42
11.1.1.0/24 RIP 100 1 12.3.1.1 Eth1/1
12.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Eth1/1
12.3.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Eth1/1
12.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.3.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Eth1/1
16.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Eth1/2
16.4.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Eth1/2
16.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
16.4.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Eth1/2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuring an additional metric for a RIP interface
Network requirements
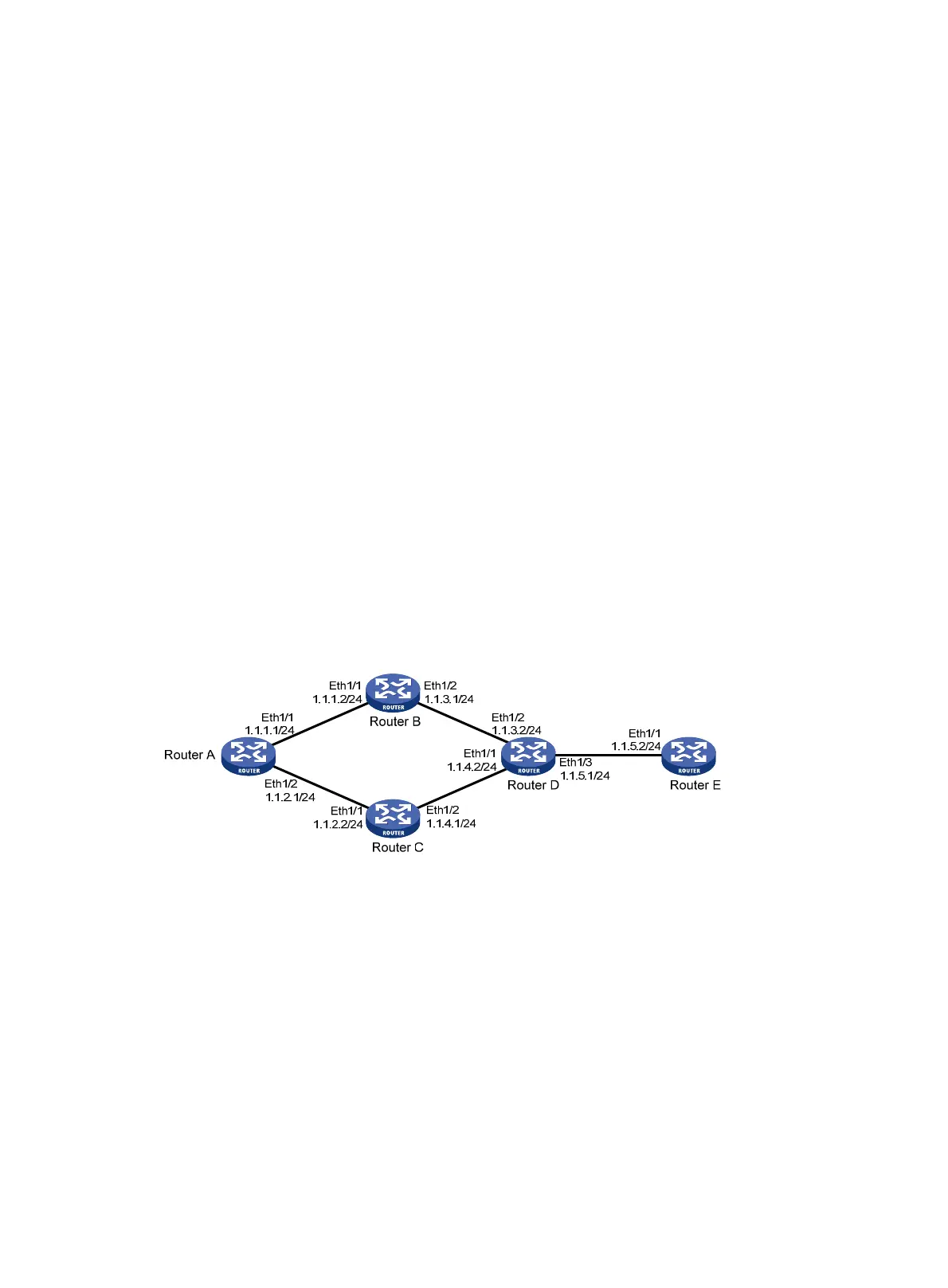
As shown in Figure 9, run RIPv2 on all the interfaces of Router A, Router B, Router C, Router D, and Router
E.
Router A has two links to Router D. The link from Router B to Router D is more stable than that from Router
C to Router D. Configure an additional metric for RIP routes received from Ethernet 1/2 on Router A so
Router A prefers route 1.1.5.0/24 learned from Router B.
Figure 9 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP:
# Configure Router A.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] rip
[RouterA-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[RouterA-rip-1] version 2
[RouterA-rip-1] undo summary
[RouterA-rip-1] quit
# Configure Router B.
<RouterB> system-view

 Loading...
Loading...











