ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
DAMPER SELECTION AND SIZING
468
DAMPER PRESSURE DROP
If the duct size, damper size, and the airflow are known, use
the method in Table 6 to determine the actual pressure drop
across the damper:
For example, for a 2304 in
2
parallel blade
damper in a 2600
in
2
duct with an airflow of 20,000 cfm, determine the pressure
drop across the damper as shown in Table 7.
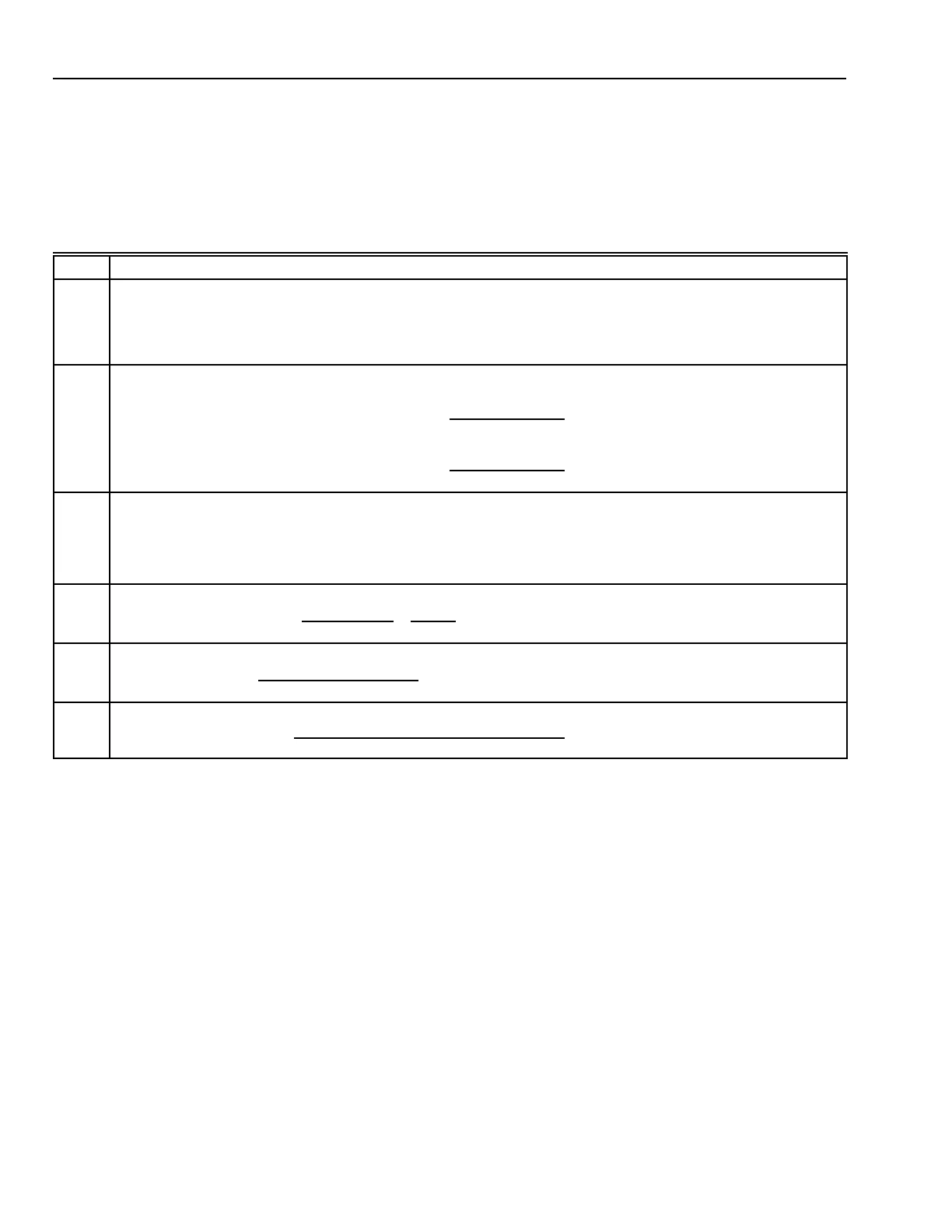
Table 6. Damper Pressure Drop Calculation Procedures
Step Procedure
1 a. Determine the number of sections required.
The area of the damper must not exceed the maximum size for a single section. If the damper area exceeds the
single section area:
b. Divide the area of the damper, the area of the duct, and the airflow by the number of damper sections.
c. Use the values from Step b in the following Steps.
2
Calculate the free area ratio
a
:
For parallel blade dampers, the free area ratio is found:
Ratio = (0.00005149 x damper area in
2
)
0.1007
x
Damper area (in
2
)
Duct area (in
2
)
For opposed blade dampers, the free area ratio is found:
Ratio = (0.00001159 x damper area in
2
)
0.0849
x
Damper area (in
2
)
Duct area (in
2
)
3 Using the ratio from Step 1, calculate the pressure drop at 1000 fpm.
For ratios ≤ 0.5:
Pressure drop (in. wc) = –0.04689 x (1 – ratio
–2.562
)
For ratios > 0.5:
Pressure drop (in. wc) = –0.01254 x (1 – ratio
–4.274
)
4 Calculate the approach velocity:
Approach velocity (fpm) =
Airflow (cfm)
Duct Area (in
2
)
x
144 in
2
1 ft
2
5 Using the approach velocity from Step 3, calculate a correction factor:
Correction factor =
10
6
[Approach velocity (fpm)]
2
6 Calculate the pressure drop across the damper:
Pressure drop (in. wc) =
Pressure drop (in. wc) at 1000 fpm (Step 2)
Correction factor (Step 4)
a
The free area of a damper is the open portion of the damper through which air flows. The free area ratio is the open area in
a damper divided by the total duct area.
 Loading...
Loading...











