Operating Instructions ACU
The minimum number of revolutions needed until the required position is reached depends on the
Actual Frequency 241 and Deceleration (Clockwise) 421 (or Deceleration Anticlockwise 423) as
well as the No. of Pole Pairs 373 of the motor.
No. of Pole Pairs 373 of motor
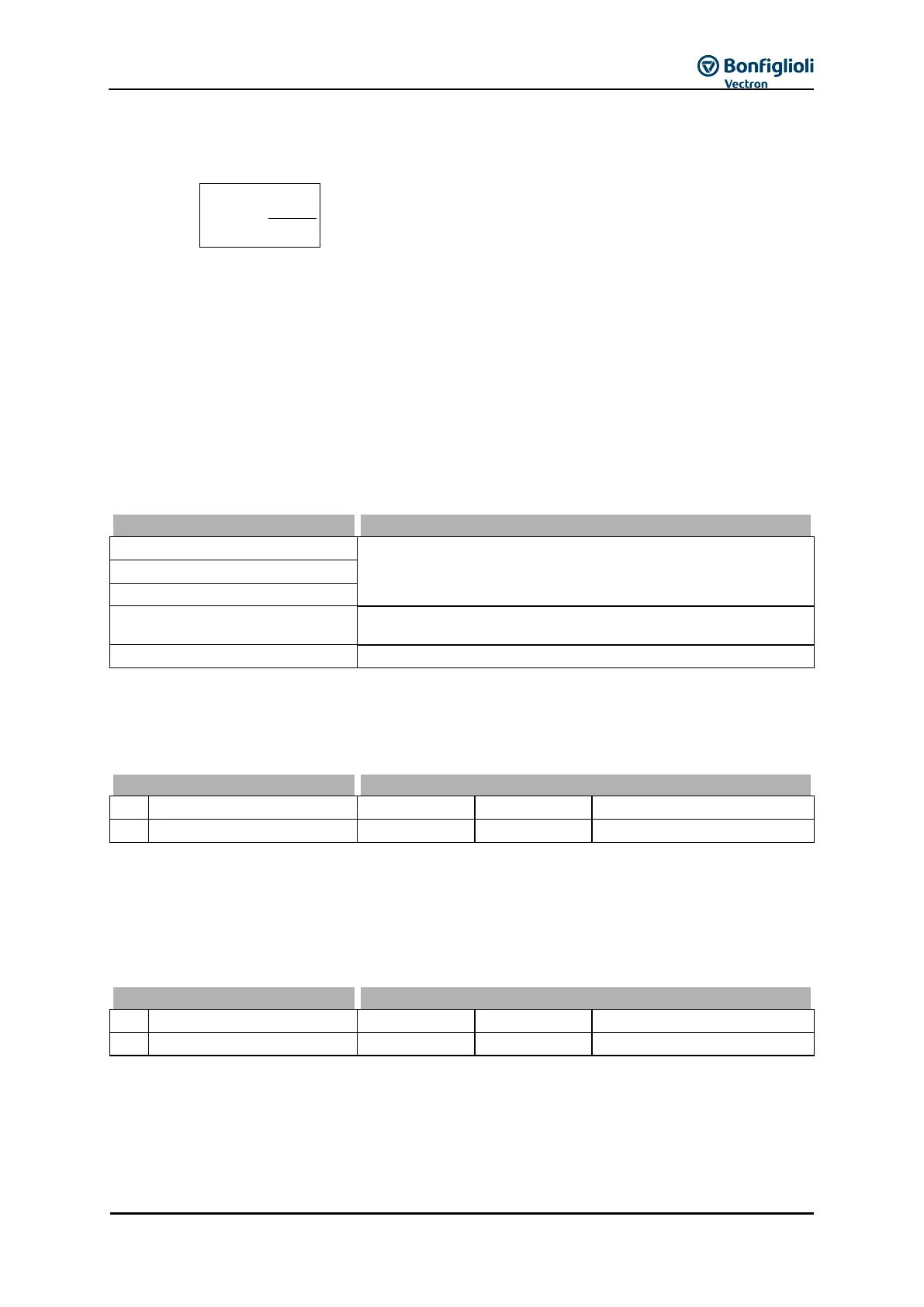
Example: f = 20 Hz, a = 5 Hz/s, p = 2 U
min
= 20
With an actual frequency of 20 Hz and a delay of 5 Hz/s, at least 20 rotations are needed until
standstill at the required position. This is the minimum value for the Positioning distance 460, a
shorter positioning distance is not possible. If the number of rotations until the required position is
reached is to be lower, the frequency must be reduced, the deceleration increased, or the reference
point must be shifted.
The digital signal for registration of the reference point and the logical assignment are to be chosen
from a selection of Signal source 459. The link of the digital inputs S2IND, S3IND and S6IND to
further functions is to be checked according to selected Configuration 30 (e. g. in configurations
110 and 210, digital input S2IND is linked to the function "Start of clockwise operation").
The signals for positioning and a stopping behavior should not be assigned to the same digital input.
The positioning starts with the change of the logic signal from
1 (HIGH) to 0 (LOW) at the reference point.
The positioning starts with the change of the logic signal from 0
(LOW) to 1 (HIGH)
The positioning begins with the change of the logic signal
The registration of the reference position via a digital signal can be influenced by a variable dead
time while the control command is read and processed. The signal running time is compensated by a
positive figure for the Signal correction 461. The setting of a negative signal correction decelerates
the processing of the digital signal.
The influences on the positioning which depend on the operating point can be corrected empirically
via the Load correction 462 parameter. If the required position is not reached, the deceleration
duration is increased by a positive load correction value. The distance between the reference point
and the required position is extended. Negative values accelerate the braking process and reduce
the positioning distance. The limit of the negative signal correction results from the application and
the Positioning distance 460.
 Loading...
Loading...











