Configuration Guide Configuring Gateway-targeted ARP Spoofing Prevention
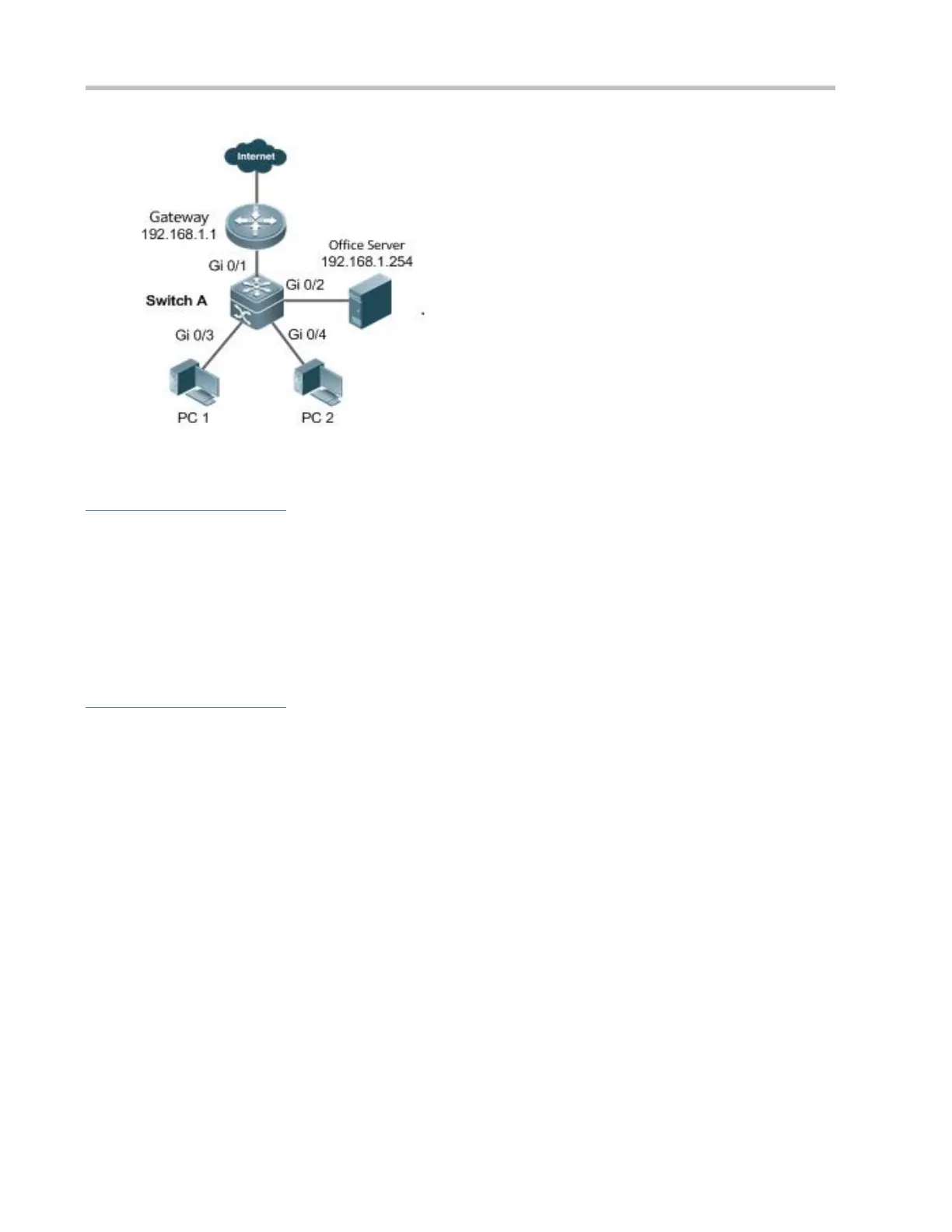
Deployment
On the access switch (Switch A), enable gateway-targeted spoofing prevention on the ports (Gi 0/3 and Gi 0/4 in this
case) directly connected to the PC. The gateway addresses include intranet gateway address and intranet server
address.
6.3 Features
Basic Concepts
ARP
ARP is a TCP/IP protocol that obtains physical addresses according to IP addresses. Its function is as follows: The host
broadcasts ARP requests to all hosts on the network and receives the returned packets to determine physical addresses of
the target IP addresses, and saves the IP addresses and hardware addresses in the local ARP cache, which can be directly
queried in response to future requests. On the same network, all the hosts using the ARP are considered as mutually trustful
to each other. Each host on the network can independently send ARP response packets; the other hosts receive the
response packets and record them in the local ARP cache without detecting their authenticity. In this way, attackers can send
forged ARP response packets to target hosts so that the messages sent from these hosts cannot reach the proper host or
reach a wrong host, thereby causing ARP spoofing.
Gateway-targeted ARP Spoofing
When User A sends an ARP packet requesting the media access control (MAC) address of a gateway, User B on the same
VLAN also receives this packet, and User B can send an ARP response packet, passing off the gateway IP address as the
source IP address of the packet, and User B's MAC address as the source MAC address. This is called gateway-targeted
ARP spoofing. After receiving the ARP response, User A regards User B's machine as the gateway, so all the packets sent

 Loading...
Loading...