271
• Router B and Router D are in the same confederation, but belong to different sub-ASs. They obtain
external route information from Router A and generate identical BGP route entries although they
have no direct connection in between.
BGP path selection configuration example
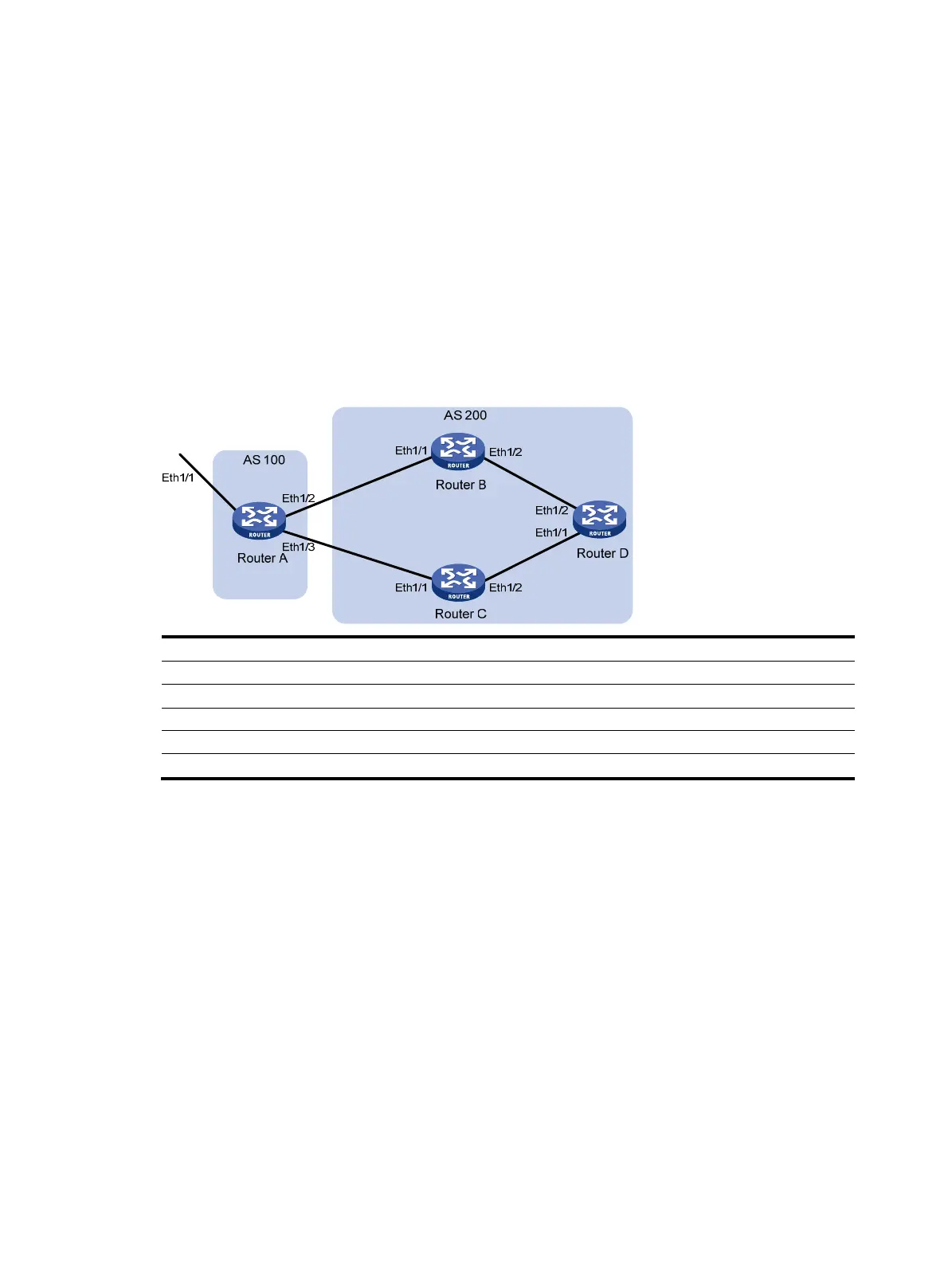
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 69, all routers run BGP. EBGP runs between Router A and Router B, and between
Router A and Router C. IBGP runs between Router B and Router D, and between Router D and Router C.
OSPF is the IGP protocol in AS 200.
Configure routing policies to make Router D give priority to the route 1.0.0.0/8 learned from Router C.
Figure 69 Network diagram
Device Interface IP address
Device
Interface IP address
Router A Eth1/1 1.0.0.1/8
Router D
Eth1/1 195.1.1.1/24
Eth1/2 192.1.1.1/24 Eth1/2 194.1.1.1/24
Eth1/3 193.1.1.1/24
Router C
Eth1/1 193.1.1.2/24
Router B Eth1/1 192.1.1.2/24
Eth1/2 195.1.1.2/24
Eth1/2 194.1.1.2/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF on Router B, Router C, and Router D:
# Configure Router B.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] ospf
[RouterB-ospf] area 0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 194.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Router C.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] ospf
[RouterC-ospf] area 0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 193.1.1.0 0.0.0.255

 Loading...
Loading...











