INDOOR AIR QUALITY FUNDAMENTALS
154
ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATION CONTROL
INDOOR AIR QUALITY CONCERNS
contaminants such as methane are produced both naturally, by
animals and decay, and by man made activity such as landfills.
Location near a fossil fuel power plant, refinery, chemical
production facility, sewage treatment plant, municipal refuse
dump or incinerator, animal feed lot, or other like facility will
have a significant effect on the air introduced into a building.
Below ground sources include radon gas and its by products.
Radon gas is found in all soils in various concentrations. It is a
product of the radioactive decay of radium. Radon, in turn,
generates other radioactive contaminants as it decays. Radon
gas enters buildings primarily through the foundation. Radon
can then decay through a succession of decay products,
producing metallic ions. These products become attached to
particulate matter suspended in the air and can then be inhaled
causing health problems.
Outdoor air pollution is monitored and regulated at the
Federal level by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA) which has set primary and secondary standards for several
pollutants known as criteria pollutants. These criteria pollutants
include: nitrogen dioxide (NO
2
), ozone (O
3
), carbon monoxide
(CO), sulfur oxides, nonmethane hydrocarbons, lead (Pb), and
total suspended particulates (TSP). The EPA estimates that 50
percent of American cities do not meet all these standards for
1996. See Tables 1 and 2.
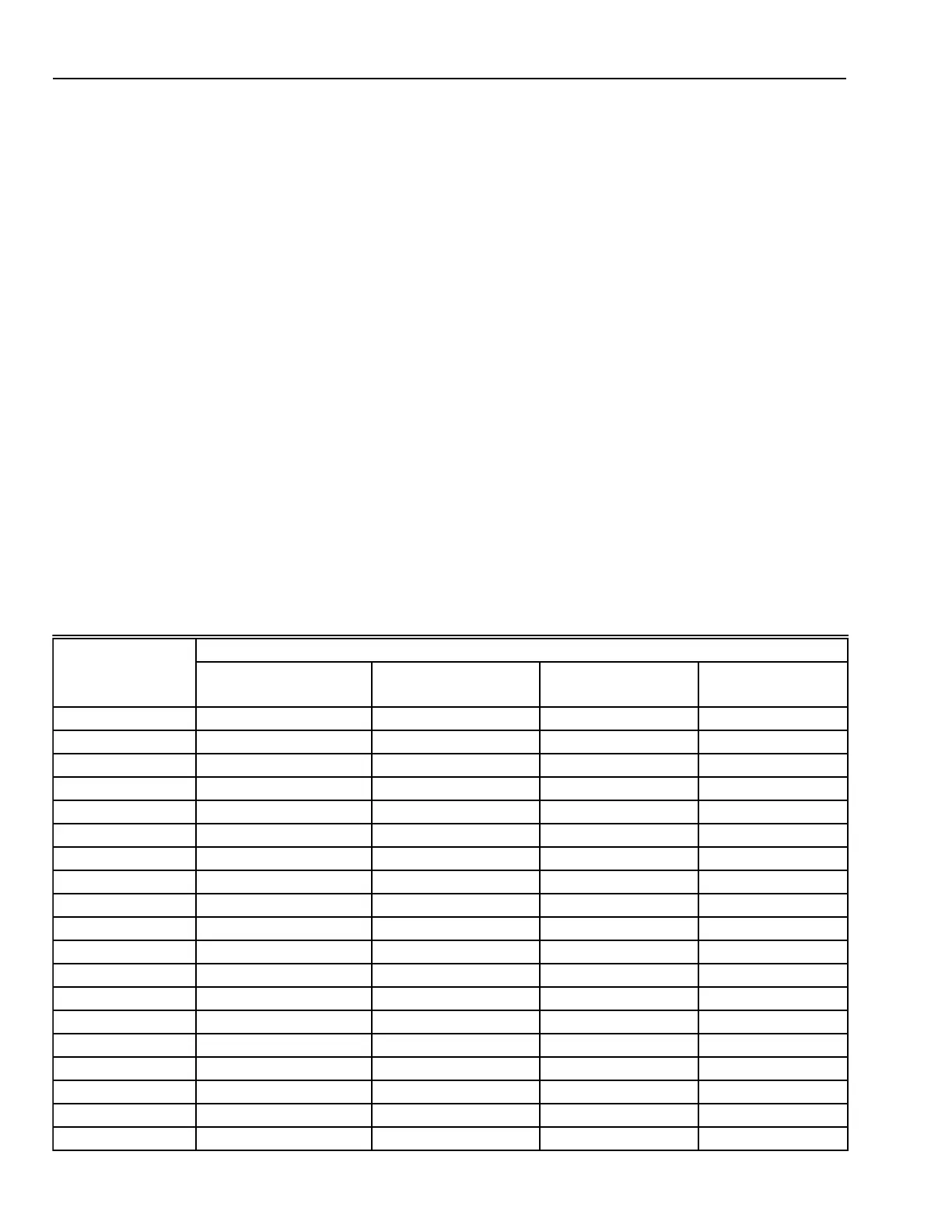
Table 1. Annual Median Concentrations for TSP, NO
2
, O
3
, & CO—1979.
a
AIR CONTAMINANTS
Air contaminants are categorized by location and type.
Location of contaminants is divided between outdoor and
indoor. Outdoor air contamination results from natural or man-
made phenomena that occur outdoors or indoors. Contaminant
types include particulate, gas, vapor, radionuclide.
CONTAMINANT SOURCES
Outdoor Contaminant Sources
Outdoor contaminant sources are divided into above ground
and below ground sources. Above ground sources are
subdivided into man made and naturally occurring sources. Man
made sources are those such as electric power generating plants,
various modes of transportation (automobile, bus, train ship,
airplane ), industrial processes, mining and smelting,
construction, and agriculture. These contaminants can be
loosely classified as dusts, fumes, mists, smogs, vapors , gases,
smokes that are solid particulate matter (smoke frequently
contains liquid particles ), and smokes that are suspended liquid
particulates. Naturally occurring contaminant sources include
pollen, fungus spores, viruses, and bacteria. Gaseous
(continued)
Concentration
µg/m
3
mg/m
3
Location TSP (annual average)
b
NO
2
(1 hr average)
O
3
(1 hr average)
CO (1 hr average)
Baltimore 43-102 45 20 1.5
Boston 67 75
—
3.5
Burbank, Ca.
—
124 39 3.5
Charleston, WV 43-70 37 14 1.2
Chicago 56-125 63 29 2.9
Cincinnati 47-87 60 24 1.0
Cleveland 58-155 89
c
26 2.0
Dallas 43-73 59
c
39 1.4
Denver 80-194 89 37 4.6
Detroit 52-135 68 14 1.8
Houston 51-147 90
c
39
d
1.0
Indianapolis 48-81 91
c
33 2.7
Los Angeles 90 85 117 2.6
Louisville 60-102 70
c
31 1.5
Milwaukee 47-105 86
c
41 1.4
Minneapolis 45-87 65
c
—
1.8
Nashville 41-82 62
c
49
d
2.6
New York 40-77 57 35 5.5
Philadelphia 51-109 85 39 3.2

 Loading...
Loading...











