248
Task Command
Display information about routes
advertised by the network command and
shortcut routes configured by the network
short-cut command.
display bgp network ipv6 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
Display BGP path attribute information. display bgp paths [ as-regular-expression ]
Display BGP IPv6 unicast address family
update group information.
display bgp update-group ipv6 [ unicast ] [ ip-address |
ipv6-address ]
display bgp update-group ipv6 [ unicast ] vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name [ ipv6-address ]
Reset IPv6 unicast BGP sessions.
reset bgp { as-number | ipv6-address | all | external | group
group-name | internal } ipv6 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
reset bgp ip-address ipv6 [ unicast ]
Clear dampened BGP IPv6 unicast routing
information and release suppressed
routes.
reset bgp dampening ipv6 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] [ network-address prefix-length ]
Clear BGP IPv6 unicast route flap
information.
reset bgp flap-info ipv6 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] [ network-address prefix-length | as-path-acl
as-path-acl-number | peer ipv6-address ]
IPv4 BGP configuration examples
Basic BGP configuration example
Network requirements
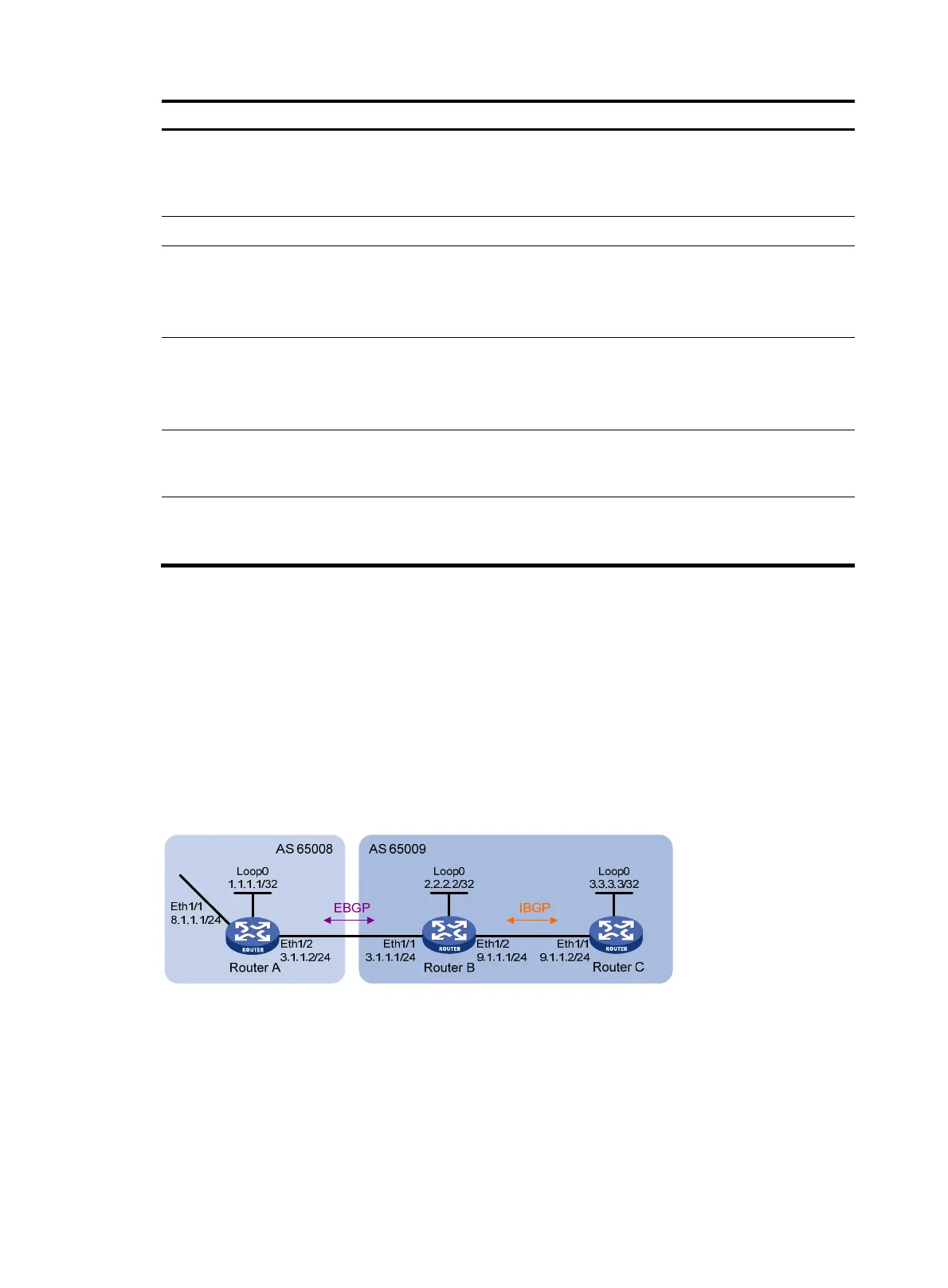
In Figure 62, run EBGP between Router A and Router B, and run IBGP between Router B and Router C so
that Router C can access the network 8.1.1.0/24 connected to Router A.
Figure 62 Network diagram
Configuration considerations
To prevent route flapping caused by port state changes, this example uses loopback interfaces to
establish IBGP connections. Because loopback interfaces are virtual interfaces, you need to use the peer
connect-interface command to specify the loopback interface as the source interface for establishing
BGP connections. Enable OSPF in AS 65009 to make sure that Router B can communicate with Router
C through loopback interfaces.

 Loading...
Loading...











