GR740-UM-DS, Nov 2017, Version 1.7 365 www.cobham.com/gaisler
GR740
The ET counter can be incremented either using an internal frequency synthesizer or by using an
external enable signal. The External ET Increment Enable bit in Configuration 0 register must be
enabled if external inputs are to be used. The external enable signal is only available in silicon revi-
sion 1.
Increment ET using internal frequency synthesizer:
The counter is incremented on the system clock only when enabled by the frequency synthesizer. The
binary frequency required to determine the counter increment is derived from the system clock using
a frequency synthesizer (FS). The frequency synthesizer is incremented with a pre-calculated incre-
ment value, which matches the available system clock frequency. The frequency synthesizer generates
a tick every time it wraps around, which makes the ET time counter to step forward with the precalcu-
lated increment value. The output of frequency synthesizer is used for enabling the increment of ET
counter. The increment rate of the ET counter and frequency synthesizer counter should be set accord-
ing to the system clock frequency. The ET counter increment rate is set by providing values to ETINC
bits in Configuration 2 register and frequency synthesizer counter is set by providing values to FSINC
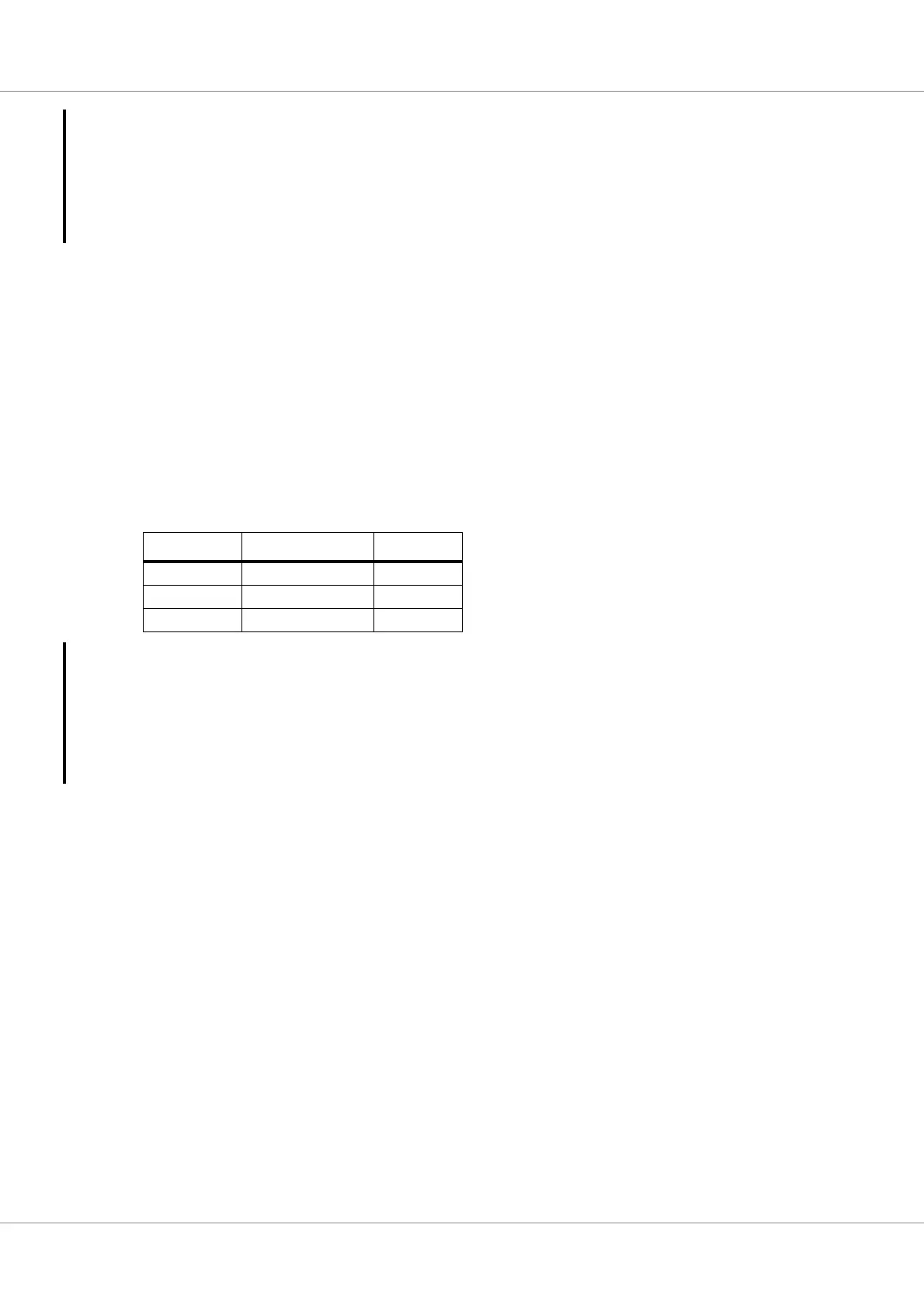
bits in Configuration 1 register. The following table specifies some example ETINC and FSINC val-
ues for some frequencies. The below values are also obtained for this core’s current implementation
consist of Coarse time width 32, Fine time width 24 and Frequency synthesizer width of 30. To calcu-
late for other frequencies and configuration refer the spreadsheet provided along with this document.
Increment ET using external input (only available in silicon revision 1):
The EP register in Configuration 0 specify whether to increment the ET counter based on rising or
falling edge of the external enable signal. Also the ETINC bits in Configuration 2 register specify
from which bit the ET counter must increment.
The following section describes the cores capabilities if it configured as initiator or target.
31.3.4 Initiator
An initiator is a SpaceWire node distributing CCSDS Time Codes and SpaceWire Time-Codes. It is
also an RMAP initiator, capable of transmitting RMAP commands and receiving RMAP replies.
There is only one active initiator in a SpaceWire network during a mission phase.
The initiator performs the following tasks
• Transmission of SpaceWire Time-Codes
The SpaceWire Time-Codes are provided by this component and transmission of those codes to tar-
gets should be performed by a SpaceWire interface.
• Transmission of CCSDS Time Codes through RMAP
• Datation, time-stamping and latency measurement
31.3.5 Target
A target is a SpaceWire node receiving CCSDS Time Codes and SpaceWire Time-Codes. A target is
also an RMAP target, capable of receiving RMAP commands and transmitting RMAP replies. There
can be one or more targets in a SpaceWire network.
Table 465.Example values of ETINC and FSINC for corresponding frequencies
Frequency ETINC FSINC
50 MHz 0 360287970
250 MHz 0 72057594
33333333 2 135107990
 Loading...
Loading...