ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
VALVE SELECTION AND SIZING
447
Two-Position Applications
Use line sized valves whenever possible. If the valve size
must be reduced, use:
h=20% x (Pm-Pr)
Where
Pm = Pressure in supply main in psig or psia (gage
or absolute pressure).
Pr = Pressure in return in psig or psia. A negative
value if a vacuum return.
STEAM VALVE SIZING EXAMPLES
EXAMPLE 1:
A two-way linear valve (V1) is needed to control high-
pressure steam flow to a steam-to-water heat exchanger. An
industrial-type valve is specified. Steam pressure in the
supply main is 80 psig with no superheat, pressure in return
is equal to atmospheric pressure, water flow is 82.5 gpm,
and the water temperature difference is 20F.
Use the steam valve C
v
formula to determine capacity
index for Valve V1 as follows:
Where:
Q=The quantity of steam required to pass
through the valve is found using the
converter valve formula:
Q=gpm x TD
w
x 0.49
Where:
gpm = 82.5 gpm water flow through exchanger
TD
w
= 20F temperature difference
0.49 = A scaling constant
Substituting this data in the formula:
Q=808.5 pounds per hour
h=The pressure drop across a valve in a
modulating application is:
h=80% x (Pm – Pr)
Where:
Pm = Upstream pressure in supply main is 80 psig.
Pr = Pressure in return is atmospheric pressure or
0 psig.
Substituting this data in the pressure drop formula:
h=0.80 x (80 – 0)
=0.80 x 80
= 64 psi
Average Radiator
of Convector
Temperature,
Deg F
Cast Iron
Radiator
Btu/Hr/EDR
a
Convector,
Btu/Hr/EDR
b
215 240 240
200 209 205
190 187 183
180 167 162
170 148 140
160 129 120
150 111 102
140 93 85
130 76 69
120 60 53
110 45 39
100 31 27
90 18 16
a
At Room Temperature.
b
At 65F Inlet Air Temperature
STEAM VALVE PRESSURE DROP
Proportional Applications
When specified, use that pressure drop (h) across the valve.
When not specified:
1. Calculate the pressure drop (h) across the valve for good
modulating control:
h=80% x (Pm – Pr)
NOTE: For a zone valve in a system using radiator orifices
use:
h=(50 to 75)% x (Pm – Pr)
Where
Pm = Pressure in supply main in psig or psia (gage
or absolute pressure).
Pr = Pressure in return in psig or psia. A negative
value if a vacuum return.
2. Determine the critical pressure drop:
h
critical
= 50% x Pma
Where:
Pma = Pressure in supply main in psia (absolute
pressure)
psia = psig + 14.7
Use the smaller value h or h
critical
when calculating C
v
.
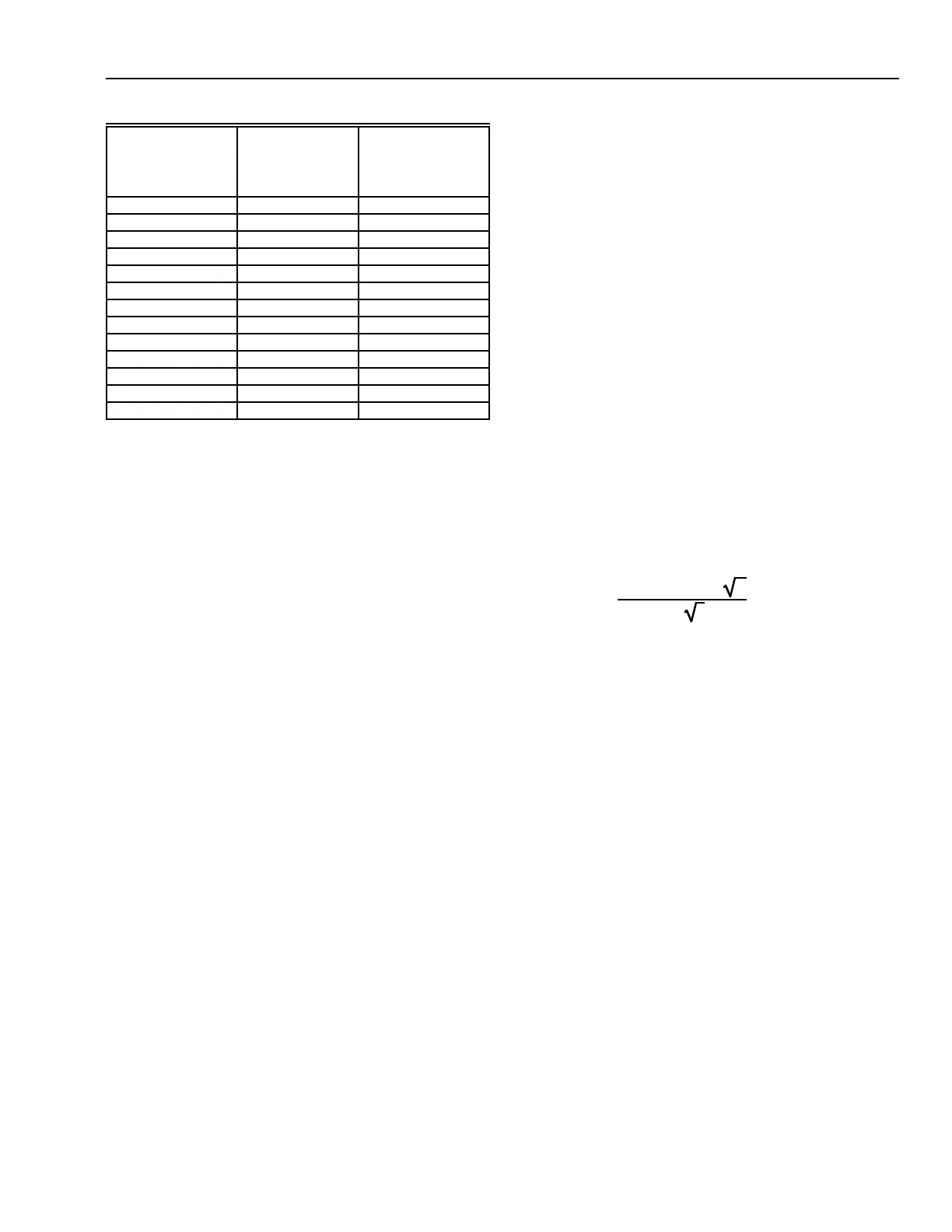
Cv =
(1 + 0.00075s)Q
V
63.5
h
Table 4. Output of Radiators and Convectors.

 Loading...
Loading...











