Brief description
1.3 Frames
Basic logic functions: Axes, coordinate systems, frames (K2)
Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
11
1.3 Frames
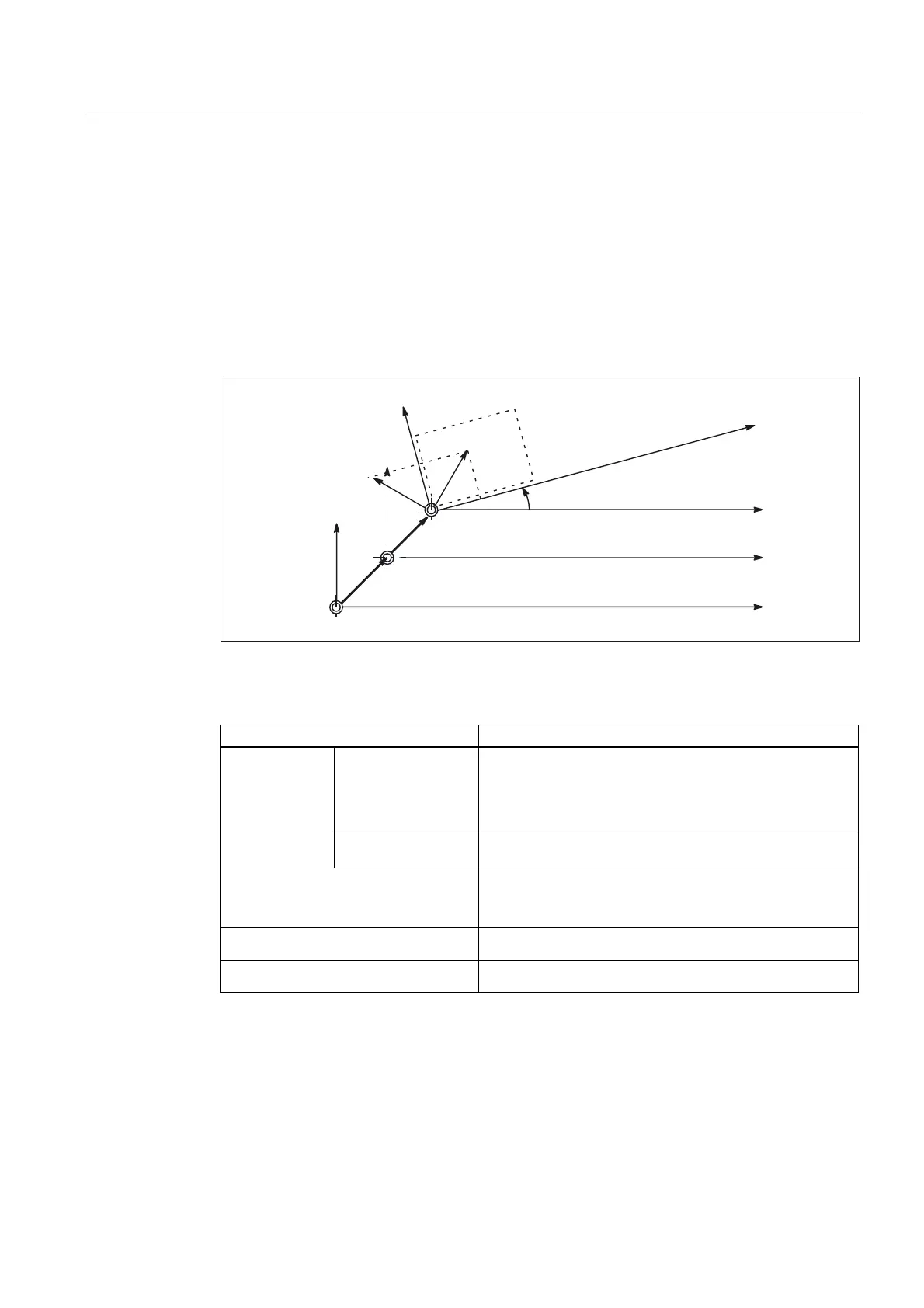
FRAME
A FRAME is a closed calculation rule that translates one Cartesian coordinate system into
another.
FRAME components
5RXJKRIIVHW
)LQHRIIVHW
5RWDWLRQ
6FDOLQJ
0LUURULQJ
Figure 1-1 FRAME components
A FRAME consists of the following components:
FRAME components Programmable with:
Rough offset
TRANS
ATRANS (additive translation component)
CTRANS (zero offset for multiple axes)
G58 (axial zero offset)
Offset
Fine offset
CFINE
G59 (axial zero offset)
Rotation ROT / ROTS
AROT / AROTS
CROTS
Scaling
SCALE
ASCALE
Mirroring
MIRROR
AMIRROR
Features in relation to axes
The rough and fine offsets, scaling and mirroring can be programmed for geometry and
special axes. A rotation can also be programmed for geometry axes.

 Loading...
Loading...






















