpreted as a request for the next data).
<3> Communication direction flag
This flag indicates the direction of communication. Its value is the same as the TRC0 bit.
IICA0
Interrupt servicing
Main processing
INTIICA0 Flag
Setting
Data
Setting

 Loading...
Loading...











