MICROPROCESSOR-BASED/DDC FUNDAMENTALS
147
ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
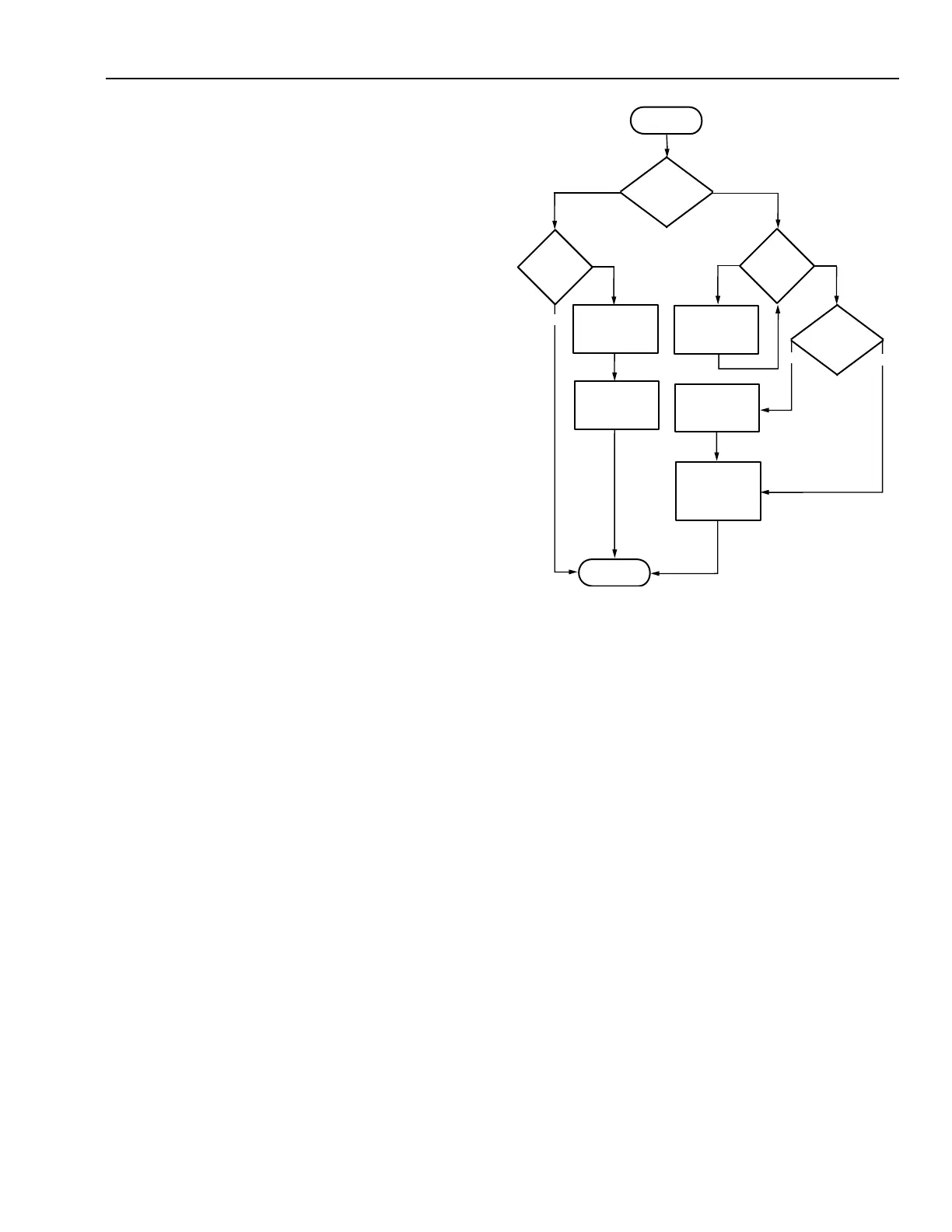
Step 3—Write a detailed sequence of operation for the process.
The hot water pump starts anytime the outside air
temperature drops to 52F, subject to a software on-off-auto
function.
When hot water pumping is proven by a current sensing
relay, converter controls are energized. Hot water temperature
setpoint varies linearly from 120F to 170F as the outside air
temperature varies from 60F to 0F. The converter steam valve
is modulated to maintain a converter leaving water temperature
according to a varying setpoint schedule.
The steam valve closes anytime hot water pumping is not
proven and anytime the valve actuator loses motive power.
Step 4—Develop the detailed flowchart.
Step 5—Write the program.
See the Air Handling System Control Applications section
and the Chiller, Boiler, and Distribution System Control
Applications section for other examples of Microprocessor-
Based/DDC systems.
Fig. 18. Flowchart Example.
M13120
NO
YES
TURN
PUMP
OFF
YES
O.A.
TEMP
EQUAL TO OR
BELOW
11°C
PUMP
ON?
START
PUMP
CLOSE
STEAM
VALVE
ENERGIZE
CONTROL
SYSTEM
CONTROL
SYSTEM
MAINTAINS
RESET
SCHEDULE
NO
CONTROL
SYSTEM
ENERGIZED
PUMP
ON?
YES
NO
YES
END
NO
START
 Loading...
Loading...











