124
<32 bits Operation >
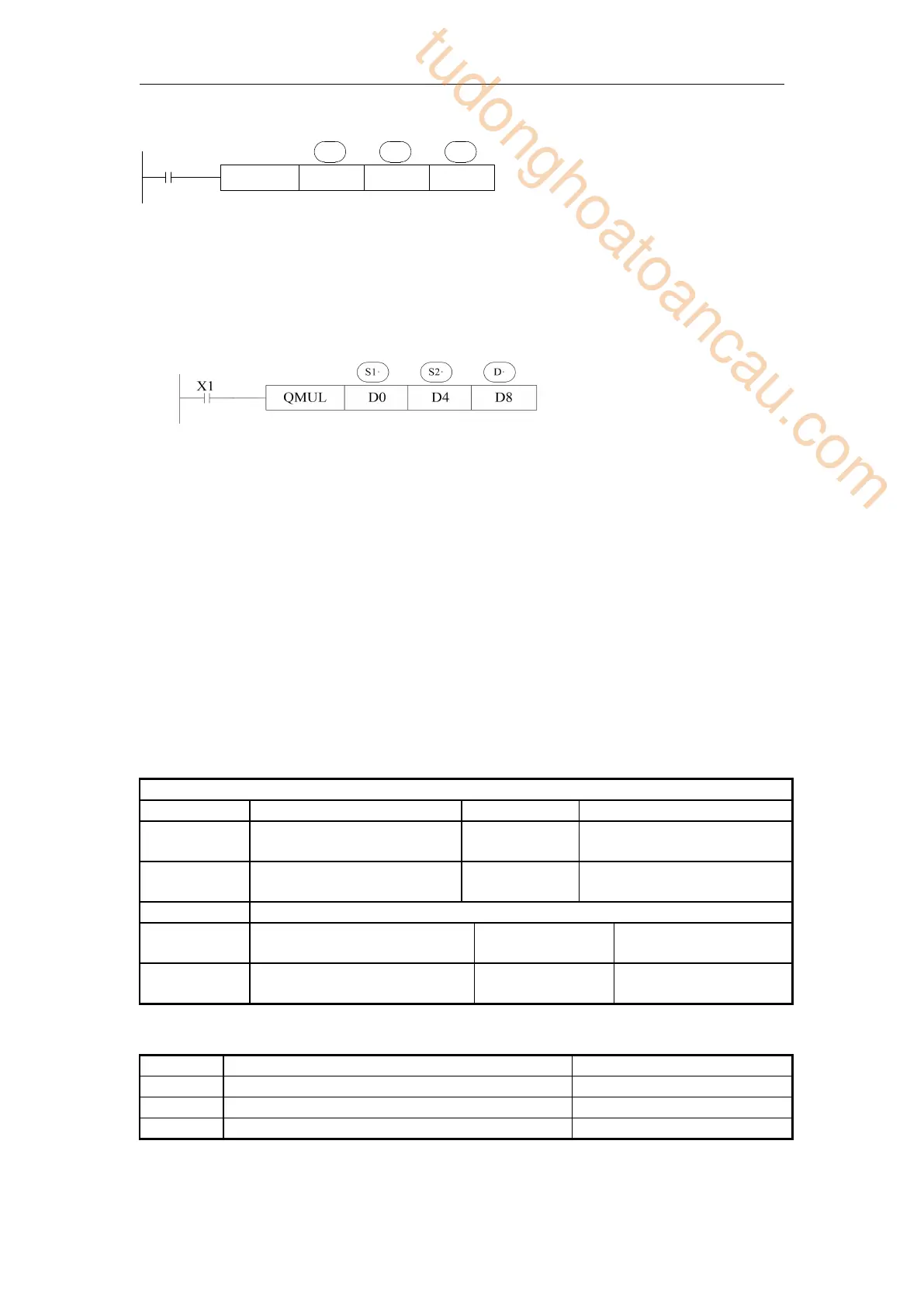
X1
DMUL D0 D2 D4
S1· S2· D·
When use32 bits operation, the result is stored at the destination device in the format of64
bits.
Even use word device,64 bits results can’t be monitored. Please change to floating value
operation for this case.
<64 bits Operation >
In 64-bit operation, a target address uses a bit soft element to get 64-bit results (occupying
four consecutive registers, so don't reuse them). When using the word element, the result of
64-bit data operation cannot be directly monitored. Floating point arithmetic is recommended
in this case.
Note: The addresses of the operands in the QMUL instruction must be even.
4-6-4 Division [DIV, DDIV, QDIV]
1)Summary
Divide two numbers and store the result
Division [DIV, DDIV, QDIV]
Normally ON/OFF,
rising/falling edge
Normal ON/OFF/falling or
rising pulse edge
2) Operands
The divide operation data address
16 bits /32 bits/64 bits, BIN
The divide operation data address
16 bits /32 bits/64 bits, BIN
16 bits /32 bits/64 bits, BIN
BIN BIN BIN
(D1, D0) × (D3, D2) → (D7, D6, D5, D4)
32 bits 32 bits → 64 bits
BIN BIN BIN
(D3,D2,D1, D0) × (D7, D6,D5,D4) → (D11, D10, D9, D8)
64 bits 64 bits → 64 bits
tudonghoatoancau.com

 Loading...
Loading...