ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATIC CONTROL
VALVE SELECTION AND SIZING
448
The critical pressure drop is found using the following
formula:
h
critical
= 50% x (psig + 14.7 psi)
h
critical
=0.50 x (80 psig upstream + 14.7 psi)
=0.50 x 94.7 psi
= 47.4 psi
The critical pressure drop (h
critical
) of 47.4 psi is used in
calculating C
v
, since it is less than the pressure drop (h) of
64 psi. Always, use the smaller of the two calculated values.
V=Specific volume (V) of steam, in cubic feet
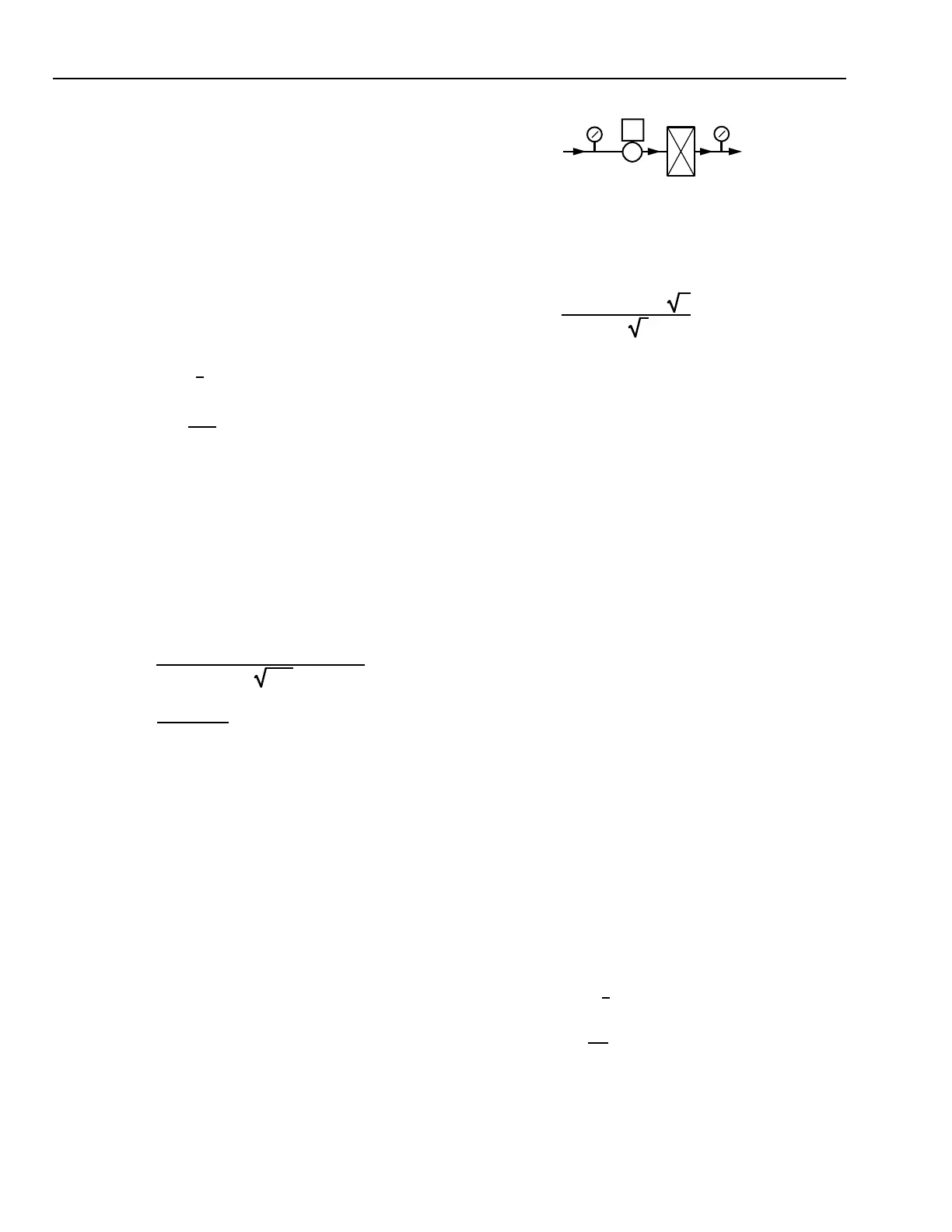
Fig. 19. Linear Valve Steam Application.
Use the steam valve C
v
formula to determine capacity
index for Valve V1 as follows:
per pound at average pressure in valve (P
avg
):
The specific volume of steam at 56.4 psig is
6.14 and the square root is 2.48.
63.5 = A scaling constant.
Substituting the quantity of steam, specific volume of
steam, and pressure drop in the C
v
formula shows that the
valve should have a C
v
of 4.6.
P
avg
= Pm –
h
2
NOTE: If P
avg
is rounded off to the nearest value in Table
5 (60 psi), the calculated C
v
is 4.5 a negligible
difference.
Select a linear valve providing close control with a capacity
index of 4 and meeting the required pressure and
temperature ratings.
NOTE: For steam valves downstream from pressure
reducing stations, the steam will be superheated in
most cases and must be considered.
EXAMPLE 2:
In Figure 19, a linear valve (V1) is needed for accurate flow
control of a steam coil that requires 750 pounds per hour of
steam. Upstream pressure in the supply main is 5 psig and
pressure in the return is 4 in. Hg vacuum minimum.
= 80 –
47.4
2
= 80 – 23.6 = 56.4 psig
C
v
=
(1 + 0.00075 x 0) x 808.5 x
63.5 47.4
=
1745.6
63.5 x 6.88
= 4.6
VALVE VI
C2336
5 PSI
SUPPLY
1.96 PSI
(VACUUM)
RETURN
STEAM
COIL
30% PRESSURE DROP, Cv = 41
80% PRESSURE DROP, Cv = 25
C
v
=
(1 + 0.00075s)Q
V
63.5
h
Where:
Q=Quantity of steam required to pass through
the valve is 750 pounds per hour.
h=The pressure drop across a valve in a
modulating application is found using:
h=80% x (Pm – Pr)
and:
Pm = Upstream pressure in supply main is 5 psig.
Pr = Pressure in return is 4 in. Hg vacuum.
NOTE: 1 in. Hg = 0.49 psi and 1 psi = 2.04 in.
Hg.
Therefore,
4 in. Hg vacuum = –1.96 psig.
h=0.80 x [5 – (–1.96)]
=0.80 x 6.96
= 5.6 psi
The critical pressure drop is found using the following
formula:
h
critical
= 50% x (psig + 14.7 psi)
h
critical
=0.50 x (5 psig upstream + 14.7 psi)
=0.50 x 19.7 psia
=9.9 psi
The pressure drop (h) of 5.6 psi is used in calculating
the C
v
, since it is less than the critical pressure drop
(h
critical
) of 9.9 psi.
V=Specific volume (V) of steam, in cubic feet
per pound at average pressure in valve (P
avg)
:
P
avg
= Pm –
h
2
= 5 –
5.6
2
= 5 – 2.8 = 2.2 psig
The specific volume of steam at 2.2 psig is
23.54 and the square root is 4.85.
 Loading...
Loading...











