10
Configuring static route FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop. Static route fast reroute
(FRR) enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of link or node failures.
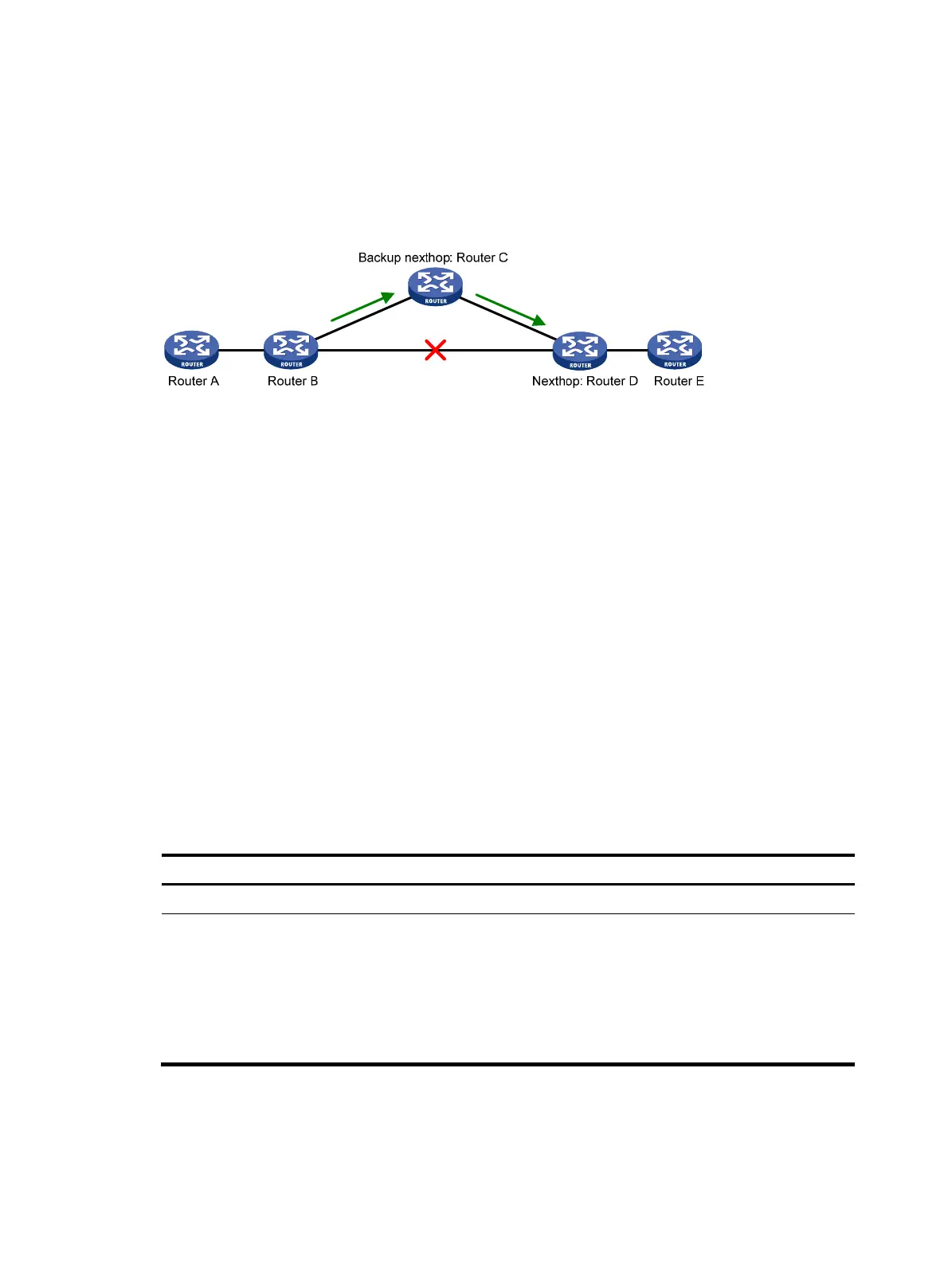
Figure 1 Network diagram
As shown in Figure 1, upon a link failure, FRR specifies a backup next hop by using a routing policy for
routes matching the specified criteria. Packets are directed to the backup next hop to avoid traffic
interruption.
Configuration guidelines
• Do not use static route FRR and BFD (for a static route) at the same time.
• Static route does not take effect when the backup output interface is unavailable.
• Equal-cost routes do not support static route FRR.
• The backup output interface and next hop cannot be modified directly or the same as the primary
output interface and next hop.
• Static route FRR is available only when the state of primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying up)
changes from bidirectional to unidirectional or down. A unidirectional link refers to the link through
which packets are forwarded only from one end to the other.
Configuration procedure
To configure static route FRR:
Ste
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view N/A
2. Configure the source
address of BFD echo
packets.
bfd echo-source-ip ip-address
By default, the source address
of BFD echo packets is not
configured.
For more information about
this command, see High
Availability Command
Reference.

 Loading...
Loading...











