GR740-UM-DS, Nov 2017, Version 1.7 104 www.cobham.com/gaisler
GR740
10.5 Fault-tolerant operation
10.5.1 Overview
For FT operation, the external memory interface data bus is widened and the extra bits are used to
store 16 or 32 checkbits corresponding to each 64 bit data word. The variant to be used can be config-
ured at run-time depending on the connected data width and the desired level of fault tolerance.
When writing, the controller generates the check bits and stores them along with the data. When read-
ing, the controller will transparently correct any correctable bit errors and provide the corrected data
on the AHB bus. However, the corrected bits are not written back to the memory so external scrub-
bing is necessary to avoid uncorrectable errors accumulating over time.
An extra corrected error output signal is asserted when a correctable read error occurs, at the same
cycle as the corrected data is delivered. This signal is connected to the memory scrubber. In case of
uncorrectable error, this is signaled by giving an AHB ERROR response. See also the AMBA
ERROR propagation description in section 5.10.
10.5.2 Error-correction properties
The memory controller uses an interleaved error correcting code which works on nibble (4-bit) units
of data. The codec can be used in two interleaving modes, mode A and mode B.
In mode A, the basic code has 16 data bits, 8 check bits and can correct one nibble error. This code is
interleaved by 4 using the pattern in table 89 to create a code with 64 data bits and 32 check bits.
This code can tolerate one nibble error in each of the A,B,C,D groups shown below. This means that
we can correct 100% of single errors in two adjacent nibbles, or in any 8/16-bit wide data bus lane,
that would correspond to a physical memory device. The code can also correct 18/23=78% of all pos-
sible random two-nibble errors.
This interleaving pattern was designed to also provide good protection in case of reduced (32/16-bit)
bus width with the same data-checkbit relation, so software will see the exact same checkbits on diag-
nostic reads.
In mode B, the basic code has 32 data bits, 8 check bits and can correct one nibble error. This code is
then interleaved by a factor of two to create a code with 64 data bits and 16 check bits.
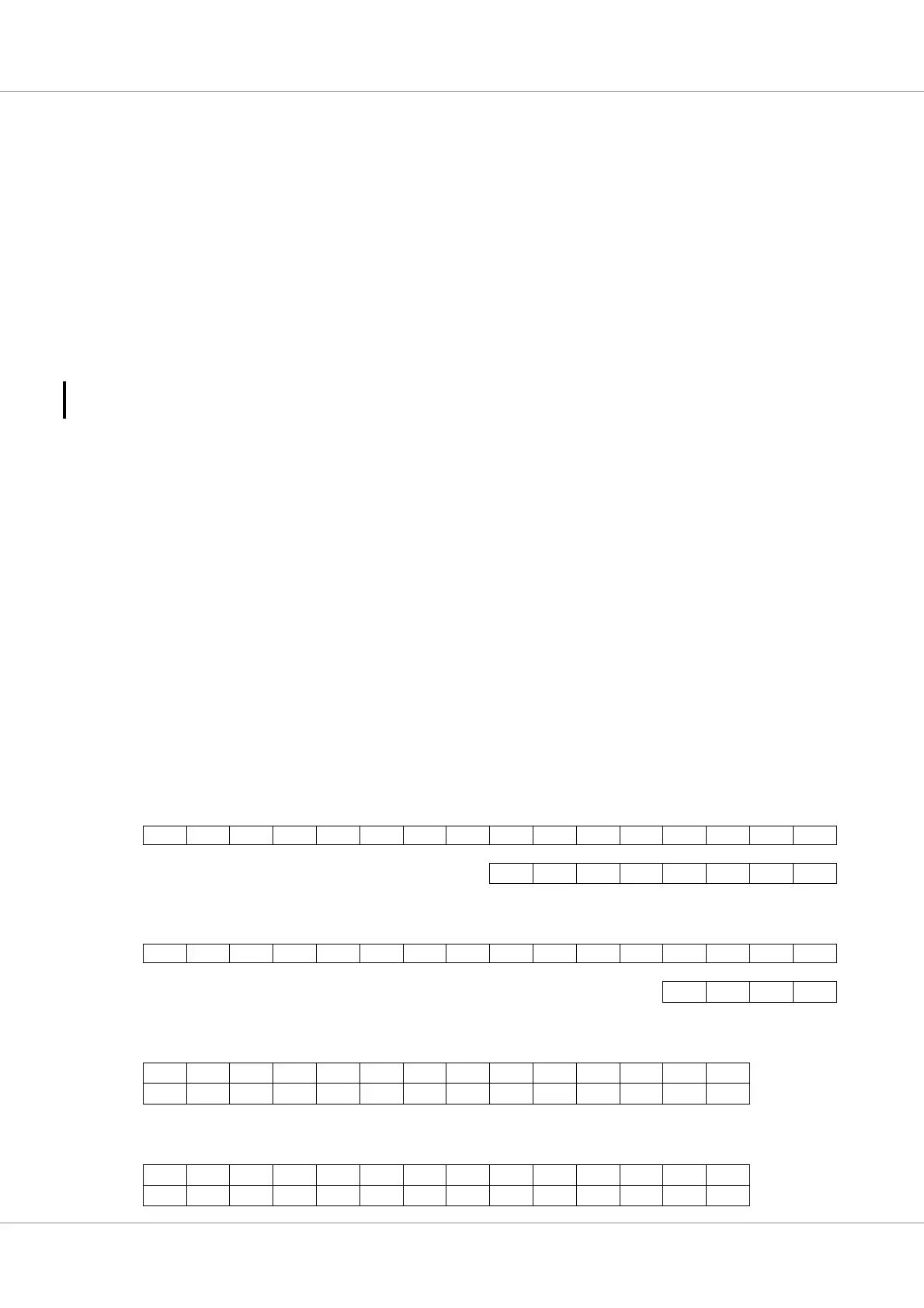
Table 89. Mode Ax4 interleaving pattern (64-bit data width)
63:60 59:56 55:52 51:48 47:44 43:40 39:36 35:32 31:28 27:24 23:20 19:16 15:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
CDABABCDBADCDCBA
127:120 119:112 111:104 103:96 95:88 87:80 79:72 71:64
C
cb
D
cb
A
cb
B
cb
C
cb
D
cb
A
cb
B
cb
Table 90. Mode Bx2 interleaving pattern (64-bit data width)
63:60 59:56 55:52 51:48 47:44 43:40 39:36 35:32 31:28 27:24 23:20 19:16 15:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
ABABABABBABABABA
95:88 87:80 79:72 71:64
A
cb
B
cb
A
cb
B
cb
Table 91. Mode Ax4 interleaving pattern (32-bit data width)
95:80 79:76 75:72 71:68 67:64 63:32 31:28 27:24 23:20 19:16 15:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
-C
cb
D
cb
A
cb
B
cb
- CDABABCD
-B
cb
A
cb
D
cb
C
cb
- BADCDCBA
Table 92. Mode Bx2 interleaving pattern (32-bit data width)
95:80 79:76 75:72 71:68 67:64 63:32 31:28 27:24 23:20 19:16 15:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
---A
cb
B
cb
- ABABABAB
---B
cb
A
cb
- BABABABA
 Loading...
Loading...