18
Summary Count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 Static 65 0 10.1.1.100 Eth1/2
Static Routing table Status : <Inactive>
Summary Count : 0
The output shows that Router A communicates with Router B through Ethernet 1/2.
Static route FRR configuration example
Network requirements
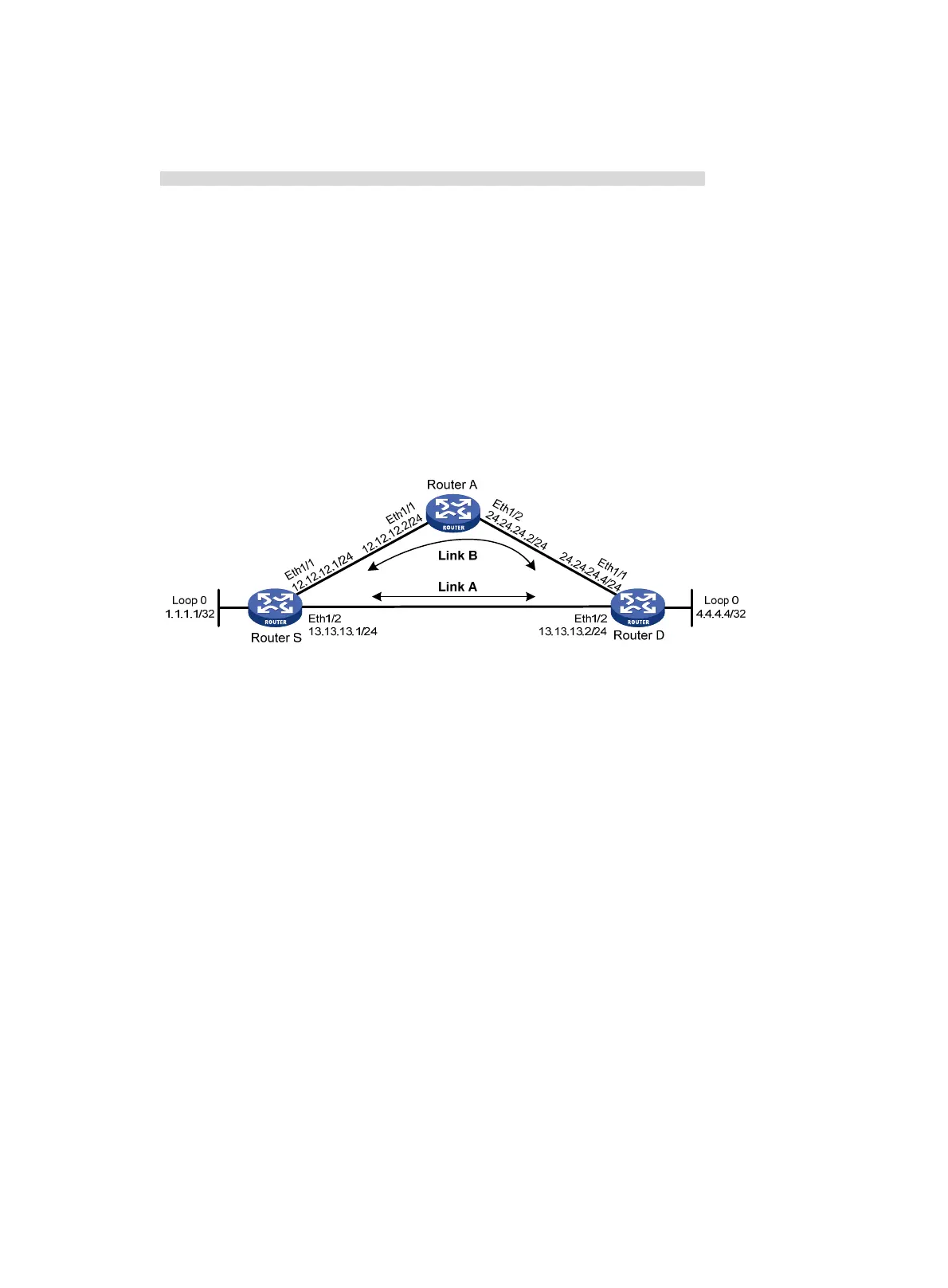
As shown in Figure 5, configure static routes on Router S, Router A, and Router D, and configure static
route FRR so when Link A becomes unidirectional, traffic can be switched to Link B immediately.
Figure 5 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes FRR on link A:
# Configure a static route on Router S, and specify Ethernet 1/1 as the backup output interface
and 12.12.12.2 as the backup next hop.
<RouterS> system-view
[RouterS] bfd echo-source-ip 4.4.4.4
[RouterS] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 ethernet 1/2 13.13.13.2 backup-interface
ethernet 1/1 backup-nexthop 12.12.12.2
# Configure a static route on Router D, and specify Ethernet 1/1 as the backup output interface
and 24.24.24.2 as the backup next hop.
<RouterD> system-view
[RouterD] bfd echo-source-ip 1.1.1.1
[RouterD] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 ethernet 1/2 13.13.13.1 backup-interface
ethernet 1/1 backup-nexthop 24.24.24.2
3. Configure static routes on Router A.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 ethernet 1/2 24.24.24.4
[RouterA] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 ethernet 1/1 12.12.12.1
Verifying the configuration
# Display route 4.4.4.4/32 on Router S to view the backup next hop information.

 Loading...
Loading...











