ENGINEERING MANUAL OF AUTOMATION CONTROL
BUILDING AIRFLOW SYSTEM CONTROL APPLICATIONS
266
Static pressure: The pressure created by air (whether in motion
or not) confined in an enclosed area such as a duct or
building due to its potential energy. Static pressure,
denoted SP, is exerted perpendicularly on all interior
walls of the enclosure (duct or building) with respect
to a reference pressure outside the enclosure. When
static pressure is above atmospheric pressure it is
positive and when below atmospheric pressure it is
negative.
Static pressure sensor or tube: A sensing device with several
holes perpendicular to an airstream for measuring
static pressure.
Total pressure: The algebraic sum of Velocity Pressure (VP)
plus Static Pressure, denoted TP. Total pressure is
derived:
TP = VP + SP
Turndown: The relationship, in percent, between the maximum
minus the minimum airflow to the maximum airflow.
For example, in a system with a maximum airflow of
2000 cfm and minimum airflow of 400 cfm, the
turndown is 80 percent.
Variable Air Volume (VAV) system: A central fan system in
which airflow in the duct varies depending on the
instantaneous load requirements of the connected VAV
terminal units.
Velocity: The speed or rate of flow of the air stream in a duct.
In this section, velocity is denoted V and is measured
in feet per minute (fpm). See General Engineering
Data section.
•Average Velocity—The sum of the air velocities from
equal area increments of a duct cross-section divided by
the number of increments. Average velocity, denoted
V
AV G
, is derived:
Where
N=Number of duct increments
•Peak Velocity—The greatest air velocity occurring in an
increment of a duct cross-section. Peak velocity is
denoted V
PK
.
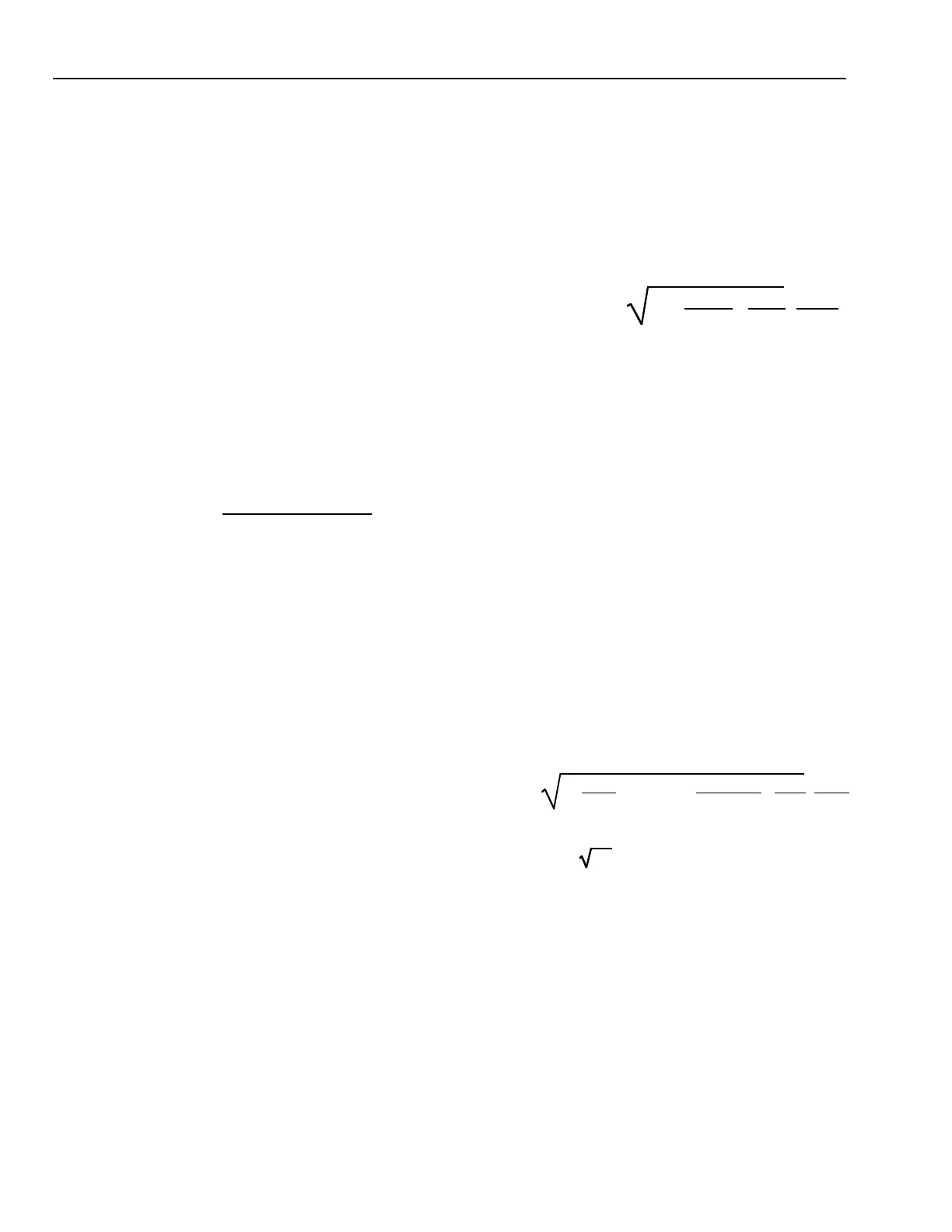
•Velocity Pressure: The pressure created by air moving
at a velocity due to its kinetic energy. Velocity pressure,
denoted VP, is always exerted in the direction of airflow
and is always a positive value. Velocity pressure and
velocity are related by the equation:
Where:
V=Velocity in fpm
G=Gravitational acceleration in feet
per second squared (ft/sec2)
VP = Velocity pressure in inches of
water column (in. wc)
Dw = Density of water at a specified
temperature measured in pounds
per cubic foot (lb/ft3)
Da = Density of the air flowing in the
duct measured in pounds per cubic
foot (lb/ft3)
1ft/12 in. = Conversion factor to convert
inches to feet
60 sec/1 min = Conversion factor to convert
seconds to minutes
The density of air (Da) is 0.075 lb/ft
3
(at 70°F,
29.92 in. wc atmospheric pressure, and 50 percent
relative humidity) and gravity (G) is = 32.2 ft/sec
2
. At
70°F, the density of water (Dw) is 62.27 lb/ft
3
. With
this data, the relationship of velocity to velocity
pressure is simplified:
This equation reduces to:
See General Engineering Data section for Velocity vs.
Ve lo city Pressure table.
Turndown % =
()
Max Flow – Min Flow
Max Flow
x 100
V =
2G x
VP Dw
Da
x
1 ft
12 in.
60 sec
1 mi
V =
2 x
32.2 ft
sec
2
x VP in. wc x
62.27 lb/ft
3
0.075 lb/ft
3
x
1 ft
12 in.
60 sec
1 mi
V = 4005 VP
V
AVG
= ∑ (V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
+…… + V
N
) / N
 Loading...
Loading...











