ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
CHILLER, BOILER, AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM CONTROL APPLICATIONS
339
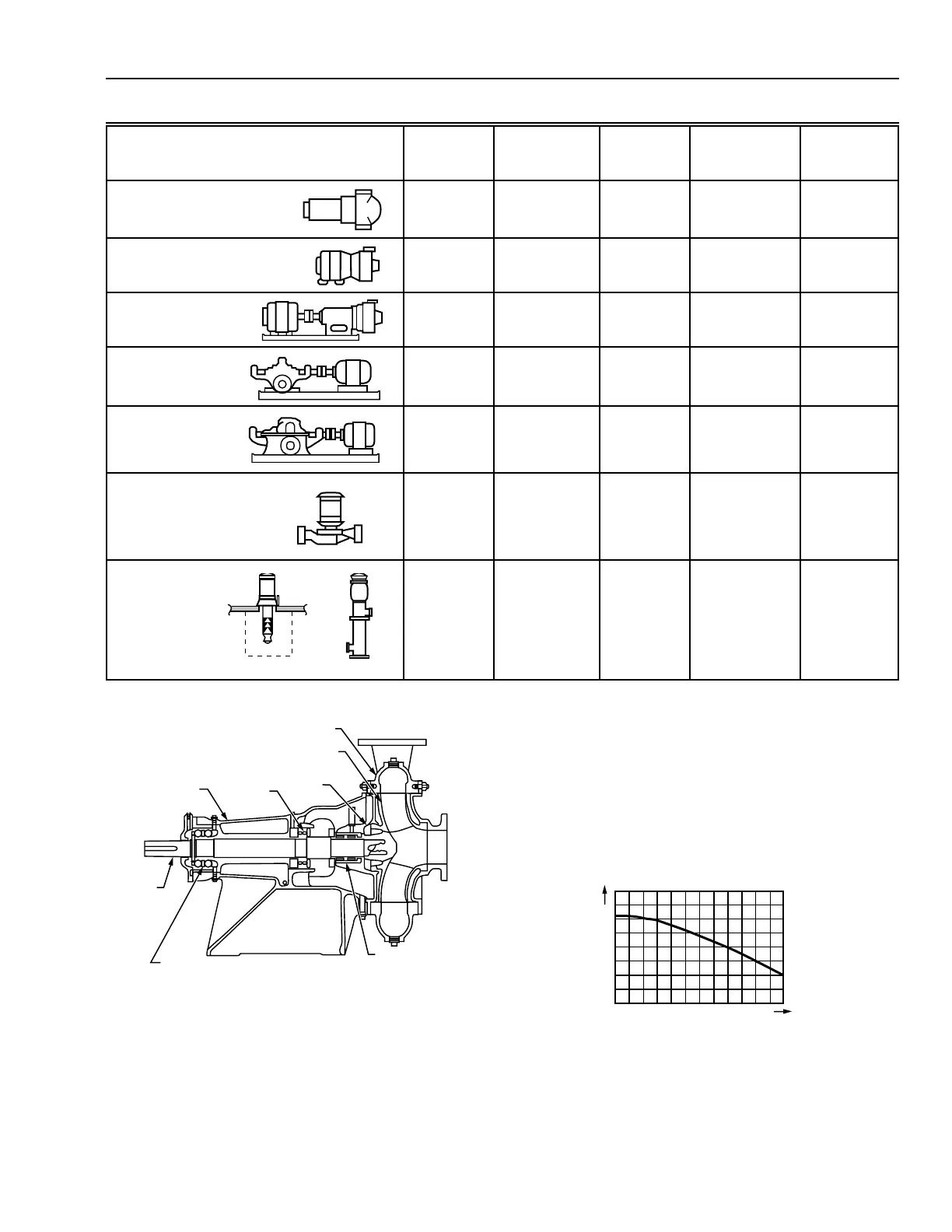
Table 2. Characteristics of Centrifugal Pump Types.
Type
Impeller
Type
No. of
Impellers Casing
Motor
Connection
Motor
Mounting
Position
Circulator
Single
suction
One Volute Flexible-
coupled
Horizontal
Close-coupled,
end suction
Single
suction
One or two Volute Close-
coupled
Horizontal
Frame-mounted,
end suction
Single
suction
One or two Volute Flexible-
coupled
Horizontal
Double suction,
horizontal
split case
Double
suction
One Volute Flexible-
coupled
Horizontal
Horizontal split
case,
multistage
Single
suction
Two to five Volute Flexible-
coupled
Horizontal
Vertical inline
Single
suction
One Volute Flexible- or
close-
coupled
Vertical
Vertical
turbine
Single
suction
One to twenty Diffuser Flexible-
coupled
Vertical
Source: ASHRAE Handbook—1996 Systems and Equipment
Fig. 52. Typical Cross-Section of an End Suction Pump.
PUMP PERFORMANCE
The performance of a given pump is expressed in a curve
showing pump head in feet versus gallons per minute (gpm).
Figure 53 shows a typical curve. The head is expressed in feet (of
water column) which describes pump operation independent of
water temperature or density. Pressure losses in piping and
components used in HVAC systems are always calculated in feet.
FRAME
INBOARD
BEARING
IMPELLER
RING
IMPELLER
CASING
ROTATING
ELEMENT
MECHANICAL
SEAL
OUTBOARD
BEARING
PUMP
SHAFT
M10509
OUTLET
INLET
Fig. 53. Typical Pump Head Capacity Curve.
C2907
FLOW
INC
TOTAL HEAD
INC
 Loading...
Loading...











