Detailed description
2.4 Frames
Basic logic functions: Axes, coordinate systems, frames (K2)
52 Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
2.4 Frames
2.4.1 Overview
Frame
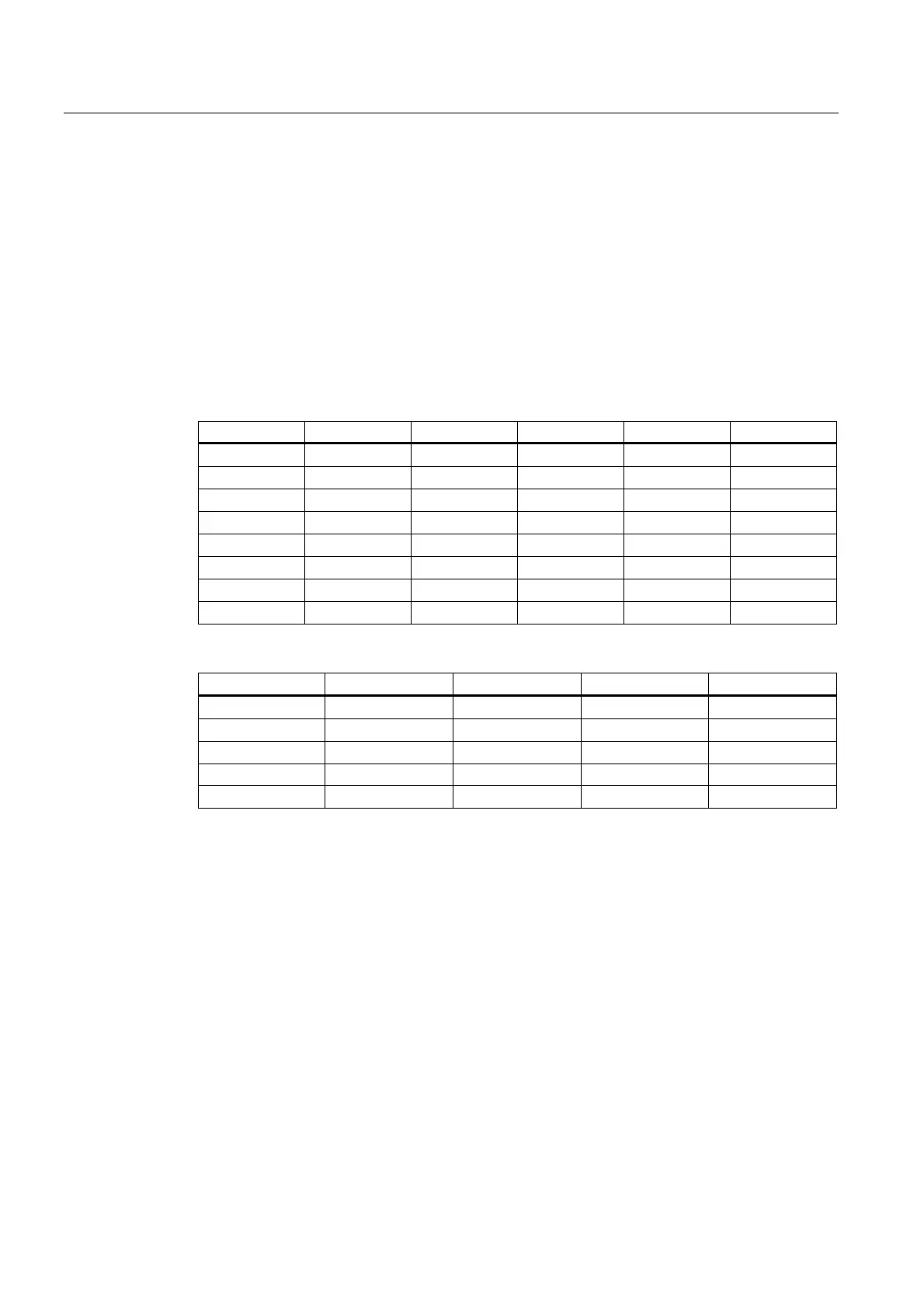
A frame is an axis-specific structure through all channel axes, in which there is a value for
each axis, for the translation, fine offset, rotation (only for geometry axes) scaling and
mirroring.
TRANS FINE ROT MIRROR SCALE
x 10.0 0.1 0.0 0 1
Y 0.0 0.0 0.0 1 1
z 0.0 0.0 45.0 0 1
chx 10.0 0.1 0 1
chy 0.0 0.0 1 1
chz 0.0 0.0 0 1
a 2.0 0.1 0 2
b 0.0 0.0 1 1
In global frames, this is valid for all machine axes.
TRANS FINE MIRROR SCALE
ax1 10.0 0.1 0 1
ax2 0.0 0.0 1 1
ax3 0.0 0.0 0 1
ax4 2.0 0.1 0 2
ax5 0.0 0.0 1 1
Activating a frame causes a static coordinate transformation to be carried out via a defined
calculation rule.

 Loading...
Loading...






















