3.8.10.9 How to Control the Adjustable
Frequency Drive
Codes available for use in the function and data elds of a
Modbus RTU message are listed in
chapter 3.8.10.10 Function Codes Supported by Modbus RTU
and chapter 3.8.10.11 Modbus Exception Codes.
3.8.10.10 Function Codes Supported by
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU supports use of the function codes (see
Table 3.40) in the function eld of a message.
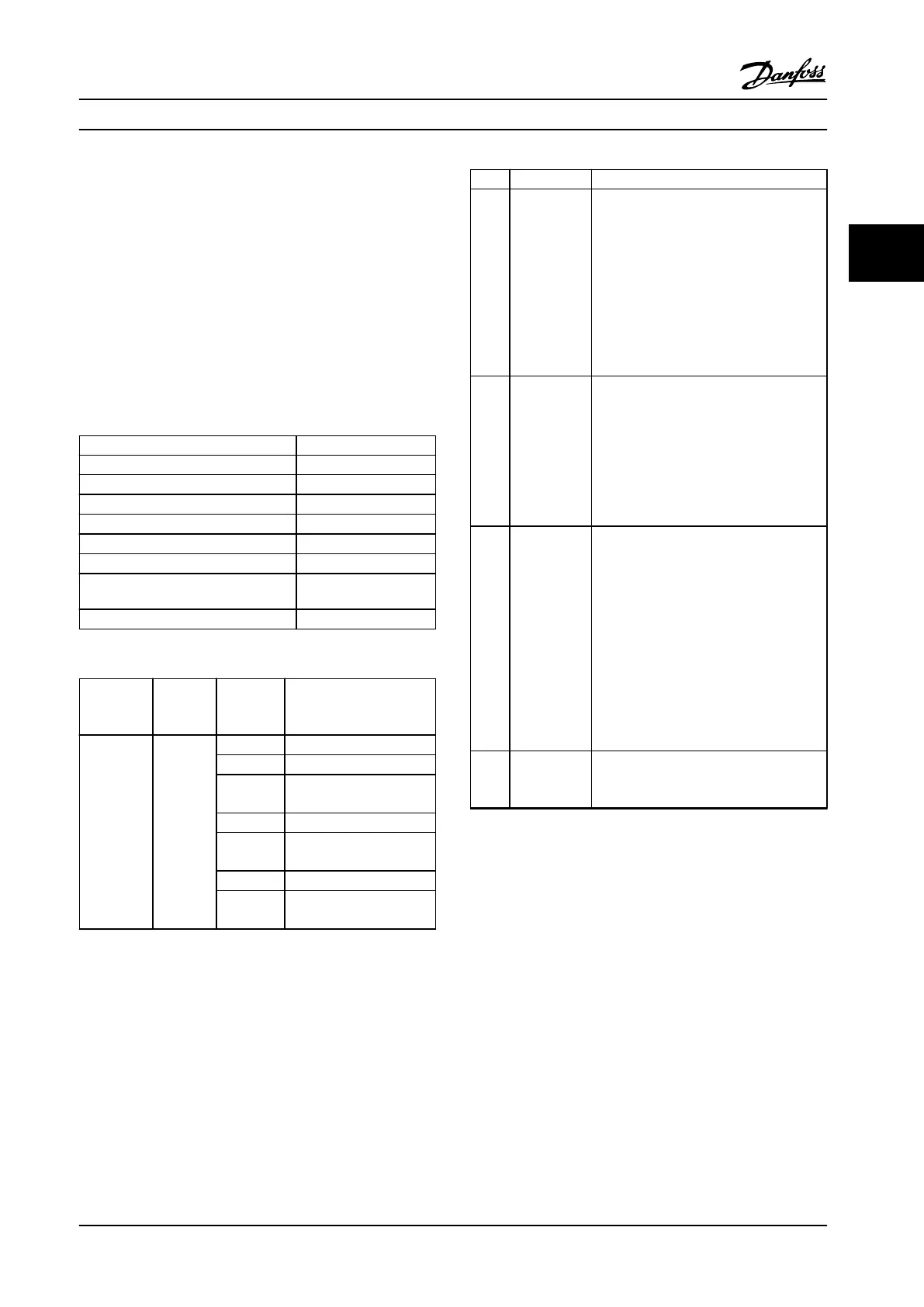
Function Function code (hex)
Read coils 1
Read holding registers 3
Write single coil 5
Write single register 6
Write multiple coils F
Write multiple registers 10
Get communication event counter B
Report slave ID 11
Table 3.40 Function Codes
Function Function
code
Sub-
function
code
Sub-function
Diagnostics 8 1 Restart communication
2 Return diagnostic register
10 Clear counters and
diagnostic register
11 Return bus message count
12 Return bus communi-
cation error count
13 Return slave error count
14 Return slave message
count
Table 3.41 Function Codes and Sub-function Codes
3.8.10.11
Modbus Exception Codes
For a full explanation of the structure of an exception code
response, refer to chapter 3.8.10.5 Function Field.
Code Name Meaning
1 Illegal
function
The function code received in the query is
not an allowable action for the server (or
slave). This may be because the function
code is only applicable to newer devices
and was not implemented in the unit
selected. It could also indicate that the
server (or slave) is in the wrong state to
process a request of this type, for example
because it is not congured and is being
asked to return register values.
2 Illegal data
address
The data address received in the query is
not an allowable address for the server (or
slave). More specically, the combination
of reference number and transfer length is
invalid. For a controller with 100 registers,
a request with oset 96 and length 4
would succeed, a request with oset 96
and length 5 generates exception 02.
3 Illegal data
value
A value contained in the query data eld
is not an allowable value for server (or
slave). This indicates a fault in the
structure of the remainder of a complex
request, such as that the implied length is
incorrect. It specically does NOT mean
that a data item submitted for storage in
a register has a value outside the
expectation of the application program,
since the Modbus protocol is unaware of
the signicance of any particular value of
any particular register.
4 Slave device
failure
An unrecoverable error occurred while the
server (or slave) was attempting to
perform the requested action.
Table 3.42 Modbus Exception Codes
3.8.11
Access to Parameters
3.8.11.1 Parameter Handling
The PNU (parameter number) is translated from the
register address contained in the Modbus read or write
message. The parameter number is translated to Modbus
as (10 x parameter number) decimal. Example: Reading
3-12 Catch up/slow-down Value (16 bit): The holding
register 3120 holds the parameters value. A value of 1352
(Decimal) means that the parameter is set to 12.52%
Reading 3-14 Preset Relative Reference (32 bit): The holding
registers 3410 and 3411 hold the parameter’s value. A
value of 11300 (decimal), means that the parameter is set
to 1113.00.
For information on the parameters, size and converting
index, consult the Programming Guide.
System Integration
Design Guide
MG20N622 Danfoss A/S © 09/2014 All rights reserved. 91
3 3

 Loading...
Loading...






















