Configuration Guide Configuring ARP Check
5 Configuring ARP Check
5.1 Overview
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packet check filters all ARP packets under ports (including wired layer-2 switching
ports, layer-2 aggregate ports (APs), and layer-2 encapsulation sub-interfaces, as well as WLAN interfaces) and discards
illegal ARP packets, so as to effectively prevent ARP deception via networks and to promote network stability. On devices
supporting ARP check, illegal ARP packets in networks will be ignored according to the legal user information (IP-based or
IP-MAC based) generated by security application modules such as IP Source Guard, global IP+MAC binding, 802.1X
authentication, GSN binding, Web authentication and port security.
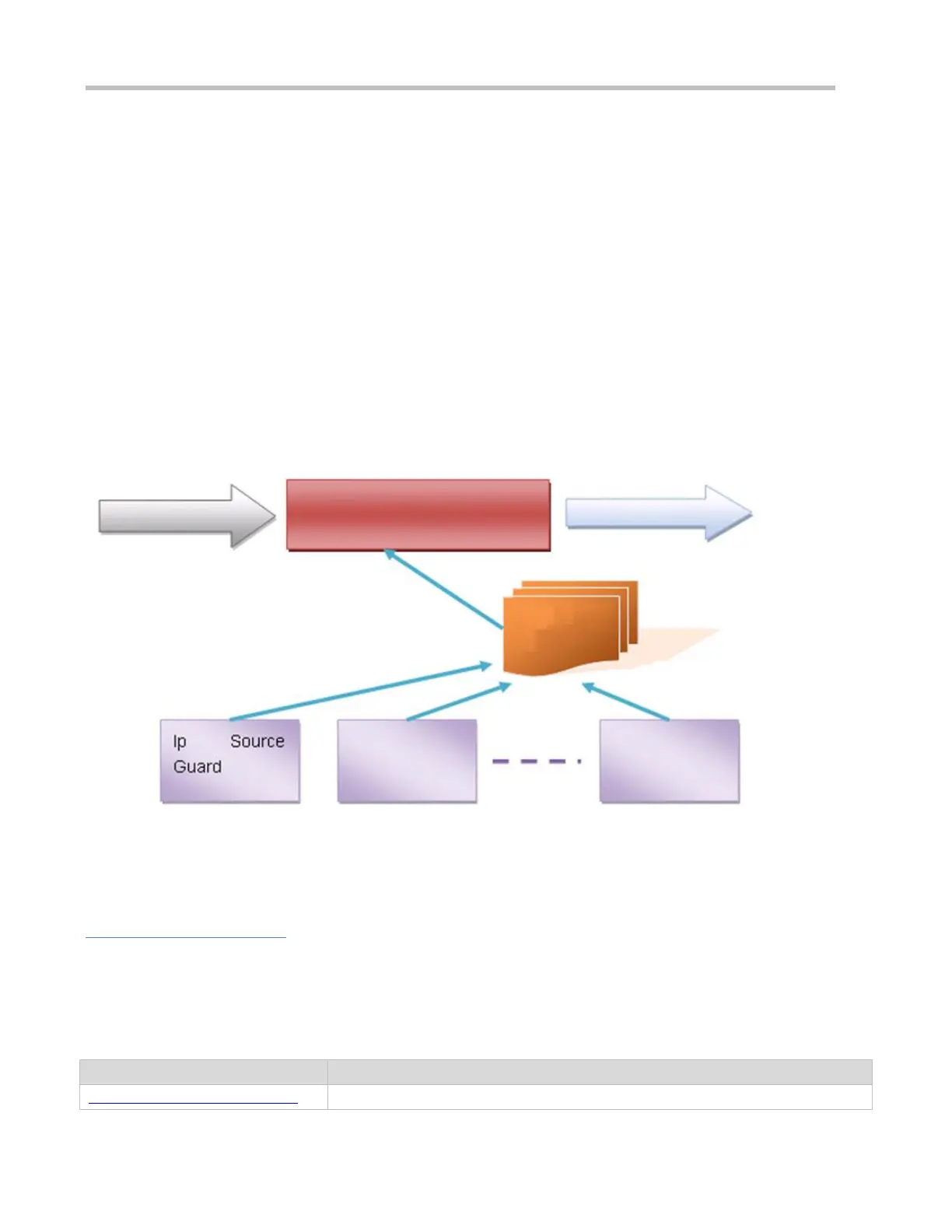
Figure 5-1
User ARP
ARP check function
Legal user ARP
Legal user
information
table
Global IP+MAC
binding function
Port security
The above figure shows that security modules generate legal user information (IP-based or IP-MAC based). ARP Check
uses the information to detect whether the Sender IP fields or the <Sender IP, Sender MAC> fields in all ARP packets at
ports matches those in the list of legal user information. If not, all unlisted ARP packets will be discarded.
Protocols and Standards
RFC826: An Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol or Converting Network Protocol Addresses
5.2 Applications
Filtering ARP packets in networks
Illegal users in networks launch attacks using forged ARP packets.

 Loading...
Loading...











