282
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
* > Network : 9:: PrefixLen : 64
NextHop : :: LocPrf :
PrefVal : 32768 OutLabel : NULL
MED : 0
Path/Ogn: i
* i Network : 9:: PrefixLen : 64
NextHop : 9::1 LocPrf : 100
PrefVal : 0 OutLabel : NULL
MED : 0
Path/Ogn: i
* >i Network : 10:: PrefixLen : 64
NextHop : 9::1 LocPrf : 100
PrefVal : 0 OutLabel : NULL
MED : 0
Path/Ogn: i
* >i Network : 50:: PrefixLen : 64
NextHop : 10::2 LocPrf : 100
PrefVal : 0 OutLabel : NULL
MED : 0
Path/Ogn: 65008i
The output shows that Router C has learned the route 50::/64.
# Ping hosts on network 50::/64 on Router C. The ping operations succeed.
IPv6 BGP route reflector configuration example
Network requirements
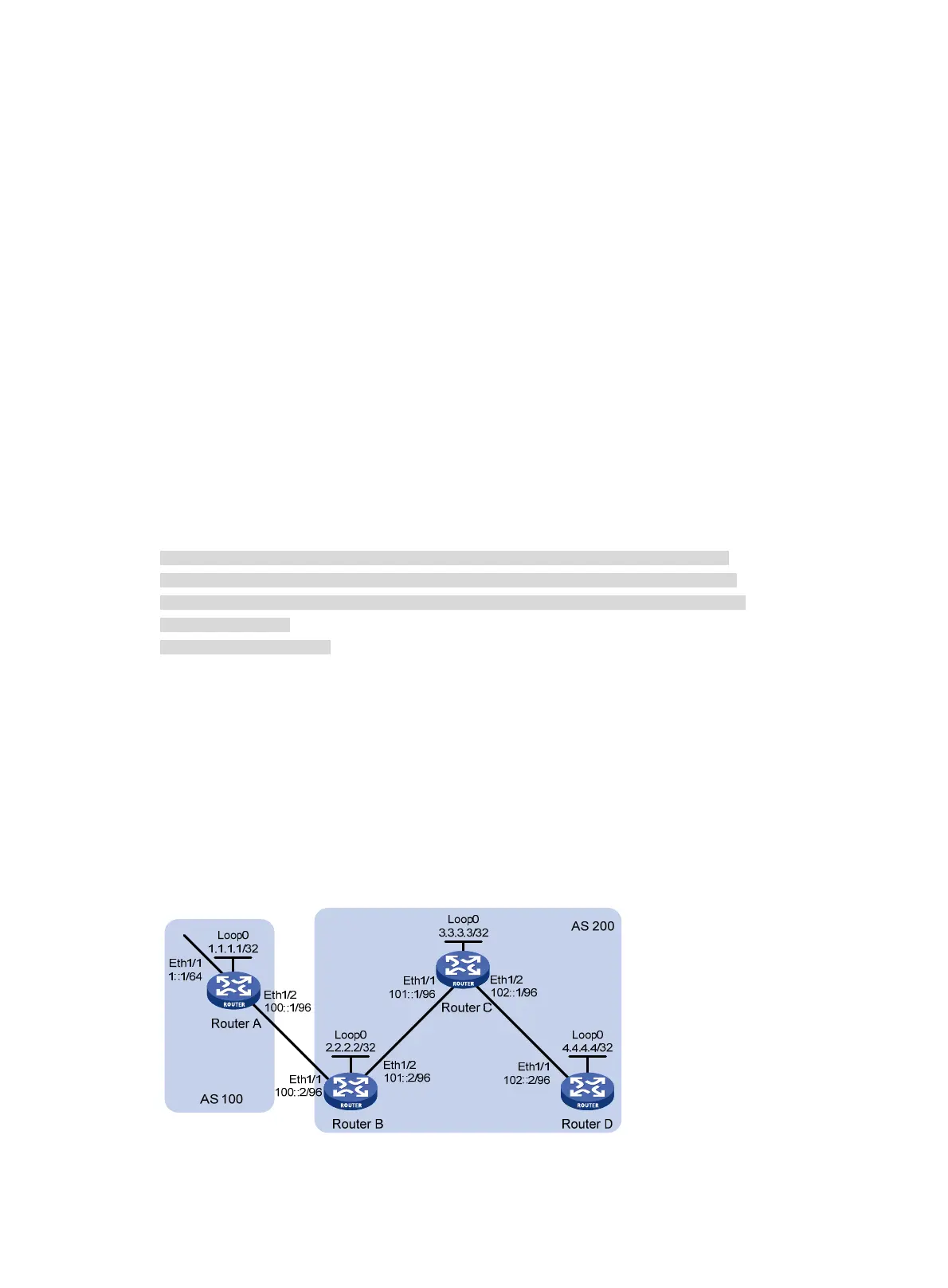
As shown in Figure 73, run EBGP between Router A and Router B, run IBGP between Router C and Router
B, and between Router C and Router D. Router C is a route reflector with clients Router B and D.
Figure 73 Network diagram
 Loading...
Loading...











